|
 |
 |
Other Health Topics:
-
Related Topics
-
Go Local
- Services and providers for Acoustic Neuroma in the U.S.
-
National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Acoustic Neuroma is the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders
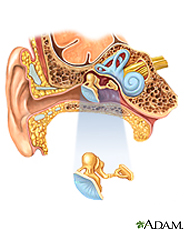
Acoustic neuroma is a non-cancerous tumor that develops on the nerve that connects the ear to the brain. The tumor usually grows slowly. As it grows, it presses against the hearing and balance nerves. At first, you may have no symptoms or mild symptoms. They can include
- Loss of hearing on one side
- Ringing in ears
- Dizziness and balance problems
Acoustic neuroma can be difficult to diagnose, because the symptoms are similar to those of middle ear problems. Ear exams, hearing tests and scans can show if you have it.
If the tumor stays small, you may only need to have it checked regularly. If you do need treatment, surgery and radiation are options. If the tumors affect both hearing nerves, it is often because of a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis. The tumor can also eventually cause numbness or paralysis of the face. If it grows large enough, it can press against the brain, becoming life-threatening.
- Acoustic Neuroma(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
-
Vestibular Schwannoma (Acoustic Neuroma) and Neurofibromatosis
 (National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
(National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
| Basics | Learn More | Multimedia & Cool Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Research | Reference Shelf | For You |
|
-
Overviews
- Acoustic Neuroma(American Hearing Research Foundation)
-
Diagnosis/Symptoms
-
Computed Tomography (CT): Head(American College of Radiology, Radiological Society of North America)
Also available in Spanish
-
MRI of the Head(American College of Radiology, Radiological Society of North America)
Also available in Spanish
- Understanding Your Audiogram(American Academy of Audiology)
-
Computed Tomography (CT): Head(American College of Radiology, Radiological Society of North America)
-
Treatment
- Acoustic Neuroma(International Radiosurgery Support Association)
- Radiosurgery: Operating on the Brain without a Scalpel(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
-
Related Issues
- Schwannomatosis(Children's Tumor Foundation)
-
Health Check Tools
-
Ten Ways to Recognize Hearing Loss
 (National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
(National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
Also available in Spanish
-
Ten Ways to Recognize Hearing Loss
-
Videos
- Acoustic Neuroma Procedure(OR-Live) - Requires media player - One hour program - 1/31/2007
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Acoustic Neuroma(OR-Live) - Requires media player - One hour program - 1/17/2007
- Stereotactic Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors(OR-Live) - Requires media player - One hour program - 6/21/2007
-
Anatomy/Physiology
- Atlas of the Body: The Ear(American Medical Association)
-
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Neuroma, Acoustic
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Neuroma, Acoustic
-
Journal Articles
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: Vestibular schwannoma quantitative polymerase chain reaction expression of estrogen and...
- Article: Fluctuating response of a cystic vestibular schwannoma to radiosurgery: case...
- Article: Self reported hearing difficulties following excision of vestibular schwannoma.
- Acoustic Neuroma -- see more articles
- Medical Encyclopedia Return to top
-
Dictionaries/Glossaries
-
NIDCD Glossary
 (National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
(National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
-
NIDCD Glossary
-
Directories
-
Directory of Organizations (Deafness and Communication Disorders)
 (National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
(National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders)
- Find a Board-Certified Neurosurgeon(American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons)
-
Directory of Organizations (Deafness and Communication Disorders)
- Organizations Return to top
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Disclaimers | Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 23 July 2008 Topic last reviewed: 10 July 2008 |