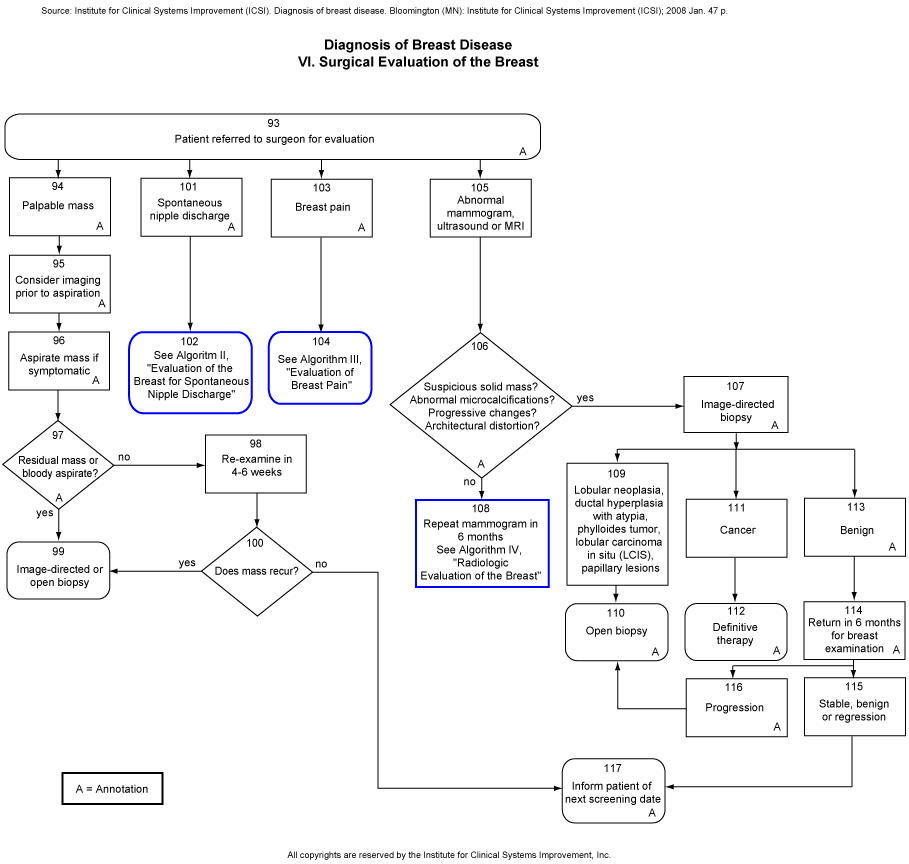
[See Algoritm II, "Evaluation of the Breast for Spontaneous Nipple Discharge"]
[See Algorithm III, "Evaluation of Breast Pain"]
[Repeat mammogram in 6 months See Algorithm IV, Radiologic Evaluation of the Breast]
Download a printable copy in PDF format.