EnergySmart Home Scale (E-Scale)
What is the EnergySmart Home Scale (E-Scale)?
The E-Scale is an easy-to-understand tool that helps homebuyers and homeowners make smart energy decisions when purchasing, renting, or updating a home. It is designed to provide clear, objective answers to basic questions:
- Will this home help me save money on energy bills?
- How many "miles per gallon" does this home get?
- How does it compare to a typical new home?
- How close is it to the "ultimate" – a Net-Zero Energy Home?
| Estimated annual energy usage is the projected amount of natural gas and electricity used annually by a home. | 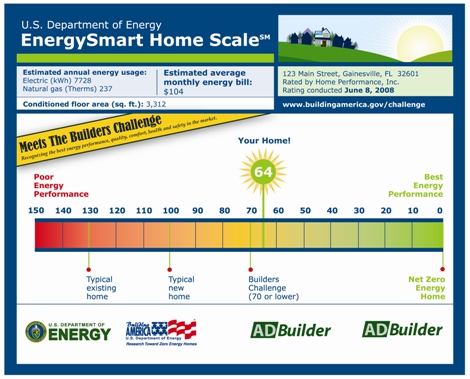 |
Estimated average monthly energy bill is the estimated annual energy bill divided by 12 months. |
| Typical existing home represents the average energy performance of the existing housing stock. | Builders Challenge (70 or lower) represents the threshold at which a home must be built to comply with the Builders Challenge. | |
| Typical new home represents the energy performance of a home built to code (2006 IECC). | Your Home represents the verified annual energy performance estimate for a specific home. In this example, a home achieving a 65 on the EnergySmart Home Scale will use only 65 percent as much energy as a typical new home - 100 on the scale - saving about 35 percent in energy use on utility bills. | |
| Energy Star is 85 on the E-Scale. | ||
| Net-Zero Energy Home A net-zero energy home annually produces with on-site renewable sources as much energy as it consumes. On-site renewable sources include energy collected on the site and used in the home (e.g., solar, wind). The site includes the home's footprint and the home site plan. The home should also provide an expected level of service and comfort. | ||
A 70 on the E-Scale indicates that a home is approximately 30% more energy efficient than a typical new home built to code. A 60 on the E-Scale would be 40% more energy efficient. The ultimate goal is to get to 0 – a Net-Zero Energy Home.
Builders may place the E-Scale on or near the home's electric panel to show potential homeowners the energy performance achieved by that particular home or model. Participating builders and partner organizations can also:
- Place their logo on the E-Scale label with program or product names
- Augment the rating with estimates of annual energy cost savings – which may help homebuyers get better mortgage terms
- Include estimates of the carbon footprint associated with the energy rating
The E-Scale is based on the well established Home Energy Rating System (HERS) Index, developed by RESNET, the Residential Energy Services Network. The energy rating for the home will be conducted by RESNET-certified energy raters for the performance pathway. RESNET has an established system for quality assurance for raters as well as providers (who oversee the raters). For more information, see the National Home Energy Rating Standards. This is the same system that underlies the Energy Star homes program. The Builders Challenge will also require third-party verification of Builders Challenge Quality Criteria.