 Review of U.S. Events Review of U.S. Events
*Compiled from both NOAA and non-NOAA sources, including U.S. and international news media reports
January 2002
Moderate to heavy snows hit parts of Georgia, the Carolinas, and Virginia during the first week of
January. Also, on the southeastern periphery of the snow, sleet and freezing rain fell, resulting in over
60,000 power outages. The hardest hit areas were in eastern North Carolina where 14 inches (35.6 cm) of
snow were reported in parts of Nash, Halifax, Montgomery, Vance, Granville, and Person counties.
Interior Maine received heavy snows on the 15th and 16th of the month as a storm system
moved across the area. Maine received a wide range of snowfall totals with 1" (2.54 cm) in the Princeton area to as high as 17" (43.2 cm) in
Bucksport. This followed an earlier storm which rapidly deepened off the coast around the 13th of
the month bringing heavy rains to coastal areas and over a foot of snow (30.5 cm) to downeast Maine.
On the 29th, record rainfall fell at several Hawaii recording stations and severe storms caused millions of dollars in flood damage. The Hilo airport shattered their January 24-hour rainfall record of 9.51 inches (241.6 mm). The new record was 12.47 inches (316.7 mm).
A powerful late January storm brought ice and heavy snows across
the Plains, Great Lakes and into New England. Heavy snow and freezing rain stranded airline
passengers, shut down schools and left thousands without electricity across the Midwest. The storm
had dumped about a foot (30.5 cm) of snow in parts of Iowa and northern Illinois including the Chicago area.
In Oklahoma, entire cities were without power, as heavy ice toppled trees and downed power lines.
More than a foot (30.5 cm) of snow fell across New Mexico's high country. At least 15 people died in traffic accidents that were blamed on the weather.
February 2002
Further south, a winter storm brought snowfall to portions of Texas, east Arkansas, north Mississippi and west Tennessee on the 5th and 6th. Searcy and Polk Counties in Arkansas reported up to 7 inches (17.8 cm) of snow.
Blowing snow cut visibility nearly to zero and shut down hundreds of miles of major highways
on the 9th, as a storm affected the northern Plains. Up to 2 feet (61 cm) of snow
fell in the Black Hills of eastern Wyoming.
For the month of February, Marquette, Michigan set a new all-time monthly snowfall record of 91.9 inches (233.4 cm). The previous record was 91.7 inches (232.9 cm) in January 1997. The new record far surpassed the old February record of 63.6 inches (161.5 cm) set in 1995.
March 2002
A snowstorm that swept from Texas to Michigan was responsible for 21 deaths, according to media reports. On
the 2nd, sleet, snow and freezing rain contributed to more than 500 traffic accidents and about 100
cancelled flights at Dallas-Fort Worth International Airport.
The National Guard was called in to help evacuate residents affected by
a storm that damaged or destroyed at least 250 homes in the worst flooding to hit eastern
Kentucky in 25 years. At least seven deaths in Tennessee were also blamed on the storm, which dumped as much as 6 to 8 inches (152-203 mm) of
rain.
Anchorage, Alaska received 28.6 inches (72.6 cm) of snow on the 16th-17th. This far surpasses the previous snowfall record for a storm, of 15.6 inches (39.6 cm) set on December 29, 1955. The snow fell at a rate of up to 2 inches (5 cm) per hour for much of the 16th, and schools were closed and flights canceled as a result of the storm.
Snow continued to fall through the end of March in Marquette, Michigan leading to a seasonal total of over 300 inches (762 cm). This surpassed the old seasonal snowfall record by 28 inches (71.12 cm). Warmer than normal water in the Great Lakes enabled lake-effect snows to persist through late winter.
April 2002
On the 15th, temperatures soared into the mid to upper 90s (34-37°C) in Nebraska. Temperatures were above 90°F (32.2°C) in Omaha and reached 97°F (36.1°C) at McCook, Nebraska. Temperatures were also high in parts of Kansas, northwest Missouri,
western Iowa and southwest Minnesota. The temperature reached 91°F (32.8°C) in the St.
Paul/Minneapolis area breaking the old daily record of 82°F (27.8°C) set in 1915 and equalled in 1976. This was the
earliest in April that 90°F (32.2°C) or higher was recorded. At the beginning of April 2002, there was 4-7 inches of snow (10.2-17.8 cm) on the ground.
A spring storm in the Tennessee and Ohio Valleys in the U.S., on the 28th caused tornadoes, high
wind and hail. The storm then moved eastward causing additional damage and spawning killer
tornadoes. The tornadoes were part of powerful storms carrying heavy rain and snow. On the
system's northern edge, up to 20 inches (51 cm) of snow fell overnight in Wisconsin. More than 40,000
people were without power in northern Wisconsin on the 28th and wet snow contributed to four
traffic deaths in Minnesota. In Maryland, a powerful tornado killed three people and leveled parts of La Plata, a small
town 25 miles (40 km) south of Washington, D.C. In Kentucky and Illinois, tornadoes caused one death in each state. In Tennessee, a
tornado injured 18 people 30 miles southeast of Nashville, and a tornado touched down in Ohio and
caused widespread damages.
May 2002
Tug Fork River, which separates West Virginia and Kentucky, crested at nearly 20ft (6.1meters) above flood stage on Friday May 3rd and led to the deaths of at least six people. Heavy rains on Tuesday May 7th in western Indiana caused riverbanks to burst and prompted evacuations. Flash flooding also led to evacuations in south-central Ohio. Storms battered central West Virginia, killing at least one person and stranding approximately two-dozen people at a campground. In Webster County, WV, 2,000 structures were damaged and 197 homes destroyed. At least two people died in the floods in Virginia. Four counties in WV, (McDowell, Mercer, Mingo and Wyoming), and two in VA, (Buchanan and Tazewell), were declared disaster areas by President Bush. Hundreds of homes and other structures have also been damaged and destroyed in Kentucky and more than 1,000 residents were evacuated from Kentucky and western Virginia.
A tornado swept through Happy, TX on the night of May 5th, 2002. The tornado killed at least two
people and injured others. The tornado was one of at
least six reported in the state on the 5th. Happy, TX is located about 30 miles (48 km) south of Amarillo.
Drought intensified in much of the eastern U.S. during the month of May, 2002.
June 2002
Heavy rain and flooding occurred in the upper Mid-west on the 9th-10th. Rainfall totals during the 48 hours beginning in the early morning of June 9 exceeded 6 inches (152 mm) in a broad area of northern Minnesota. However, local totals far exceeded 12 inches (305 mm) in places such as Roseau, Lake of the Woods and Koochiching counties. Additional rainfall later in the month compounded flood problems in northern Minnesota.
As of the end of June, nearly 2.8 million acres (1.1 million hectares) had been burned by wildfires in the U.S. This is over two and half times the 10-year average. Fires in Arizona burned over 550,000 acres (222,600 hectares) and destroyed at least 400 homes.
Separate fires near Durango and Denver, Colorado consumed 70,000 and 140,000 acres (28,330 and 56,660 hectares) respectively by the end of June, destroying dozens of homes. The latter (the Hayman Fire) was the largest fire in Colorado's history and prompted President Bush to declare the area south of Denver a disaster area.
July 2002
During the first week of July, major flooding occurred in parts of Texas due to region-wide accumulations of 5-15 inches (127-381 mm) of rainfall in the San Antonio/Austin area. San Antonio airport received over 9.5 inches (241 mm) of rain on the 1st and over 10 inches (254 mm) on the 2nd. Around 2 dozen counties were declared disaster areas and costs from the flooding were in the hundreds of millions of dollars. At least 9 deaths were attributed to the disaster. Additional rain fell in the middle of the month across parts of Texas adding to flooding problems and preventing rivers from receding.
During July 6-14, a heatwave affected the western United States, where numerous all-time high temperature records were broken. On July 13, Death Valley, CA recorded a high temperature of 127�F (52.8�C) with a low of 100�F (37.8�C), or a mean temperature of 113.5�F (45.3�C). This is the second warmest mean temperature at Death Valley since records began at the current station in 1961.
Drought conditions intensified across parts of the Southeast, the High Plains and much of the West during July 2002.
August 2002
Monmouth County, New Jersey declared a state of emergency after storms ripped through the area on the 2nd. High winds and lightning damaged homes and property and left emergency crews clearing debris from roads and restoring power to around 140,000 homes.
In North Carolina on the evening of the 25th, up to 8 inches (203 mm) of rain fell in the area north and east of Raleigh This led to flash flooding in several counties along with some road closures. Heavy rain continued across eastern North Carolina through the 26th and 27th.
For information on tropical storms in the Atlantic during August (Bertha, Cristobal and Dolly), see the Atlantic Hurricane Season summary page.
September 2002
On the 2nd, a tornado ripped through the town of Ladysmith, in northwestern Wisconsin. A few dozen injuries were reported and significant structural damage occurred in the town of 4,000 residents.
The remnants of Tropical Storm Fay dumped heavy rains and spawned tornadoes on the 7th, as the storm moved inland over Texas. Up to a foot (305 mm) of rain fell in Freeport and West Columbia, in coastal Brazoria County and 5 to 8 inches (127-203 mm) were reported in Matagorda and Wharton counties.
The remnants of tropical storm Hanna brought heavy rain to much of the eastern third of the United States on the 13-15th, stretching from the Gulf Coast to the mid-Atlantic. Rainfall spread from the Florida Panhandle northward across the Appalachians into the Ohio Valley and the Northeast, with flash
flooding reported in scattered parts of Georgia, South Carolina and Florida. This storm brought much needed rains to parts of the Southeast which had been suffering from extended drought conditions. Two to five inch (51-127 mm) rainfall amounts were common across portions of western Florida, Georgia, and the Carolinas.
Thunderstorms preceding a strong cold front brought severe weather and tornadoes on the 20th to areas of Ohio and Indiana. Of at least 50 homes that were destroyed in Indiana, 20 of those were in the town of Martinsville where a tornado struck. According to the state emergency management agency, this was the worst outbreak of severe weather in Indiana since June 1990.
For information on tropical storms in the Atlantic during September (Edouard, Fay, Gustav, Hanna, Isidore, Josephine, Kyle and Lili), see the Atlantic Hurricane Season summary page.
October 2002
On October 3rd, Hurricane Lili came ashore in western Louisiana bringing additional rain to areas already affected by Tropical Storm Isidore in September. More rainfall later in October led to a rank of second wettest October on record for Louisiana and Texas. Further details on flooding and rainfall in the Southeast and parts of the Gulf Coast are given on the Atlantic Hurricane Season summary page.
Severe weather occurred in south Texas on October 24, as thunderstorms produced tornadoes that caused one fatality and 14 injuries in the Corpus Christi area. Storm damage in the city was estimated as high as $100 million, and Texas Governor Rick Perry declared Nueces County a disaster area.
An intrusion of Arctic air produced record low temperatures across parts of the upper Midwest during the last week of October. Williston, North Dakota dropped to -23�C (-9�F) on October 30, which is the coldest low temperature ever recorded during the month of October at Williston.
It was the warmest October in Alaska since 1938, and only the 8th time on record that Anchorage had no snow during the month.
November 2002
A major outbreak of severe weather and tornadoes occurred across the U.S. Tennessee and Ohio valley region on the 10th-11th, producing damage in 13 states. A total of 75 tornadoes touched down on the 10th, resulting in at least 36 deaths. A tornado rated as F-4 on the Fujita Scale struck Van Wert county in Ohio. In Tennessee, the community of Mossy Grove was nearly destroyed by a mile-wide tornado that claimed 12 lives.
Severe to exceptional drought continued throughout much of the western United States. Two months of above average precipitation in the eastern U.S. brought significant relief to long-term drought conditions.
December 2002
A signicant snow and ice storm affected much of the eastern half of the United States during the 3rd-5th. In the Carolinas, electric utilities provider Duke Power characterized the ice storm as the worst in the company's history, with 1.2 million customers or nearly half its entire customer base without power on the morning of the 5th. This surpassed electrical outages inflicted by Hurricane Hugo as it swept through the central Carolinas in September 1989.
A powerful Pacific storm system plowed into the western United States during the 13th-16th, producing high winds, heavy rains, significant mountain snowfall and causing 9 deaths. Rainfall amounts exceeding 254 mm (10 inches) occurred in parts of California, and wind gusts over 70 km/hr (~40 knots or 45 mph) produced up to 1.9 million power outages during the period. Some higher elevation locations in the Sierra Nevada mountains received up to 254 cm (100 inches) of snow during the 12th-16th.
A major winter storm affected much of the eastern United States during December 23-25, 2002. Significant accumulations of snow were reported from the Texas panhandle, through Oklahoma, Kansas, Missouri and northern Arkansas during the 23rd-24th, causing 12 deaths. Springfield, MO reported 33cm (13 inches) of snow, or 52 cm (20.5 inches) for the month, for a new December snowfall record. Snow spread eastward from parts of the Ohio Valley and into the Northeast on Christmas Day, with some locations experiencing the snowiest Christmas Day ever recorded.
For more information on Weather and Climate Extremes, refer to ...
The Climate of 2002
Extreme Weather and Climate Events

 Review of Global Events Review of Global Events
*Compiled from both NOAA and non-NOAA sources, including U.S. and international news media reports
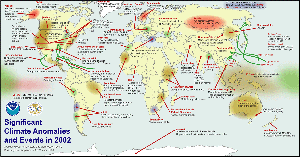
larger image
January 2002
Heavy snowfall and low temperatures during the first week in January caused damage to property and crops in parts of southeast Europe. Across Albania, the Albanian army made food deliveries to remote villages that had been cut off by snow, while in Bulgaria, snow depths of 1.8 meters (~ 6 feet) blocked roads and rail routes in the northern part of the country. In Greece, a state of emergency was declared in several provinces due to heavy snow, with damage to crops reported in the country's agricultural areas. More than three-quarters of all flights from the Athens International Airport were canceled during the height of the storm around the 4th and the Acropolis was closed to visitors.
According to media reports, hailstones the size of tennis balls damaged hundreds of homes as severe thunderstorms passed through eastern Australia. Heavy rains from the storms, which struck the northeastern coast of New South Wales state late on
the 16th, also extinguished many of the large bushfires that threatened the outskirts of Sydney since Christmas 2001.
On the 22nd, Tropical Cyclone Dina skirted Mauritius and Reunion islands to the north and
west while tracking westward across the southern Indian Ocean. Dina passed close enough to these
islands to produce damaging winds and soaking rains. On the southeast side of
Mauritius, the main airport clocked peak wind gusts of 150 km/hr (80 knots or 93 mph), and rainfall exceeded 120 mm (4.7
inches).
Media reported that seven people were killed on the 28th as strong winds affected the United Kingdom, overturning vehicles, disrupting travel and leaving tens of thousands of homes without power. The UK Met Office recorded winds up to 227 km/hr (141 mph) atop the Cairngorm mountains in central Scotland.
Unusually warm weather across southern Russia brought snowmelt and significant flooding along the Kuban River in the Krasnodar territory adjacent to the Black Sea. More than 3,000 residents were evacuated, and hundreds of houses were flooded in several villages along the river, with some of the worst flooding reported in the town of Temyruk.
February 2002
Heavy monsoon rains brought serious flooding to parts of Java and the greater Jakarta area during late January and early February. Damage to agriculture and infrastructure was estimated at $200 million (USD) across Indonesia, where at least 150 people lost their lives in the Java and Jakarta provinces.
Tropical Cyclone Chris developed in the Indian Ocean on the 3rd and made landfall in the Australian Northern Territory on the 6th about 100 km (62 miles) east of Port Hedland with maximum sustained winds near 65 m/s (~125 knots or 145 mph). The cyclone brought heavy rains to much of northern and central portions of Western Australia and February precipitation surpluses exceeded 150 mm (5.91 inches) locally. February rainfall records were broken across parts of central Western Australia as Chris dissipated over the interior.
Tropical Cyclone Guillaume developed off the northeast coast of Madagascar on the 15th and brought significant rainfall to northern portions of the island during its developmental stages. The city of Toamasina along the northeast coast of the Malagasy Republic received over 800 mm (31.5 inches) of rain during the 1st-16th. Guillaume moved southeast and strengthened, passing east of the Mascarene Islands on the 19th.
On February 19, strong thunderstorms brought torrential rains and hail to the Bolivian capital of La Paz. At least 63 people were killed and 100 injured as flash floods destroyed 50 homes and left more than 500 homeless. According to the Bolivian National Meteorological Service, the city had never received such heavy rainfall in the 50 years records have been kept. The mayor of La Paz estimated damages to the city of nearly $100 million (USD).
Stormy conditions that began in January continued in February across the British Isles, as storm systems accompanied by heavy rains and strong wind affected the United Kingdom and caused flooding along the Ouse and Severn rivers. The UK Met Office reported that England and Wales experienced the wettest February since 1990, and many areas in Scotland received two to three times the normal February precipitation amount.
March 2002
In the western Pacific Ocean, Typhoon Mitag affected the islands in the Federated States of Micronesia during the first few days of March, impacting the main island of Yap on the third. Maximum sustained winds were near 95 knots (~50 m/s or 110 mph) as the storm passed the island, and the combination of strong winds, heavy rains and a large tidal surge flooded many areas and destroyed many crops.
A series of dust storms originating from the Gobi Desert affected the northern provinces of China, from Inner Mongolia eastward to the Yellow Sea. Beijing experienced visibilities that dropped to less than 90 meters (100 yards) on the 20th. China�s State Forestry Administration estimated that 130 million people across 1.4 million square kilometers (540,500 square miles) of northern China were affected by the dust storm. Drought across a large area of northern China influenced the severity of the dust storms, according to the China Meteorological Administration. By mid-month, the large plume of dust had crossed into the Sea of Japan, affecting South Korea and Japan.
Showers and thunderstorms were persistent throughout the month across portions of Peru and Ecuador along with areas of flooding. Coastal provinces of Ecuador, including Guayas, Los Rios and Manabi were most severely affected, with flooding responsible for 16 deaths and over 1,700 homeless throughout the country. Flooding in Peru during the 16th-25th caused 13 deaths and damaged over 400 houses.
Relatively dry weather dominated much of Brazil during March, but an increase in precipitation during January and February prompted government officials to lift electricity rationing measures that had been in place since June 2001. Many reservoirs which supply water to hydropower plants had returned to more normal levels by the end of March.
April 2002
In India, a tornado devastated several villages in the state of West Bengal on April 3rd. The tornado killed 5 people, destroyed over 400 houses and rendered 5,000 people homeless.
Tropical Cyclone Bonnie developed in the Timor Sea on the 10th and brought locally heavy rains and gusty winds to Timor and Sumba during the 10th-11th. Flash flooding associated with the storm killed 19 people on Sumba.
At least 16 million people were short of drinking water across China as one of the worst droughts in decades affected parts the country. In the southeast coastal province of Guangdong, rainfall in April was over 100 mm (3.94 inches) below average, curtailing agriculture and affecting already low reservoir storage. Drought conditions extended south across Taiwan, where water was shipped in from China due to the acute shortages of drinking water.
Large forest fires burned in parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and Belize. Drought affected Central America during the past 2 years, contributing to conditions suitable for wildfires.
May 2002
Tropical cyclone Kesiny made landfall along the northern tip of Madagascar on the 9th, with maximum sustained winds near 110 km/hr (60 knots or 68 mph). The cyclone trekked slowly south into the interior of the Malagasy Republic before dissipating. Torrential rains ravaged the northern half of the country for days after the storm moved inland and weakened, with over 40 deaths attributed to flooding. In the port city of Toamasina, the country's second largest city, May rainfall totaled 1,271 mm (50 inches). The normal monthly amount is 228 mm (9 inches).
A severe heat wave which affected much of central and southeastern India during May 9-15 resulted in over 1,000 deaths as daily high temperatures reached as high as 50�C (122�F). In neighboring Pakistan, at least 29 deaths were attributed to the high heat in the central and southern parts of the country.
A tropical disturbance brought heavy thunderstorms to Jamaica during the last 10 days of May, causing serious flooding across the island and resulting in at least 7 deaths. Damage estimates from the flooding are near $6 million (USD), with around $1 million in damage to the Jamaican water supply system.
Thunderstorms producing torrential rain affected Nicaragua and Honduras during the last week of May. The government of Nicaragua issued a state of emergency on May 30th, as flooding washed out roads and bridges and displaced around 3,000 people from their homes. Some of the worst flooding was around the capital city of Managua, where the airport was closed on the 28th due to extensive flooding in the city. On the 27th, the Honduran government declared a state of emergency after heavy rains flooded the capital, Tegucigalpa, and left more than 100,000 people stranded.
A severe heat wave which affected much of central and southeastern India during May 9-15 resulted in over 1,000 deaths as daily high temperatures reached as high as 50�C (122�F). In neighboring Pakistan, at least 29 deaths were attributed to the high heat in the central and southern parts of the country.
In one of the worst ferry disasters since the 1980s, up to 300 people were drowned when a ferry sank in a storm about 160 km (100 miles) south of Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Since the April onset of the rainy season in Kenya, at least 72 people died due to flooding, mainly in the western part of the country. Numerous rivers flooded, displacing many from their homes. Some of the worst flooding occurred in the city of Budulangi located in Nyanza province.
June 2002
A storm system which brought heavy rains to lower elevations of central Chile early in the month dumped heavy snow across the Andes Mountains. Significant snow accumulations blocked the main road link between Chile and Argentina on the 3rd.
Across northeastern Nigeria, high heat with daily maximum temperatures over 40�C (104�F) resulted in at least 60 deaths in the city of Maiduguri during the first week of June.
News reports indicated that eight people were found dead on the 7th, after fierce thunderstorms swept across Europe, leaving a trail of flooded roads, collapsed houses and downed bridges from France to Poland. Regional officials in northeastern Italy declared a state of emergency, while in Austria the military was deployed to battle the effects of flooding.
Flooding that has been characterized as some of the worst in a century affected large portions of central and northern China, including the provinces of Shaanxi, Fujin, Sichuan and Guizhou. At least 500 people died in the floods, which began in early June in areas around the Yangtze River. In the worst affected province of Shaanxi, torrential rains from the 8th-10th produced devastating floods which killed 152 people.
Heavy rains along a frontal system brought extensive flooding to parts of southern Russia between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea during the 17th-18th. At least 102 people were killed, with more than 40,000 houses flooded. In addition, over 200 bridges and more than 1,500 km (900 miles) of road were damaged in one of the worst natural disasters in the region since the 1930s, as reported by media sources. The worst affected areas include Stavropol, Krasnodar and Chechnya where Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered the deployment of 12,000 military personnel to deal with the effects of the flooding.
July 2002
Typhoon Rammasun crossed the Philippine Sea on the 1st and reached peak intensity over the East China Sea during the 3rd-4th with maximum sustained winds near 200 km/hr (~110 knots or 125 mph). The storm lashed coastal China with flooding rains, resulting in at least 6 deaths. Rammasun weakened into a tropical storm before making landfall in South Korea late on the 5th.
Typhoon Halong passed just south of Guam on the 10th, producing heavy rains and winds gusting to 70 km/hr (~40 knots or 45 mph) on the island. Halong weakened into a tropical storm before crossing the island of Honshu on Japan on the 16th with maximum sustained winds near 75 km/hr (40 knots or 45 mph). The storm forced hundreds of schools to close in Tokyo, seriously disrupted transportation and caused power outages to over 23,000 households.
A series of winter storms affected southeast Peru and parts of southwestern Bolivia during July. In Peru, a state of emergency was declared on the 13th, where snow and freezing weather were responsible for the deaths of 59 people and thousands of livestock. Across the Bolivian department of Potosi, the cold, snowy weather resulted in 4 deaths with cattle losses as high as 50 percent.
A storm system that affected much of South Africa during July 15-21 brought heavy amounts of rain to the lower elevations with snow across higher elevations of the eastern Cape of Good Hope province and eastern Lesotho. The adverse weather conditions were responsible for 17 deaths.
Violent thunderstorms which developed in the Henan province of central China on the 19th produced egg-sized hail in the city of Zhengzhou. The storms killed at least 25 people and injured 200.
Numerous wildfires, sparked by lightning and aided by very dry conditions, burned out of control in parts of northern and central Quebec during July. Nearly 85 fires were reported, with the largest fire charring more than 400 square miles (100,000 hectares) of forest.
August 2002
Monsoon rainfall in India remained light and intermittent during June-August 2002, with heavier rains restricted to the northeast part of the country. In the southeastern state of Andhra Pradesh, more than 75 percent of the districts were declared drought-affected. Drought in India was reportedly the worst since 1987, with monsoon precipitation 19 percent below normal.
Torrential rains brought severe flooding to central Europe during August 2002, with some of the worst flooding in more than a century observed across parts of Germany, the Czech Republic, the Slovak Republic and Hungary. The floods caused over 100 deaths and damage estimated at near $20 billion (USD). The most severely affected regions included the northern Waldviertel area of Lower Austria where the river Kamp reached its highest level since records began in 1896. The Vltava River burst its banks on the 13th, with river levels at Prague surpassing the record previously set in 1890. In Germany, the Elbe River brought the worst flooding in nearly 150 years to the city of Dresden.
Typhoon Rusa passed near the Japanese island of Amami O Shima on the 29th with maximum sustained winds near 150 km/hr (~80 knots or 90 mph).
Rusa then recurved northward across the East China Sea before making landfall along the south coast of South Korea on the 31st with maximum sustained winds of 130 km/hr (70 knots or 80 mph). The typhoon was the worst to strike South Korea since 1959, causing 200 deaths and dumping between 300 and 500 mm (11.8 and 19.7 inches) of rain on parts of the country in less than 12 hours. Rusa damaged more than 20,000 buildings and washed away at least 200 bridges and highways.
Flooding in the Yangtze valley of China threatened Dongting Lake, one of China's largest freshwater lakes located in Hunan province in eastern China. Nearly 900,000 people worked to keep the swollen lake from bursting its banks as floodwaters from the Yangtze River brought the lake to dangerously high levels.
In eastern Nepal, heavy monsoon rains swept through a mountainous village causing a landslide that resulted in up to 65 fatalities. Seasonal flooding across South Asia (Nepal, India and Bangladesh) was responsible for over 1,000 deaths since the rainy season began in June.
September 2002
Flooding along the lower stretches of the Mekong River during the last week of August into early September was extensive across parts of Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand and Laos. River flooding was responsible for over 150 deaths across Indochina, with around 120,000 people in Cambodia evacuated to emergency shelters .
Typhoon Sinlaku crossed the Japanese island of Okinawa on September 4th with maximum sustained winds of 175 km/hr (95 knots or 110 mph). Winds in the city of Kadena gusted to 183 km/hr (99 knots or 114 mph) as the typhoon passed by. Sinlaku tracked into Zhejiang province on the 7th, making landfall near the city of Wenzhou. The storm prompted the evacuation of over 300,000 people and was blamed for at least 9 deaths.
Showers and thunderstorms which developed along a cold front affected much of southern France during the 7th-9th. The storms caused flooding that claimed 26 lives, including at least one lightning fatality. The hardest hit area was near the southern French city of Nimes.
Tropical Storm Hagupit tracked into China's Guangdong province on the 11th with maximum sustained winds of 85 km/hr (~45 knots or 50 mph). In the city of Hong Kong, government offices and the stock exchange were closed as heavy rains and gusty winds affected the city. In the Jiangxi province, flooding associated with the storm destroyed 4,000 houses and flooded 159 villages. Approximately 180,000 people were affected by Tropical Storm Hagupit and over 109,000 hectares (270,000 acres) of farmland destroyed.
Hurricane Isidore reached brushed the Cayman Islands on the 19th and crossed into western Cuba by the 21st, locally dumping over 600 mm (24 inches) of rain along with maximum sustained winds near 165 km/hr (~90 knots or 105 mph). Isidore then moved westward, making landfall along the northern Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico on the 22nd with maximum sustained winds near 205 km/hr (~110 knots or 125 mph). At least 2 people were killed in Mexico from Isidore, and over 300,000 left homeless as strong winds and flooding rains caused significant damage.
A slow moving storm system which tracked across the Mediterranean was responsible for heavy rains across Albania during the 21st-26th. Nearly double the normal September rainfall occurred in less than a week, causing severe flooding across parts of the country. The Prime Minister declared a "State of Natural Disaster" in nine Albanian provinces, where over 15,000 houses were flooded and over 26,000 hectares (64,000 acres) of agricultral land submerged.
Tropical Storm Lili passed through the Windward Islands on the 23rd. On Barbados, 139 homes were badly damaged and 275,000 people lost electric power as maximum sustained winds were near 95 km/hr (~50 knots or 55 mph). Lili dissipated south of Haiti on the 26th but regained its intensity and skirted the north coast of Jamaica on the 29th. Lili reached hurricane strength on the 30th, passing near the Cayman Islands and crossing western Cuba on October 1. Lili was the second hurricane in less than 2 weeks to strike western Cuba, and it forced the evacuation of thousands of people.
October 2002
Typhoon Higos passed over coastal areas of eastern Japan on the 1st. Maximum sustained winds were near 150 km/hr (80 knots or 90 mph). Ports and highways were closed, hundreds of flights cancelled and tens of thousands of homes left without electricity as the typhoon passed through. The storm was responsible for 4 deaths in Japan.
Hurricane Kenna made landfall along the central Pacific coast of Mexico just north of Puerto Vallarta on October 25 with maximum sustained wind speeds of 230 km/hr (120 knots or 140 mph). Kenna was the third most powerful hurricane to ever strike Mexico from the Pacific.
A strong storm system affected much of northwest Europe on the 27th, bringing strong winds and heavy rainfall. Wind speeds reaching up to 165 km/hr (89 knots or 103 mph) uprooted trees, smashed cars and damaged buildings. The storm was responsible for a total of 30 deaths across Europe, including Britain, the Netherlands, France, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Poland, Switzerland and Sweden. The majority of the fatalities were caused by falling trees.
In Australia, drought affected over 90 percent of New South Wales and threatened to move the country into an economic recession. In the rural sector, about 40,000 jobs were lost due to drought over the past three months, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The Australian Bureau of Agriculture and Resource Economics predicted a 16 percent drop in the gross value of farm production throughout the country.
Drought affected much of the Horn of Africa, with nearly 6 million people in Ethiopia in need of food aid. In neighboring Eritrea, prolonged drought seriously affected agricultural and livestock production this year, which threatened the lives of more than a million people.
In Paraguay, a 2-year drought affected Chaco region which includes the Department of Boqueron. The government of Paraguay declared a national emergency, as food and water reserves were depleted and approximately 5,000 people were impacted by food and water shortages.
November 2002
A strong storm occurred in Spain and Portugal during November 13th. The storm led to several deaths as construction cranes toppled over in the high winds in 2 separate incidents on mainland Spain. The storm and high seas also contributed to the sinking of an oil tanker off the Spanish coast, resulting in an extensive oil spill. Winds gusted to around 130 km/hr (70 knots or 80 mph) in Portugal and trees and power lines were torn down by the high winds in both nations.
In North Africa, a strong cold front trekked across Morocco during the 17th-18th and produced severe flooding which caused at least 37 deaths. Flood damage also ignited a fire at a large oil refinery in the industrial town of Mohammedia.
Stormy weather extended northward across southern Europe, where flooding and mudslides were reported through much of northern Italy and the Swiss Alps. Wet weather throughout much of November caused numerous rivers and streams to rise above flood stage, flooding thousands of homes and businesses.
In China, water from the Yellow River was diverted to supply the drought-stricken city of Tianjin. A long-term drought produced serious water shortages in Tianjin, located along the coast of north China.
Across Africa, Ethiopian government officials reported that nearly 6 million people are threatened by drought, with nearly 1.4 million under immediate risk of starvation. In Zambia, drought that destroyed grazing pastures threatened the country's rare white rhino population. Six
consecutive poor harvests due to a lack of rainfall in Mauritania adversely impacted farmers and decimated livestock herds.
December 2002
Wildfires which burned in New South Wales in early December were characterized by media sources as the worst in nearly 30 years. Around 70 brush fires burned north, south and west of the city of Sydney, with about 20 houses destroyed by the flames. Nearly 3,000 firefighters responded to the blazes.
Typhoon Pongsona impacted the island of Guam on the 8th with wind speeds exceeding 240 km/hr (130 knots or 150 mph). The storm destroyed thousands of homes and cut off all electricity, water and power on the island. President Bush declared the U.S. territory a federal disaster area on the 8th. Tiyan, Guam recorded 500 mm (19.67 inches) of rain which set a new record for daily rainfall during the month of December. The old daily rainfall record was 351 mm (13.81 inches) produced by Typhoon Paka in 1997.
Thunderstorms associated with a cold front brought excessive rains to parts of Brazil on the 9th, where mudslides impacted the city of Angra dos Reis, located about 160 km (100 miles) west of Rio de Janeiro. Mudslides buried houses and killed at least 34 people. Rainfall totals exceeded 125 mm (5 inches) in less than 24 hours, as reported by the National Meteorological Institute of Brazil.
In Indonesia, a mudslide triggered by heavy rains swept through Pacet village of East Java on the 11th, causing at least 24 fatalities.
For more information on Weather and Climate Extremes, refer to ...
The Climate of 2002
Extreme Weather and Climate Events

For further information, contact:
Jay Lawrimore
NOAA/National Climatic Data Center
151 Patton Avenue
Asheville, NC 28801-5001
fax: 828-271-4328
email: Jay.Lawrimore@noaa.gov
-or-
Scott Stephens
NOAA/National Climatic Data Center
151 Patton Avenue
Asheville, NC 28801-5001
fax: 828-271-4328
email: Scott.Stephens@noaa.gov
 NCDC / Climate Monitoring / 2002 / Annual / Events / Search / Help NCDC / Climate Monitoring / 2002 / Annual / Events / Search / Help
http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/climate/research/2002/ann/events.html
Downloaded Saturday, 04-Oct-2008 10:09:34 EDT
Last Updated Friday, 22-Jul-2005 10:28:42 EDT by Scott.Stephens@noaa.gov
Please see the NCDC Contact Page if you have questions or comments.
|

