About Your Breasts
Types of Breast Changes
Finding Breast Changes
Breast Changes During Your Lifetime That Are Not Cancer
Getting a Second Opinion
Follow-Up Tests to Tell You More
Finding the Support You Need
For More Information
Chart 1: Possible Mammogram Results and Follow-Up Care
Chart 2: Possible Biopsy Results and Follow-Up Care
About Your Breasts
Breast Basics
The breast is a
gland
that produces milk in late pregnancy and after childbirth.
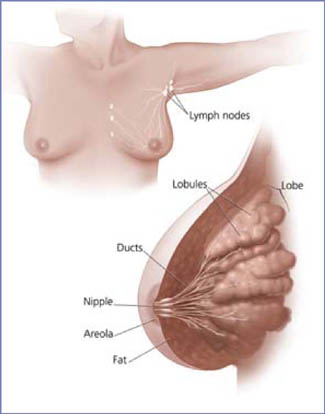
What are breasts made of?
- Each breast is made of
lobes.
- Lobes are groups of milk glands called
lobules.
- Lobules are arranged around thin tubes called
ducts.
- Ducts carry the milk to the nipple.
- These lobules and ducts make up the
glandular tissue.
What is the lymphatic system?
The breasts also contain
lymph vessels, which carry a clear fluid called
lymph.
- The lymph vessels lead to small, round organs called
lymph nodes.
Groups of lymph nodes are found near the breast in the underarm, above the collarbone, in the chest behind the breastbone, and in many other parts of the body.
- The lymph nodes trap bacteria, cancer cells, or other harmful substances that may be in the
lymphatic system. Their job is to make sure harmful substances are safely removed from the body.
| See your health care provider about a breast change when you have:
|
- A lump in or near your breast or under your arm
- Thick or firm tissue in or near your breast or under your arm
- Nipple discharge or tenderness
- A nipple pulled back (inverted) into the breast
- Itching or skin changes such as redness, scales, dimples, or puckers
- A change in breast size or shape
If you notice a lump in one breast, check the other breast. If both breasts feel the same, it may be normal.
You should still see your health care provider for a
clinical breast exam
to see if more tests are needed.
|
Types of Breast Changes
Breast changes occur in almost all women.
Most of these changes are not
cancer. However, some breast changes may be signs of cancer. Breast changes that are not cancer are called
benign. For more information
on benign breast changes that are more likely to happen
during certain times of your life, see
Breast Changes During Your Lifetime That Are Not Cancer 1.
Most women have some type of lumpiness in their breasts. Some areas may be more dense than others and can feel lumpy in an exam. What you are feeling may be glandular breast tissue.
Many women have swelling, tenderness, and pain in their breasts before and sometimes during their periods. You may also feel one or more lumps during this time because of extra fluid in your breasts.
Because some lumps are caused by normal
hormone
changes, your health care provider may suggest watching the lump for a month or two to see if it changes or goes away.
Single lumps can appear at any time and come in various types and sizes. Most lumps are not cancer, but your health care provider should always check the lump carefully. He or she may do more tests to make sure the lump is not cancer.
See Chart 1: Possible Mammogram Results and Follow-Up Care 2 for more information about these types of lumps.
Check with your health care provider if you notice any kind of lump. Even if you had a lump in the past that turned out to be benign, you can't be sure that a new lump is also benign.
Nipple discharge
is common for some women. It is fluid that comes from the nipple in different colors or textures. Usually, it is not a sign of cancer. For example, birth control pills and other medicines, such as sedatives, can cause a little discharge. Certain
infections
also cause nipple discharge. However, for women who are going through or have passed
menopause, nipple discharge can be a sign of cancer.
See your doctor if you have nipple discharge for the first time, or a change in your discharge's color or texture. He or she may send a sample of the discharge to be checked at a lab.
Finding Breast Changes
There are two ways to find breast changes:
- Clinical breast exams--a breast exam done by your health care provider
-
Mammograms
--an
x-ray
of your breasts
One way to find breast changes is with a clinical breast exam done by your health care provider. He or she will check your breasts and underarms for any lumps, nipple discharge, or other possible changes. This breast exam should be part of a routine medical check-up.
The best tool for finding breast cancer is a mammogram. A mammogram is a picture of the breast that is made by using low-dose x-rays. It is currently recommended that women over age 40 receive a mammogram every 1 to 2 years.
Some women check their own breasts for changes. If you find a change, it's important to call your health care provider for an appointment. Make sure to watch the change you found until you see your provider. But a breast self-exam and a clinical breast exam are not substitutes for mammograms.
|
Questions to ask your health care provider about a breast change
|
- How can I tell the difference between my usual lumps and
lumps I need to do something about?
- How will you be able to tell what kind of breast change I have?
- What should we do to watch this change over time?
|
Mammograms are used for both
screening
and
diagnosis.
A
screening mammogram
is used to find breast changes in women who have no signs of breast cancer. Most women get two x-rays of each breast.
If your recent screening mammogram revealed a breast change
since your last one, or if you or your health care provider
noticed a change, he or she will probably recommend a
diagnostic mammogram.
More x-rays are taken during a diagnostic mammogram than a screening mammogram to get clearer, more detailed pictures of the breast. It is also used to rule out other breast problems.
| Tip
|
|
Take your original mammogram and
copy of the medical report with you if you change doctors
or centers or need a second opinion.
|
A
digital mammogram
is another way to take a picture of your breasts. The procedure for having a digital mammogram is the same as a screening mammogram, except that it records the x-ray images in computer code instead of on x-ray film.
 It is important to see your doctor and get a mammogram
every 1 to 2 years after age 40 to find breast changes.
It is important to see your doctor and get a mammogram
every 1 to 2 years after age 40 to find breast changes.
Here are mammograms of three different women. Doctors look at these x-rays for any breast changes that don't look normal.
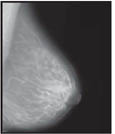
Normal |
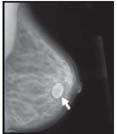
Benign Cyst
(Not Cancer)
|
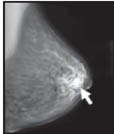
Cancer
|
| Mammograms and Breast Implants
|
|
When you go for your mammogram, tell staff if you have a
breast implant.
A
technologist who is trained in x-raying patients with implants will do your mammogram. Breast implants can hide some breast tissue and make it harder to read your mammograms.
If you got implants for cosmetic reasons:
- You still need to get screening mammograms, with extra pictures to help get an accurate reading.
If you got an implant after having a
mastectomy
for breast cancer:
- You should continue to get mammograms of your other breast. Ask your doctor if you still need mammograms of the breast with the implant.
|
Ask your doctor when you will get your results. You should get a written report of your mammogram results within 30 days of getting the x-ray. This is the law. Be sure the mammogram facility has your current address.
If your results were normal, it means the
radiologist
did not find anything that needs follow-up.
If your results were abnormal, it means the radiologist found:
- A change from a past mammogram
- A change that needs more follow-up
The radiologist will look at your x-rays for breast changes that do not look normal. The doctor will look for differences between your breasts. He or she will compare your past mammograms with your most recent one to check for changes. The doctor will also look for lumps and
calcifications.
The size, shape, and edges of a lump sometimes can give doctors more information about whether or not it is cancer. On a mammogram, a growth that is benign often looks smooth and round with a clear, defined edge. On the other hand, breast cancer often has a jagged outline and an irregular shape. (See
Chart 1: Possible Mammogram Results and Follow-Up Care 2.)
A calcification is a deposit of the mineral
calcium
in the breast tissue. Calcifications appear as small white spots on a mammogram. There are two types:
Depending on how many calcium specks you have, how big they are, and what they look like, your doctor may suggest that you:
- Have a different type of mammogram that allows the radiologist to have a closer look at the area
- Have another screening mammogram, usually within 6 months
- Have a test called a
biopsy 3.
| Calcium in the diet does not
create calcium deposits (calcifications) in the breast. |
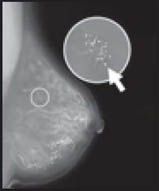 |
Calcification |
|
 |
"I used to think
whenever a mammogram found
a lump or a mass,
it was probably cancer--it turns out that most
breast changes are not cancer.
That's one thing I sure didn't mind being wrong about."
Anne, Age 60 |
|
No. Although they are not perfect, mammograms are the best method to find breast changes. If your mammogram shows a breast change, sometimes other tests are needed to better understand it. Even if the doctor sees something on the mammogram, it does not mean it is cancer.
Sometimes your doctor needs more information about a change on your mammogram. Your doctor may do follow-up tests such as an
ultrasound
or more mammograms. The only way to find out if an abnormal result is cancer is to do a biopsy. It is important to know that most abnormal findings are not cancer.
Breast Changes During Your Lifetime That Are Not Cancer
You might notice different kinds of breast changes at
different times in your life. Many of these are caused by
changes in your hormone levels and are a normal part of getting
older.
Younger women may have more glandular (more dense, less fatty)
breast tissue than older women who have stopped having their period
(menopause). This kind of tissue is where breast changes usually occur.
Before or during your period, you might have lumpiness,
tenderness, and pain in your breasts. The lumpiness and pain
usually go away by the end of your period.
During pregnancy, your breasts may feel lumpy,
as the glands that produce milk increase in number and get larger.
Still, breast cancer has been found in pregnant women,
so talk with your doctor if you have questions about any breast lumps.
 |
"Everything changes over time, including your body.
The important thing is to work with your doctor
to deal with the changes in a calm and
sensible way."
--Carmen, Age 70 |
While breastfeeding, you may get an infection called
mastitis that happens when a milk duct becomes blocked.
Mastitis causes the breast to look red and feel lumpy, warm, and
tender. Mastitis is often treated with
antibiotics.
Sometimes the duct may need to be drained. If the redness or mastitis does not go away with treatment, call your doctor, as you may need further care.
As you approach menopause, your periods may become less frequent. Changing hormone levels also can make your breasts:
- Feel tender, even when you are not having your period
- Feel more dense
- Feel more "lumpy" than they did before
As you age, other breast changes are more common, such as:
-
Intraductal papilloma. This is a growth inside the nipple that looks like a wart. It can be removed by surgery without changing the way the breast looks.
-
Mammary duct ectasia.
As you near menopause, ducts beneath the nipple can become swollen and clogged. This can be painful and cause nipple discharge. The problem is treated with warm packs, antibiotics, and sometimes surgery to remove the duct.
If you are taking hormones, such as hormone replacement therapy
(HRT), birth control pills, or injections, when getting your mammogram be sure to let your doctor know. Hormones may cause your breasts to be more dense. This can limit your doctor's ability to read a mammogram.
When you stop having periods (menopause), your hormone levels drop, and your breast tissue becomes less dense and more fatty. You may stop having the lumps, pain, or nipple discharge you used to have. And because your breast tissue is less dense, mammograms can be easier to read. This means doctors are more likely to find breast changes or early breast cancer.
Getting a Second Opinion
 |
"I wasn't sure if it was okay to ask for a
second opinion... it's good to know that lots of other people
are asking. After all, it is my body; I owe it to myself to be sure."
--Marie, Age 55 |
After seeing your health care provider, you may want to get a second opinion from another health care provider. Sometimes, a second opinion may be covered by your health insurance. Many women feel uneasy about asking for a second opinion, but it is very common. Your health care provider will not be surprised or offended if you seek a second opinion. A second opinion might help you feel more confident that you are making the best choices about your health.
Follow-Up Tests to Tell You More
Doctors often use ultrasound or biopsies to follow up after finding signs of a breast change.
An ultrasound uses sound waves to make a picture of breast tissue. This picture is called a
sonogram. It helps doctors look more
closely at lumps. An
ultrasound shows if a lump is solid or filled with fluid
(cyst).
(See Chart 1: Possible Cysts are usually not cancer. Mammogram Results and Follow-Up Care 2.)
An ultrasound also can help
your doctor decide if more tests are needed.
It is important to know that
an ultrasound may not find all abnormal
changes.
A Cyst: The Most
Common Breast Change
|
|
A cyst is a lump filled with fluid.
If a cyst is found, your doctor
may decide to:
- Remove fluid in the cyst to make it go away
- Look at it with an ultrasound
- Watch it closely over time
|
During a biopsy, the doctor removes some cells or tissue,
an area of small calcium deposits, or the whole lump.
The tissue is sent to a lab where a doctor called a
pathologist
will look at the cells. He or she checks the cells for cancer or other diseases. Biopsies are usually done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day as your test. Biopsies are the only way to find out if cells are cancer.
| Questions you might want to ask if your health care provider suggests a biopsy:
|
- What type of biopsy will I have? Why? How much tissue will be removed?
- Will only part of the lump or the whole lump be removed?
- Will the shape of my breast change?
- Will I have a scar?
- Where will the biopsy be done? How long will it take?
- Will I be awake?
- Will it hurt?
- Will there be any side effects?
- What tests will be done on the tissue?
- When will I know the results?
- Will I be able to go back to work the same day?
|
| After the biopsy, you might want to ask:
|
- What do the results mean?
- Do I need to have other tests?
- Will I need follow-up tests or treatment?
- How do I care for the biopsy site?
- Is it okay if I exercise?
- Does my result mean I am at
higher risk
for breast cancer?
Sometimes it's hard--even for the experts--to tell benign breast changes from cancer. If you have any questions about your biopsy results, have more than one doctor look at the results.
|
The most common types of biopsies are:
Fine-needle
aspiration
only takes a few minutes and can be done in the doctor's office. It is often done when a doctor finds a lump that appears to be a cyst. The doctor tries to remove fluid from the lump using a thin needle and a syringe. If the lump is a cyst, removing the fluid will make it go away. If the cyst returns, it can be drained again. Because cysts are rarely cancer, doctors test the fluid only if it is bloody or if there are other reasons to be concerned. If the lump is solid, cells can be taken out with the needle. These cells are checked for cancer.
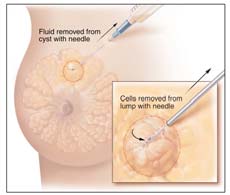 |
Fine-Needle Aspiration |
This type of biopsy can be done in the doctor's office or hospital. A core needle biopsy is a type of biopsy that uses a needle with a special cutting edge. The core needle is inserted through a small cut in the skin. A small core of tissue is removed. More than one tissue sample can be taken through the same small cut in the skin. This test may cause a bruise but rarely leaves a scar.
During the biopsy, the doctor may insert a guided
probe into the area of the breast change. The probe gently vacuums tissue samples from the area.
Sometimes the doctor uses other methods to guide the core needle or probe to the breast change. These include:
- Ultrasound-guided needle biopsy. Doctors use ultrasound to guide the needle during the biopsy. This method is used when lumps are hard to feel on a breast exam or see on a mammogram.
- Stereotactic core needle biopsy localization. A three-dimensional (3-D) x-ray guides a biopsy needle to a lump or other change that cannot be felt on a breast exam. With one type of equipment, you lie face down on an exam table with a hole in it. The hole allows your breast to hang below the table, where the x-ray machine and needle are. Or, special equipment can be attached to a standard mammogram machine to x-ray your breast from two angles.
A surgical biopsy is an operation to remove part or all of the breast lump. Most of the time, you have the biopsy and go home the same day. Sometimes a doctor will do a surgical biopsy as the first step. Other times, a doctor may do a surgical biopsy if the results of a needle biopsy do not give enough information.
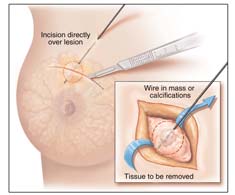 |
Surgical
Biopsy |
Sometimes, a needle is used to guide a surgical biopsy. A
mammogram or ultrasound is used to find breast
changes that cannot be felt. Once the breast change is
found, a radiologist puts a needle into the breast so
that the tip of the needle is at the area of breast change
(called
needle localization). Then a fine wire is placed through the needle. The needle may be removed and the wire stays in place. You may be asked to walk to another room or to the operating room for the biopsy. During surgery, the doctor uses the tip of the wire as a guide to what tissue to take out.
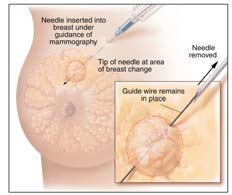 |
Needle
Localization |
On average, you should get your biopsy results from your doctor 7 to 10 days after your biopsy.
The biopsy results will tell your doctor if you have:
- Benign breast changes
- Changes that may increase your chances of getting breast cancer
- Cancer cells in the lining of your breast ducts
- Cancer cells that have spread into nearby breast tissue
Here are more detailed descriptions of biopsy results.
- Fibroadenomas--Hard, round lumps that feel like rubber
- Fat necrosis--Painless, round, firm lumps
- Sclerosing adenosis--Growths that may contain
calcifications and are often painful
Your health care provider will probably suggest that you get follow-up care for these types of benign changes. See Chart 2: Possible Biopsy Results and Follow-Up Care 4 for more information.
Two types of changes that may increase your chances of getting breast cancer
 |
Even though I was scared,
I am glad I went for a follow-up to find out
what I had. Now my doctor and I can
do something about the breast change.--Jackie, Age 63 |
ADH and LCIS are not cancer. However, having ADH or LCIS in one breast does mean that you have a higher risk of getting cancer in either breast. Your doctor will want to follow your breast health very closely if you have ADH or LCIS. For example, your doctor may suggest that you:
- Get more mammograms or see him or her more often
- Take a drug, called
tamoxifen, which has been shown to lower some women's risk of getting breast cancer
- Take part in
clinical trials
of promising new preventive treatments. In a cancer prevention trial, a large group of people is studied to help find better ways of preventing or lowering the chances of getting cancer.
A very small number of women with LCIS have surgery to remove both their breasts. They do this to try to keep breast cancer from developing. Talk to your doctor about what is best for you. See
Chart 2: Possible Biopsy Results and Follow-Up Care 4 for more information about ADH and LCIS.
DCIS
is a condition in which cancer cells are only found inside the lining of a breast duct. The abnormal cells have not spread outside the duct to the surrounding breast tissue. Therefore, most women with DCIS are cured with treatment. However, if not treated, DCIS sometimes spreads to other parts of the breast (also called invasive breast cancer). Your doctor may discuss some of these treatment choices for DCIS:
- Getting breast-sparing surgery (the surgeon removes only your cancer and some normal tissue around it) with
radiation
therapy
- Getting breast-sparing surgery without radiation therapy
- Getting a total mastectomy (surgery to remove the entire breast)
- Taking the drug tamoxifen after surgery and radiation to lower the chances of the cancer coming back
See
Chart 2: Possible Biopsy Results and Follow-Up Care 4 for more information about DCIS.
| Getting a Second Opinion
|
|
You can ask to have another pathologist review your biopsy results. This is important because biopsy results determine treatment(s) for breast changes and diseases. Ask your medical team to help you with this process.
|
Even if you have breast cancer that has spread to other parts of your breast, finding it early gives you the best chance to get treatment that may save your breasts and your life. It's also true that women with breast cancer that has spread have reasons for hope.
Some women with breast cancer may want to take part in a clinical trial. Clinical trials are research studies to find better ways to treat cancer. Some studies on new cancer-fighting drugs, drug combinations, and ways of giving treatment have already begun to show good results.
For more information about breast cancer and its treatments, call 1-800-4-CANCER for a free copy of What You Need To Know About Breast Cancer or visit www.cancer.gov and search for "breast cancer." (See
For More Information 5.)
Finding the Support You Need
It can be scary when you find out about a breast change, get an abnormal mammogram result, or learn you have breast cancer. Many women have found it helpful to:
- Ask friends or loved ones for support. Take someone with you while you are learning about your testing and treatment choices.
- Ask your doctor or nurse to:
- Help you understand medical terms that are confusing
- Tell you how other people have handled the types of feelings that you are having
- Contact the organizations listed in For more Information 5.
For More Information
The following organizations can give you more information on mammograms, breast changes, finding breast cancer early, and different breast cancer treatments.
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
You can find out more from these free NCI services:
Cancer Information Service
| Toll free: | 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237)
|
| TTY: | 1-800-332-8615 |
- Answers to your questions about cancer
- Tips to prevent and screen for cancer
- Informational materials
- Other resources
NCI Online
Web site: www.cancer.gov
This Web site provides current and accurate information from the National Cancer Institute. Through instant messaging (LiveHelp), Information Specialists can answer your questions about cancer and provide help in navigating NCI's Web site. You will find a wide range of cancer information, including:
- Treatment options
- Clinical trials
- Ways to reduce cancer risk
- Prevention and screening information
- Ways to cope with cancer
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
CMS provides information about Medicare benefits to pay for screening mammograms.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
CDC conducts, supports, and promotes efforts to prevent cancer
and increase early detection of cancer. CDC's National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program provides free breast and cervical cancer screening and diagnostic services to women with low incomes.
National Women's Health Information Center (NWHIC)
| Toll free: | 1-800-994-WOMAN (1-800-994-9662) |
| TTY: | 1-888-220-5446 |
| Web site: | www.4woman.gov |
NWHIC provides a gateway to women's health information.
NWHIC is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office on Women's Health.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The FDA has information about
mammography
on its Web site, including a section for consumers, a list of FDA-approved mammography facilities, and laws about how these facilities are run.
Chart 1: Possible Mammogram Results and Follow-Up Care
| Conditions |
Features |
What Your Doctor May Recommend |
|
Cysts
|
-
Fluid-filled lumps
-
Usually not cancer
-
Occur most often in women ages 35-50
-
Often in both breasts
-
Some too small to be felt
|
-
Doctors often watch cysts over time or use fine-needle aspiration to remove the
fluid from the cyst.
-
Ultrasound may be used to see whether a lump is solid or filled with fluid.
|
| Fibroadenoma |
-
Hard, round, benign growth
-
Feels like rubber; moves around easily
-
Usually painless
-
Often found by the woman herself
-
Appears on mammogram as smooth, round lumps with clearly defined edges
-
Can get bigger when the woman is pregnant or nursing
|
-
Sometimes diagnosed with fine-needle aspiration
-
If the fibroadenoma does not appear normal, the doctor may suggest taking it
out to make sure it is benign.
|
| Macrocalcifications |
-
Appear on a mammogram as large calcium deposits
-
Often caused by aging
-
Usually not cancer
|
-
Have another mammogram to have a closer look at the area
-
A biopsy may be used for diagnosis
|
| Mass |
-
May be round and smooth or have irregular borders
-
May be caused by normal hormone changes
|
-
A mammogram and/or ultrasound may be used to see whether a lump is solid or filled with fluid
-
A biopsy may be used for diagnosis
|
| Microcalcifications |
-
Appear on a mammogram as tiny specks of calcium that might be found in an area
of rapidly dividing cells
-
If they are found grouped together in a certain way, they may be a sign of
cancer.
|
-
Have another mammogram to have a closer look at the area
-
A biopsy may be used for diagnosis
|
 |
Chart 2: Possible Biopsy Results and Follow-Up Care
| Conditions |
Features |
What Your Doctor May Recommend |
|
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia (ADH)
|
|
-
Getting more mammograms and/or seeing the doctor more often
-
Taking tamoxifen
|
| Cancer |
-
Abnormal cells dividing without control in the breast
-
Could spread to other parts of the body
|
-
Surgery
-
Chemotherapy
-
Radiation therapy
-
Hormonal therapy
-
Biological therapy
-
Treatment may depend on the stage of the disease
|
|
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
|
-
Cancer cells in the breast ducts
-
Has not spread to other parts of the breast
-
May develop into cancer that spreads to other parts of the breast (invasive
breast cancer)
|
-
Breast-sparing surgery and radiation therapy
(with or without tamoxifen)
-
Breast-sparing surgery without radiation therapy
(with or without tamoxifen)
-
Total mastectomy (with or without tamoxifen)
|
|
Fat Necrosis
|
-
Painless, round, firm lumps
-
Formed by damaged fatty tissue
-
May occur after surgery to the breast
-
Often occurs in response to a bruise or blow to the breast, although a woman
might not recall being injured
|
-
Sometimes removed with surgical biopsy because it can look like cancer
|
|
Fibroadenoma
|
-
Hard, round, benign growth
-
Feels like rubber; moves around easily
-
Usually painless
-
Often found by the woman herself
-
Appears on mammogram as smooth, round lumps with clearly defined edges
-
Can get bigger when the woman is pregnant or nursing
|
-
Sometimes diagnosed with fine-needle aspiration
-
If the fibroadenoma does not appear normal, the doctor may suggest taking it
out to make sure it is benign
|
|
Intraductal Papilloma
|
-
Growth inside the nipple that looks like a wart
-
May cause nipple discharge
|
-
Surgery to remove the growth
|
| Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS) |
-
Abnormal cells found in the lobules
-
Not cancerous but associated with a greater chance of getting cancer in either
breast in the future
|
-
Regular check-ups to look for signs of breast cancer
-
Tamoxifen may be suggested
-
Evaluation of breast cancer risk by your doctor
|
|
Sclerosing Adenosis
|
-
Too much tissue growth in lobules
-
Can contain calcifications
-
Often painful
-
Changes usually very small but can produce lumps
|
-
Clinical breast exam
-
Annual mammogram
-
More tests if breast changes are noted on breast self-exam, clinical breast
exam, or mammogram
|
More information on these conditions can be found on www.cancer.gov or by
calling 1-800-4-CANCER.
|