WEB FOCUSES
Top of pageBiological sciences archive

Cancer stem cells
Cancer stem cells are defined as those cells within a tumour that can self-renew and drive tumorigenesis. Rare cancer stem cells have been isolated from a number of human tumours, including haematopoietic, brain, colon and breast cancers. The cancer stem-cell concept has important implications for cancer therapy. However, the generality of the cancer stem-cell hypothesis has also been challenged, most recently in a paper by Sean Morrison and colleagues included in this web focus.
Voltage sensing by membrane proteins
The electrical potential across cellular membranes is sensed by specialized proteins — typically, voltage-gated ion channels. Until recently, the mechanism by which 'voltage sensors' respond to potential changes was unclear. But since the first, and very surprising, structure of a voltage-sensing domain 5 years ago, much progress has been made. This focus celebrates the twists and turns of that progress in an archive of Nature papers from the past 5 years.

Personal genomes
As the number of human beings with their genomes fully sequenced ticks higher and direct-to-consumer gene profiling companies push the limits of what medical genetics can do, the once fantastical notion that any given human can walk into a doctor's office with her genome on a hard drive looks more and more like a reality. Still the question remains to be answered: how do we use this wealth information? In this Nature web focus we proudly present the challenges this approaching reality poses for technology, the legal and ethical confines of research, and the ability of genomics to translate into clinical utility. Here you'll also find the latest additions to the human genome menagerie, males from Africa and Asia.

Malaria
Malaria continues to claim a significant number of lives worldwide, estimated at ~ 1 million each year. The genome sequence of the most prominent human parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, was published in Nature in 2002. We are now proud to present the genome sequences of two additional human parasites, Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium knowlesi, along with a Review article discussing the scientific discoveries that have been aided by this information. In addition, we present a collection of papers illustrating highlights in malaria research that were published in recent years.
Frontiers in HIV/AIDS
An effective vaccine and new drugs to treat HIV/AIDS are urgently needed. These challenges require improved understanding of the biology of the virus, its interaction with infected cells and the immune response. This web focus presents selected recent research papers published in Nature and highlights topical issues in the field.

Symbiosis
Life depends on relationships. The enormous technological progress achieved in recent years has made it possible to investigate the 'simple' one-on-one interactions between two species as well as defining the associations between complex microbial communities and humans. These efforts have provided insights reaching from the identification of the participating partners to defining beneficial molecular and cellular interactions. This web focus both reflects the broad scope of symbiosis research and demonstrates how similar the underlying concepts are, independent of the system investigated. It is certainly a fascinating and fast-moving field, as we hope is portrayed in this selection of papers.
Reaching for regenerative medicine
One could argue that regenerative medicine is more theory than practice: only a handful of therapies such as skin grafts and heart transplants are happening today. However, research on regeneration of mammalian tissues and organs has intensified over the past decade, with the discovery of new ways to isolate and even create stem cells that can restore function, at least in rodents. Now the challenge—a formidable one—is learning what is necessary to make it work in patients. In this web focus, we have brought together content from Nature and Nature Reports Stem Cells to highlight where we are with the basic science, and the challenge of making medicine from stem cells, whether derived from adult tissue, reprogrammed cultured cells or embryos.

Protein transport and trafficking
Proteins are transported across cellular membranes and between membrane-bound organelles inside vesicles by carrier proteins. Understanding these processes has been a major goal of cell biology for several decades. Increasingly, efforts are focusing on providing a molecular description of the structures and mechanisms of the complex protein components that are required to carry out these processes. This special web focus presents a selection of papers covering the latest advances in this area, which will be of interest to a wide range of biologists engaged in different fields of research.

Drosophila
Nature is delighted to present a special issue on Drosophila biology, genomics and evolution. Papers include reviews on the unique place of the fruit fly in laboratory studies in many fields of biology, and analyses of ten novel Drosophila primary genome sequences. These sequences allowed researchers to examine genes and transcripts on an entire phylogenetic framework simultaneously, and will assist studies in most areas of biology.

Circuits and innate behaviour
Neuroscientists have made great progress in understanding the mechanisms and processes of innate behaviours, such as sexual behaviour, olfaction, sleep and touch, as well as the anatomical and molecular circuits that mediate them. In this Nature web focus, we highlight some recent advances and technical breakthroughs that offer great promise for the dissection of these circuits and their functions in the future.

ENCODE
The ENCODE project — standing for ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements — has set out to identify all the functional elements in the human genome. Detailed in the 14 June 2007 issue of Nature, a pilot project on 1% of the genome reveals new insights about how the information coded in the DNA blueprint is turned into functioning systems in the living cell.

Plant—microbe interactions
Plant—microbe encounters can be friendly or hostile. Densely colonized soil contains beneficial mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia, which associate with roots and provide plants with mineral nutrients and fixed nitrogen, respectively, in exchange for carbon. By contrast, plants are constantly exposed to a range of fungal, bacterial and viral pathogens, and have evolved unique defense mechanisms to fight these infections. We hope you will enjoy this selection of papers covering recent scientific discoveries concerning these interesting and diverse relationships.

Marsupial genomics
Marsupials split off from the main mammalian lineage millions of years ago, and have been studied by biologists for years to discover what they can tell us about ancient mammals, particularly the evolution of mammalian sex chromosomes. Plus they are cute! The first marsupial genome has been sequenced and analysed from a tiny opossum named Monodelphis domestica. This Nature web focus presents the original research, and an archive of marsupial genetics and genomics.
Technical breakthroughs in neuroscience
This special Nature web focus brings together exclusive coverage of the discovery, along with recent papers describing and utilizing cutting-edge technology for understanding and controlling brain and behaviour.

Linnaeus at 300
"God created; Linnaeus arranged". No scientist has done more to bring order to the natural world than Carl Linnaeus, born three centuries ago this year in 1707. His introduction of systematic classification into botany and more widely provided the foundations on which all subsequent natural history has been built. From the Enlightenment onwards, to try and arrange nature's profusions in a rational way has been to put oneself into Linnaeus's debt.

Neanderthal DNA
This special Nature web focus brings together exclusive video and audio coverage of the Neanderthal DNA sequencing project along with a number of recent papers highlighting genetic and genomic discoveries that could shed light on the origin of distinctively human innovations

Honeybee genome
Honeybees have fascinating social structure and advanced societies despite having brains that are five orders of magnitude smaller than humans. An international consortium here reports the genome sequence of the honeybee. Initial analysis of gene content and evolution yields insight into how they accomplish such complex organisation and behaviours such as the famous 'waggle dance'. This special Nature web focus celebrates the publication of the honeybee genome with video interviews and news analysis of the primary research papers, and a comprehensive archive of all matters Apis mellifera.

Signalling in plants
Over the last decade our understanding of plant signalling pathways has increased a great extent, in part due to the use of genetic tools in Arabidopsis. This has assisted in the identification of hormonal, developmental and environmental signal transduction pathways and cross-talk between them. A flavour of the excitement in the plant signalling pathways field can be obtained in the research articles and reviews presented in this Nature web focus.
Hominid evolution and development.
Childhood is perhaps the defining feature of humanity. But when and how did it evolve? The dearth of fossils that combine evidence from the head and body makes the 3.3-million-year-old partial skeleton of Australopithecus afarensis — the earliest known juvenile hominid skeleton of any kind – an important discovery. A special Nature web focus includes exclusive video interviews with the scientists behind this find alongside their research, news and features, further analysis on the Nature Podcast, and an archive of related palaeontological finds. Selected articles are free access.
Brain-machine interfaces
Brain-machine interfaces promise to aid paralyzed patients by re-routing movement-related signals around damaged parts of the nervous system. A new study in Nature demonstrates a human with spinal injury manipulating a screen cursor and robotic devices by thought alone. Implanted electrodes in his motor cortex recorded neural activity, and translated it into movement commands. A second study, in monkeys, shows that brain-machine interfaces can operate at high speed, greatly increasing their clinical potential. This Nature Web Focus includes exclusive interviews and video footage of experiments, alongside papers that paved the way for these recent advances.
25 years of Embryonic Stem Cells
This year marks the 25th anniversary of two papers reporting the first isolation of mouse ES cells. The first impact of the mouse ES papers was enabling targeted gene knock outs in mice, which has revolutionized mouse genetics and developmental biology. Seventeen years later, Jamie Thomson isolated ES cells from human embryos, a technical achievement that has become of the great milestones in human biomedical research. To mark this occasion, Nature is featuring papers that show the progression of ES cell research. We hope you find it a compelling story.

Antimicrobials
The development of new antimicrobial drugs is urgently needed in the battle against infectious diseases. The discovery of a new antimicrobial — platensimycin — represents a previously unknown class of antibiotics. This Nature web focus features the latest on this discovery and includes a News & Views article, and specially selected papers on antibiotic function, resistance and development.
Metalloproteins
Proteins that contain transition metals are involved in a wide range of biologically-important processes, including natural product and cofactor biosynthesis, histone demethylation, and methane oxidation. To highlight this exciting field, this Nature web focus presents a selection of recently published papers and an archive that explore the structures, mechanisms, and biological activities of several unusual metalloproteins.
DNA replication
The pioneering in vitro studies of the Kornberg laboratory on bacterial and phage DNA replication are now 40 years old. But it would be misplaced to think that the question of how their DNA is replicated has been solved. Three papers in Nature's 2 Feb 2006 issue highlight the continuing value bacteria and phages offer in studies of the mechanism of DNA duplication.
Cell & Membrane Biology
Sealed membrane systems are a defining feature of cellular life. They provide a barrier between the cell and its external environment and, in eukaryotes, divide the interior of the cell into functionally distinct compartments.
A flavour of the current excitement in cell and membrane biology can be obtained in the research articles and reviews presented in this Nature web focus.

HapMap
In this Web Focus we present the first edition of the International HapMap project. See Nature's Human Genome Collection for the definitive historical record of the sequences and analyses of the Human Genome Project. Image: Fuli Yu

Making Stem Cells
Nature has published two new methods for deriving embryonic stem cells that aim to overcome ethical objections to using human embryos for research. But while it remains to be seen whether these particular methods will translate widely to research clinics, there is no doubt that technically innovative and elegant methodologies will propel the stem-cell field forward.
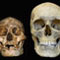
Flores Man
With the discovery of Flores Man, a new species of human from just 18,000 years ago, reported in this issue of Nature, the Pacific Rim is yet again proving to be the dusty attic of evolution - full of unusual and often bizarre artefacts of biology. Here, we gather together the papers on Flores Man, as well as recent papers from Nature on other oddities that have sprung up from this fascinating region.

1918 influenza pandemic
Produced with support from Retroscreen Virology Ltd.
In 1918, a highly virulent form of the influenza virus killed at least 20 million people worldwide. Understanding the origin of the virus that caused this pandemic has been a long-standing goal because of the risk that a similar virus could arise and devastate human populations today.

The chimpanzee genome -
The first of the chimpanzee's chromosomes has been sequenced. What can this accomplishment tell us about how we have come to look and act so differently from our chimp relatives?

Senescence
Is growing old a good thing? As cells mature they naturally stop dividing and enter a period called senescence. But cellular senescence can also be induced prematurely by certain oncogenes involved in cancer development. In this web focus, Nature shows that, as previously suggested by in vitro studies, oncogene-induced cellular senescence represents a safety mechanism to suppress tumour progression in vivo.
Riches in stem-cell niches
Produced with support from Abcam
In the world of stem-cell research, attention is increasingly focused on the microenvironments within an organism where stem cells reside - the stem-cell niches. There is now evidence that the molecular signals exchanged between stem cells and other cells within these niches are key factors in stem-cell control. Finding and identifying these signals has become a major thrust in stem-cell research.

Dictyostelium discoideum genome Free access
The slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum has been an important laboratory model for over 50 years. These social amoebae normally live in forest soil where they hunt bacteria and yeast, and have therefore excelled in studies of how cells sense and move towards attractants in their environment.

Avian Flu
Welcome to this Web Focus on Avian Flu, containing news and scientific reports warning about the potential for a new human flu pandemic in the near future.

End of polio - the final assault
Produced with support from March of Dimes and Rotary International
Welcome to this Web Focus celebrating the 50th anniversary of the first effective vaccine against polio, in which we provide a selection of news, commentary, reviews and research papers.
DNA metabolism
The genome is the fundamental entity of a cell. Many processes are therefore directed at ensuring its faithful duplication and at repairing endogenous and exogenous damage to it. Intimate links between these two facets of DNA metabolism have been increasingly recognized. Here we highlight Nature's most recent papers on replication and repair.

Landmark papers in cell biology 2004
Produced with support from Invitrogen
The structural analysis of increasingly complex macromolecular systems is revolutionising our understanding of cell biology. Nature has been at the forefront of this revolution having recently published a string of landmark papers that provide fundamental insights into cellular function.

The chicken genome - Free access
No matter what side of the road they're on, chickens are an extremely important model for many fields of biology. Read Nature's extensive resource for the chicken genome with free access to the latest original research, as with all our primary genome content.
Cell cycle and cell division
The regulation of cell cycle progression and cell division is at the heart of cell biological research. Understanding the central mechanisms also offers new insights into cancer biology. Gathered here is a selection of recent research and comment from the pages of Nature, including groundbreaking research from today's issue. This focus also includes our recent Nature Insight Cell division and Cancer.

RNA interference
Produced with support from Qiagen
Cells utilize RNA interference (RNAi) to regulate protein expression in many contexts. Gathered here is a selection of the latest research and commentary on RNAi published in the pages of Nature, as well as news and reviews, and an animation offers the chance to view the RNAi process in action.
Sensory transduction
The transduction of environmental stimuli into a cellular response is known as sensory transduction. The last few years have seen huge advances in understanding the specialized cellular mechanisms of transduction, and in identifying the molecules involved. This special web focus presents recent research highlights from the pages of Nature.

Malaria
Malaria kills more than a million people each year. Experts say there is a greater hope of beating the disease now than ever before - but more money, better and cheaper drugs, and treatment strategies involving local participation will be needed. Nature presents a free web focus, collecting research, news features and reviews.

Athens Olympics special
It's the Olympic games in Athens this month. news@nature.com's special report includes features on what it takes to win gold, the ongoing battle between drug-takers and testers, competitors who push their bodies to the limit - and sometimes beyond, and interactive graphics on how to build the perfect endurance athlete.

Francis Crick: 1916-2004
The co-discoverer of the structure of DNA died this week. In this web focus, we chart the career of this astonishing scientist, including a comprehensive archive of his myriad writings in Nature.

John Maynard Smith
From Eton to Sussex, from aircraft engineer to original thinker in evolutionary biology; the life and work of John Maynard Smith, who died in April 2004, is celebrated in this web focus, including a selection of his most important research and writings, all available free.

Muscle crossbridge 50-year anniversary
In 1954, two Nature papers uncovered the story of one of the most intriguing of biological problems: the conversion of chemical energy to mechanical work. A decade-by-decade snapshot from Nature's archive of subsequent publications on muscle crossbridges celebrates 50 years of research.

The rat genome - Free access
The rat, both scourge and servant to mankind, has had its genome sequence completed. Read Nature's free focus, including news, features, interactive graphics and access to a special issue of Genome Research.

Bird flu
Nature keeps track of the key events and scientific discoveries as researchers assess the threat of another flu pandemic.

GM crops: Time to choose
Today, just four countries account for 99% of the world's commercially grown transgenic crops. Others have been stalling over whether to embrace transgenic agriculture, but won't be able to put off the decision much longer. Here, Nature examines the state of play with special features and interactive graphics.

Determining lifespan
Why do humans age, when fairly similar creatures (such as turtles) apparently do not? Here, we present the latest research on a molecule that appears to mimic the well-documented lifespan-extending attributes of eating fewer calories. Also featured is a comprehensive archive on ageing research, from nematodes to humans.

Ocean genomics
Despite the sequencing of microbial genomes now being almost routine, recent studies powerfully demonstrate how genomics can lead to a new understanding of biodiversity and ecology. This collection highlights the significance of genome sequences from key components of the ocean's food web.
Germ cells
Boy meets girl, sperm meets egg. This timeless tale is increasingly being played out in a culture dish, such is the progress in germ cell biology in recent times. Here, Nature presents the latest research on the establishment of the germline.
Y chromosome - Free access
The Y chromosome - with the genes to make a man - has been sequenced. Often regarded as a genetic wasteland, the sequence reveals that we may have underestimated its powers.

SARS
Nature's reporters pose key questions about the SARS outbreak, and assess our preparedness to deal with future viral threats.
Ion channels: structure and function
Ion channels allow the movement of ions across cell membranes, and therefore fundamental physiological processes such as muscle contraction. This collection of papers illustrates the structural revolution that the field is currently experiencing.

Proteomics
The techniques and methodologies that promises to transform biological and medical research.
Double Helix: 50 years of DNA
Nature presents a collection of articles and graphics that celebrate the historical, scientific and cultural impacts of the discovery of the double helix.

Dolly the sheep
Dolly, the world's first animal to be cloned from an adult cell, died in February 2003. Here, Nature reflects on the life of this extraordinary sheep.
The mouse genome - Free access
Nature is proud to present the complete initial sequence and analysis of the mouse genome - the experimental key to the human genome

Computational biology
Biology is overwhelmed with data. Here, Nature's focus on Computational Biology provides a diverse set of reviews giving an overview of the areas of molecular cell biology that are embracing the application of mathematical theory to advance discovery.

Stem cells
A one-stop shop for a selection of excellent articles and features on stem cells handpicked from the pages of Nature, including the specially commissioned Stem cell Insight.

Toumaï: Face of the deep
At between 6 and 7 million years old, Toumaï is the earliest known record of the human family. To celebrate the discovery of this skull, we are proud to offer a selection of ten of the very best from Nature's archives.

Anthrax
Recent events have confirmed that bioterrorism is no longer a threat but a reality. To provide wide-ranging access to the latest scientific information about anthrax and other potential bioweapons, Nature presents research, news and features from our archive.
