|
DEA
Offices & Telephone Nos.
Denver—303-705-7300
Colorado Springs—719-866-6100
Grand Junction—970-683-3220
Glenwood Springs—970-945-0744
Durango—970-385-5147 |
State Facts
Population: 4,665,177
State Prison Population: 20,293
Probation Population: 58,108
Violent Crime Rate
National Ranking: 25 |
2007
Federal Drug Seizures
Cocaine: 44.0 kgs.
Heroin: 2.5 kgs.
Methamphetamine: 8.0 kgs.
Marijuana: 1,149.5 kgs.
Hashish: 0.0 kgs.
MDMA: 0.0 kgs.
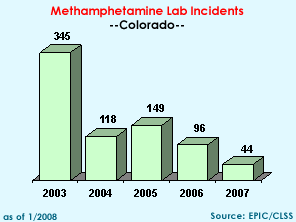
Meth
Lab Incidents: 44
(DEA, state, and local) |
Drug
Situation: Mexican poly-drug trafficking organizations control most of the methamphetamine, cocaine, marijuana, and heroin distribution in Colorado. Asian groups, many with ties to Canada, have been increasingly active in the distribution of club drugs and marijuana. Dealers with ties to larger criminal organizations in Texas, California, and Mexico are involved in all types of drug distribution throughout the state.
 Cocaine: Enforcement activities reflect a steady supply of cocaine coming into and through Colorado. Cocaine trafficking organizations with sources of supply in Mexico or along the Southwest Border often deal in multi-kilogram amounts. Crack is available in the larger metropolitan areas of Colorado, generally in street level amounts. Cocaine is trafficked by Mexican poly-drug organizations typically capable of distributing other drugs as well. Cocaine: Enforcement activities reflect a steady supply of cocaine coming into and through Colorado. Cocaine trafficking organizations with sources of supply in Mexico or along the Southwest Border often deal in multi-kilogram amounts. Crack is available in the larger metropolitan areas of Colorado, generally in street level amounts. Cocaine is trafficked by Mexican poly-drug organizations typically capable of distributing other drugs as well.
 Heroin: Mexican black tar heroin is the predominant type of heroin found in Colorado and is available in the major metropolitan areas of Colorado. Mexican brown heroin is also found to a lesser degree. Various law enforcement and treatment indicators suggest that heroin availability and use may be on the rise in Colorado. Heroin is trafficked by Mexican poly-drug organizations typically capable of distributing both heroin and cocaine. Heroin: Mexican black tar heroin is the predominant type of heroin found in Colorado and is available in the major metropolitan areas of Colorado. Mexican brown heroin is also found to a lesser degree. Various law enforcement and treatment indicators suggest that heroin availability and use may be on the rise in Colorado. Heroin is trafficked by Mexican poly-drug organizations typically capable of distributing both heroin and cocaine.
 Methamphetamine:
Most of the methamphetamine available in Colorado originates in Mexico. In recent years, the potency of methamphetamine produced in Mexico has risen to levels comparable to that made in smaller, local clandestine laboratories. While clandestine laboratories remain problematic to law enforcement in Colorado, the number of such laboratories has diminished dramatically. This is possibly due to the increasing supply of Mexican-produced methamphetamine. Despite a lower number of clandestine laboratories, these operations still represent a threat to the public safety and the environment. Methamphetamine:
Most of the methamphetamine available in Colorado originates in Mexico. In recent years, the potency of methamphetamine produced in Mexico has risen to levels comparable to that made in smaller, local clandestine laboratories. While clandestine laboratories remain problematic to law enforcement in Colorado, the number of such laboratories has diminished dramatically. This is possibly due to the increasing supply of Mexican-produced methamphetamine. Despite a lower number of clandestine laboratories, these operations still represent a threat to the public safety and the environment.
  Club
Drugs: The category of substances known as “club drugs” is most often associated with nightclubs and private parties. DEA investigations indicate that violence, pornography, and prostitution often play key roles in club drug trafficking and abuse. MDMA generally is distributed by independent traffickers or loosely-knit organizations with both domestic and foreign sources of supply. Asian gangs play a significant role in club drug distribution. LSD, Ketamine, and gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) are also distributed and used in the nightclub scene. Club
Drugs: The category of substances known as “club drugs” is most often associated with nightclubs and private parties. DEA investigations indicate that violence, pornography, and prostitution often play key roles in club drug trafficking and abuse. MDMA generally is distributed by independent traffickers or loosely-knit organizations with both domestic and foreign sources of supply. Asian gangs play a significant role in club drug distribution. LSD, Ketamine, and gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) are also distributed and used in the nightclub scene.
  Marijuana:
Marijuana is available throughout Colorado and is the most widely abused drug in the state. The most abundant supply of marijuana is Mexican-grown and is brought into and through Colorado by poly-drug trafficking organizations. The highly potent form of marijuana known as “BC Bud” is significantly more expensive, and is smuggled from British Columbia, Canada, and the Pacific Northwest. Indoor marijuana grow operations are regularly found by law enforcement and appear to be increasing in number. These operations range from very simple to extremely complex. Some residences have been converted entirely to grow houses. Grow operations are conducted by independent traffickers, loosely organized groups, and Asian gangs. Generally, these groups also have the ability to distribute marijuana from Canada and the Pacific Northwest as well. Colorado’s Amendment 20, which took effect June 1, 2001, allows for the use and possession of small amounts of marijuana for sick and dying patients. It provides protection against prosecution under state law, which is where the majority of marijuana small-use and possession cases occur. A 2005 vote in the City and County of Denver legalized ounce or smaller amounts of marijuana for personal recreational use. The proponents of this measure introduced a similar marijuana measure proposing changes in state law for Colorado voters to decide in 2006. Amendment 44 failed in the 2006 vote. Marijuana:
Marijuana is available throughout Colorado and is the most widely abused drug in the state. The most abundant supply of marijuana is Mexican-grown and is brought into and through Colorado by poly-drug trafficking organizations. The highly potent form of marijuana known as “BC Bud” is significantly more expensive, and is smuggled from British Columbia, Canada, and the Pacific Northwest. Indoor marijuana grow operations are regularly found by law enforcement and appear to be increasing in number. These operations range from very simple to extremely complex. Some residences have been converted entirely to grow houses. Grow operations are conducted by independent traffickers, loosely organized groups, and Asian gangs. Generally, these groups also have the ability to distribute marijuana from Canada and the Pacific Northwest as well. Colorado’s Amendment 20, which took effect June 1, 2001, allows for the use and possession of small amounts of marijuana for sick and dying patients. It provides protection against prosecution under state law, which is where the majority of marijuana small-use and possession cases occur. A 2005 vote in the City and County of Denver legalized ounce or smaller amounts of marijuana for personal recreational use. The proponents of this measure introduced a similar marijuana measure proposing changes in state law for Colorado voters to decide in 2006. Amendment 44 failed in the 2006 vote.
Pharmaceutical Diversion: Current investigations indicate that diversion of hydrocodone products such as Vicodin®, and oxycodone products (such as brand name and generic OxyContin®) continues to be a problem in Colorado. Primary methods of diversion being reported are forged prescriptions, employee theft, and the Internet. Benzodiazepines (such as Xanax® and Valium®), methadone, MS Contin®, Darvon® and Darvocet® were also identified as being among the most commonly abused and diverted pharmaceuticals in Colorado.
 Other
Drugs: Pharmaceutical opiates/opioids are the drugs of choice among drug abusing medical professionals in Colorado. Hydrocodone (Vicodin) and Darvocet are the two controlled substances most commonly abused, with various forms of prescription fraud and retail diversion being the methods for obtaining them. The diversion and abuse of OxyContin (oxycodone) is a significant problem in Colorado. Other
Drugs: Pharmaceutical opiates/opioids are the drugs of choice among drug abusing medical professionals in Colorado. Hydrocodone (Vicodin) and Darvocet are the two controlled substances most commonly abused, with various forms of prescription fraud and retail diversion being the methods for obtaining them. The diversion and abuse of OxyContin (oxycodone) is a significant problem in Colorado.
DEA Mobile Enforcement Teams: This cooperative program with state and local law enforcement counterparts was conceived in 1995 in response to the overwhelming problem of drug-related violent crime in towns and cities across the nation. Since the inception of the MET Program, 473 deployments have been completed nationwide, resulting in 19,643 arrests. There have been approximately two dozen Mobile Enforcement Team (MET) deployments in the State of Colorado since the inception of the program: Lakewood, Durango, Edgewater, Avon, Eagle/Garfield Counties, Pueblo (2), La Plata County, Longmont, El Paso County, Englewood, Jefferson County (2), San Luis Valley, Adams County, Boulder County, Larimer County, and four deployments in Denver. In March 2005, the METs prioritized investigations to target and dismantle methamphetamine trafficking organizations and clandestine laboratory operators. Three recent MET deployments have specifically targeted methamphetamine trafficking organizations in Jefferson County, Larimer County, and Boulder County. During 2006, the MET deployed in Summit County to dismantle multiple poly-drug distributors, resulting in 34 arrests.
DEA
Regional Enforcement Teams: This program was designed to augment existing DEA division resources by targeting drug organizations operating in the United States where there is a lack of sufficient local drug law enforcement. This Program was conceived in 1999 in response to the threat posed by drug trafficking organizations that have established networks of cells to conduct drug trafficking operations in smaller, non-traditional trafficking locations in the United States. As of January 31, 2005, there have been 27 deployments nationwide, and one deployment in the U.S. Virgin Islands, resulting in 671 arrests. There have been no RET deployments in the State of Colorado.
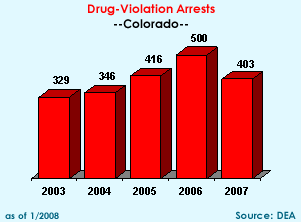 Other
Enforcement Operations: A 2003 Denver MET deployment, which
assisted a local task force in the investigation of a Denver area Mexican
methamphetamine trafficking organization, resulted in the arrests of
21 individuals and the seizure of 9 pounds of methamphetamine. The methamphetamine
seized and purchased through undercover buys was consistently in excess
of 90 percent pure. Other
Enforcement Operations: A 2003 Denver MET deployment, which
assisted a local task force in the investigation of a Denver area Mexican
methamphetamine trafficking organization, resulted in the arrests of
21 individuals and the seizure of 9 pounds of methamphetamine. The methamphetamine
seized and purchased through undercover buys was consistently in excess
of 90 percent pure.
Special
Topics: In 1996, a High Intensity Drug Trafficking Area (HIDTA) was designated in Colorado and is comprised of Adams, Arapahoe, Boulder, Denver, Douglas, Eagle, El Paso, Garfield, Grand, Jefferson, LaPlata, Larimer, Pueblo, Mesa, Moffat, Routt, and Weld counties.
More information
about the Denver Division Office.
Sources
Factsheet
last updated:
3/2008
Click
here for last year's factsheet >>
|

