
 |
|
 |

|
Reliability of Estimations, 1998
Because the data presented on this tape are based on a sample, they will differ somewhat from data that would have been obtained if a complete census had been taken using the same schedules, instructions, and procedures. The standard error (SE) is primarily a measure of the variability that occurs by chance because a sample, rather than the entire universe, is surveyed. The SE also reflects part of the measurement error, but it does not measure any systematic biases in the data. The chances are about 95 in 100 that an estimate from the sample differs from the value that would be obtained from a complete census by less than twice the SE. However, SE's typically underestimate the true errors of the statistics because they reflect only errors due to sampling.
To derive error estimates that would be applicable to a wide variety of statistics, variances for a wide variety of estimates were approximated using SUDAAN software. SUDAAN computes standard errors by using a first-order Taylor approximation of the deviation of estimates from their expected values. A description of the software and the approach it uses has been published. The calculated variances were fitted into curves using the empirically determined relationship between the size of an estimate X and its relative variance (rel var X). This relationship is expressed as:
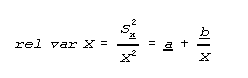
where a and b are regression estimates determined by the SAS regression procedure, using ordinary least squares. The relative standard error is then derived by determining the square root of the relative variance from the curve.
Standard errors for aggregate estimates may be approximated using the general formula:
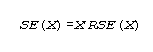
where X is the estimate and RSE(X) is the relative standard error of the estimate. The relative standard error (RSE(X)) may be estimated using the following general formula (7):
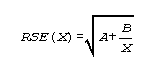
where X is the estimate and A and B are the appropriate coefficients from table I.
Table I. Parameters used to compute standard error of numbers by type of estimate
|
Type of estimate |
Parameters |
|
|
A |
B |
|
|
Agency |
0.008569 |
12.292928 |
|
Home health agency |
||
|
Current patient |
0.027473 |
1113.899256 |
|
Discharge |
0.031375 |
5418.466673 |
|
Hospice |
||
|
Current patient |
0.022992 |
84.643286 |
|
Discharge |
0.028381 |
1024.690308 |
To approximate the relative standard error (RSE(p)) and the standard error (SE(p)) of a percent p, the appropriate values of parameter B from table I are used in the following equations:
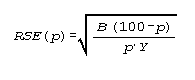
and
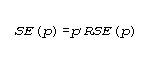
where
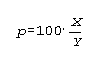
X = the
numerator of the estimated percent
Y = the
denominator of the estimated percent
The standard error of a percent is valid only when one of the following conditions is satisfied: the relative standard error of the denominator is 5 percent or less or the relative standard errors of the numerator and the denominator are both 10 percent or less.
National Home and
Hospice Care Data |
This page last reviewed
January 11, 2007
|
 National Home and
Hospice Care Data
National Home and
Hospice Care Data