 Get
E-Mail Updates on HIV/AIDS and African Americans Get
E-Mail Updates on HIV/AIDS and African Americans
 Of all racial and ethnic groups in the United States, HIV and AIDS have hit
African Americans the hardest. The reasons are not directly related to race or ethnicity, but rather to some of the barriers faced by many
African Americans.
These barriers can
include poverty (being poor), sexually
transmitted diseases, and stigma (negative
attitudes, beliefs, and actions directed at
people living with HIV/AIDS or directed at
people who do things that might put them at
risk for HIV). Of all racial and ethnic groups in the United States, HIV and AIDS have hit
African Americans the hardest. The reasons are not directly related to race or ethnicity, but rather to some of the barriers faced by many
African Americans.
These barriers can
include poverty (being poor), sexually
transmitted diseases, and stigma (negative
attitudes, beliefs, and actions directed at
people living with HIV/AIDS or directed at
people who do things that might put them at
risk for HIV).
When we look at HIV/AIDS by race and ethnicity, we see that African Americans
have
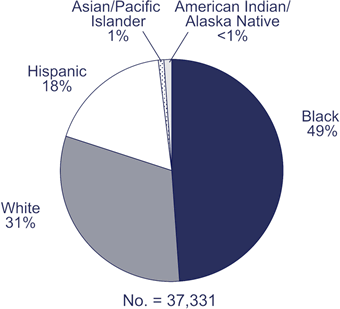
- More illness. Even though blacks (including African Americans) account for
about 13% of the US population, they account for about half (49%) of the people who get HIV and AIDS.
- Shorter survival times. Blacks with AIDS often don’t live as long as people of other races and ethnic groups with AIDS. This is due to the barriers mentioned above.
- More deaths. For African Americans and other blacks, HIV/AIDS is a leading cause of death.
As the pie chart below shows, in 2005, about half (49%) of the people diagnosed with HIV/AIDS were
black (according to information from 33 states).
Children are included in these data.
The reality is similar for children: HIV/AIDS affects black children the most. In 2005,
104 (63%) of the 166 children under the age of 13 diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in 33 states were
black.
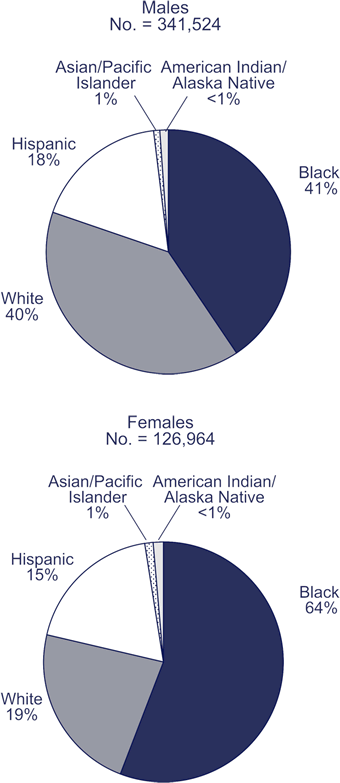
As the pie charts below show, blacks account for about half of all people living with
HIV/AIDS within each sex category. According to information from 33 states, during 2005,
- among men, 41% of men living with HIV/AIDS were black
- among women, 64% of women living with HIV/AIDS were black
For black men, the most common ways of getting HIV are (in order)
- having unprotected sex with another man who has HIV
- sharing injection drug works (like needles or syringes) with someone who has HIV
- having unprotected sex with a woman who has HIV
For black women, the most common ways of getting HIV are (in order)
- having unprotected sex with a man who has HIV
- sharing injection drug works (like needles or syringes) with someone who has HIV
Blacks at higher risk for HIV are those
- who are unaware of their partner's risk factors
- with other STDs (which affect more blacks than any other racial or ethnic group)
- who live in poverty (which is about one quarter [25%] of all blacks)
For details on HIV/AIDS in African American communities,
read the CDC fact sheet
HIV/AIDS among African Americans. |