-
-
- Terminology and Weather Symbols
-
- FRONTS
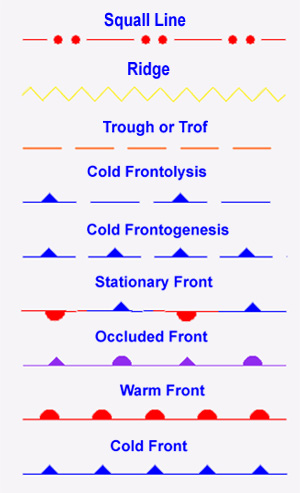
- Cold front
- -The leading edge of a relatively colder air mass which separates two air masses in which
the gradients of temperature and moisture are maximized. In the northern hemisphere winds
ahead of the front will be southwest and shift into the northwest with frontal passage.
- Frontogenesis
- -The formation of a front occurs when two adjacent air masses with different densities
and temperatures meet and strengthen the discontinuity between the air masses. It occurs
most frequently over continental land areas such as over the Eastern US when the air mass
moves out over the ocean. It is the opposite of frontolysis.
- Frontolysis
- -The weakening or dissipation of a front occurs when two adjacent air masses lose
contrasting properties such as the density and temperature. It is the opposite of
frontogenesis.
- Occluded front
- - The union of two fronts, formed as a cold front overtakes a warm front or
quasi-stationary front refers to a cold front occlusion. When a warm front overtakes a
cold front or quasi-stationary front the process is termed a warm front occlusion. These
processes lead to the dissipation of the front in which there is no gradient in
temperature and moisture.
- Ridge
- - an elongated area of relatively high pressure that is typically associated with a
anti-cyclonic wind shift.
- Stationary front
- - A front that has not moved appreciably from its previous analyzed position.
- Trough
- - [Trof], an elongated area of relatively low pressure that is typically associated with
a cyclonic wind shift.
- Warm front
- The leading edge of a relatively warmer surface air mass which
separates two distinctly different air masses. The gradients of temperature and moisture
are maximized in the frontal zone. Ahead of a typical warm front in the northern
hemisphere, winds are from the southeast and behind the front winds will shift to the
southwest.
- LOW & HIGH PRESSURE SYSTEMS AND MISCELLANEOUS KEY TERMS USED
-

- Low pressure with a number such as 99 means 999
mb and with 03 means 1003 mb. High pressure with a number such as 25
means 1025 mb.
-
- Extratropical low
- - A low pressure center which refers to a migratory frontal cyclone of center and higher
latitudes. Tropical cyclones occasionally evolve into extratropical lows losing tropical
characteristics and become associated with frontal discontinuity.
-
- Low pressure
- - An area of low pressure identified with counterclockwise circulation in the northern
hemisphere and clockwise in the southern hemisphere. Also, defined as a cyclone.
-
- High pressure
- - An area of higher pressure identified with a clockwise circulation in the northern
hemisphere and a counterclockwise circulation in the southern hemisphere. Also, defined as
an anticyclone.
-
- New
- - The term "NEW" may be used in lieu of a forecast track position of a high or
low pressure center when the center is expected to form by a specific time. For example, a
surface analysis may depict a 24-hour position of a new low pressure center with an
"X" at the 24-hour position followed by the term "NEW", the date and
time in UTC which indicates the low is expected to form by 24 hours.
-
- Rapidly intensifying
- - Indicates an expected rapid intensification of a cyclone with surface pressure
expected to fall by at least 24 millibar (mb) within 24 hours.
-
- Station plot
- Click for information on coding used with the surface preliminary analysis
or for a list of "present weather"
symbols.
-
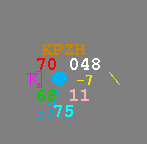
| Weather Parameter |
Weather Symbol Decoded |
| Station ID |
KPZH |
| Temperature (fahrenheit or celsius) |
70 degree F |
| Present weather |
 thunderstorm |
| Dew point temperature (fahrenheit or
celsius) |
68 degree F |
| Wind speed, direction, sky cover |
 SSW
25 kt
overcast |
| Station Pressure (mb) |
048 = 1004.8 mb |
| 3 hour pressure tendency |
-7 \ = -0.7 mb pressure decrease with
steady pressure fall |
| optional wave height (feet or meter) |
11 ft |
| Sea Surface Temperature (fahrenheit or
celsius) |
75 degrees F |
-
-
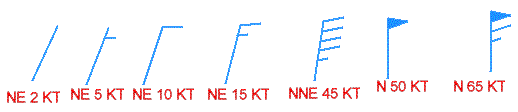
- Squall
- - A sudden wind increase characterized by a duration of minutes and followed by a sudden
decrease in winds.
Windspeed & Direction
FOG

- Fog
- -Over the marine environment the term fog refers to visibility greater than or equal to
1/2 NM and less than 3 NM. Fog is the visible aggregate of minute water droplets suspended
in the atmosphere near the surface.
-
- Dense fog
- -Over the marine environment the term dense fog refers to visibility less than 1/2 NM.
Fog is the visible aggregate of minute water droplets suspended in the atmosphere near the
surface. Usually dense fog occurs when air that is lying over a warmer surface such as the
Gulf Stream is advected across a colder water surface and the lower layer of the air mass
is cooled below its dew point.
-
- Sea fog
- - Common advection fog caused by transport of moist air over a cold body of water.
FREEZING SPRAY
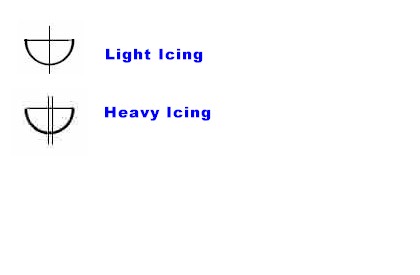
- Freezing spray
- - Spray in which supercooled water droplets freeze upon contact with exposed objects
below the freezing point of water. It usually develops in areas with winds of at least 25
knots.
-
Categories of Freezing Spray/Icing
| Light |
Moderate |
Heavy |
| Less than 0.7 cm/hr |
0.7 cm/hr to less than or equal to 2.0 cm/hr |
Greater than 2.0 cm/hr |
| Less than 0.3 ins/hr |
0.3 ins/hr to less than or equal to 0.8 ins/hr |
Greater than 0.8 ins/hr |
CONVENTIONS USED WITH WARNINGS FOR EXTRATROPICAL SYSTEMS
Extratropical Systems
Complex gale/storm
- -An area in which gale/storm force winds are forecast or are occurring, but in which
more than one center is the generating these winds.
-
- Developing Gale
- -Refers to an extratropical low or an area in which gale force winds of 34 knots (39
mph) to 47 knots (54 mph) are "expected" by a certain time period. On surface
analysis charts, a "DEVELOPING GALE" label indicates gale force winds within the next 24 hours.
When the label is used on the 48 hour surface forecast and 96 hour surface
forecast charts, gale force winds are expected to develop by 72 hours and 120 hours,
respectively.
-
- Developing Storm
- -Refers to an extratropical low or an area in which storm force winds of 48 knots (55
mph) to 63 knots (73 mph) are "expected" by a certain time period. On surface analysis
charts, a "DEVELOPING STORM" label indicates storm force winds forecast within the next 24 hours.
When the label is used on the 48 hour surface and 96 hour surface charts,
storm force winds are expected to develop by 72 hours and 120 hours, respectively.
-
- Developing Hurricane Force
- -Refers to an extratropical low or an area in which hurricane force winds of 64 knots (74 mph) or higher
are "expected" by a certain time period. On surface analysis
charts, a "DEVELOPING HURRICANE FORCE" label indicates hurricane force winds forecast within the next 24 hours.
When the label is used on the 48 hour surface and 96 hour surface charts,
hurricane force winds are expected to develop by 72 hours and 120 hours, respectively.
- Gale
- - Refers to an extratropical low or an area of sustained surface winds (averaged over
a ten minute period, momentary gusts may be higher) of
34 knots (39 mph) to 47 knots (54 mph).
-
- Storm
- - Refers to a extratropical low or an area of sustained winds (averaged over
a ten minute period, momentary gusts may be higher) of
48 knots (55 mph) to 63 knots (73 mph).
-
- Hurricane Force
- - Refers to a extratropical low or an area of sustained winds (averaged over
a ten minute period, momentary gusts may be higher) in excess of
64 knots or higher(74 mph).
Small Craft Advisory
- - Refers to areas within the coastal waters with sustained winds of 18
knots (21 mph) to 33 knots (38 mph).
Heavy Freezing Spray
- -Spray in which supercooled water droplets freeze upon contact with exposed objects
below the freezing point of water at the rate of greater than 2 cm/hr. It usually develops
in areas with winds of at least 25knots.
-
-
- CONVENTIONS USED WITH WARNINGS FOR TROPICAL SYSTEMS
- Tropical Systems
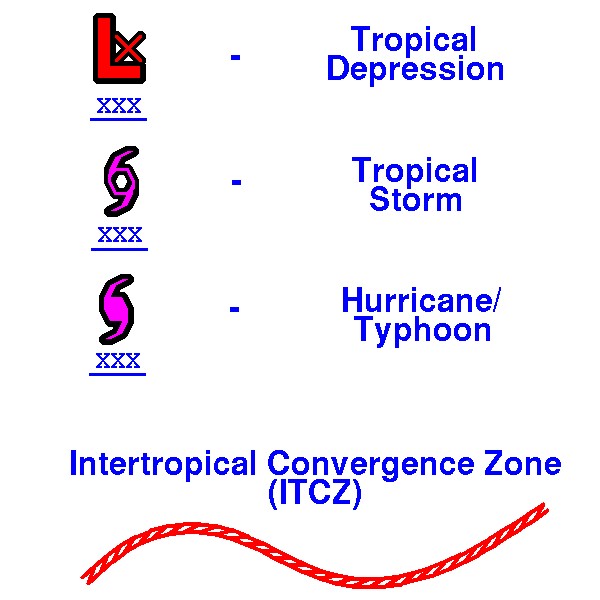
- Hurricane
- - A tropical cyclone with closed contours, a strong and very pronounced circulation, and
one minute maximum sustained surface winds 64 knots (74 mph) or greater. A system is
called a hurricane over the North Atlantic, Gulf of Mexico, North Pacific E of the
dateline, and the South Pacific E of 160E.
-
- Intertropical Convergence Zone
- - (ITCZ) The region where the northeasterly and southeasterly trade winds converge,
forming an often continuous band of clouds or thunderstorms near the equator.
-
- Tropical cyclone
- - A non-frontal, warm-core, low pressure system of synoptic scale, developing over
tropical or subtropical waters with definite organized convection (thunderstorms) and a
well defined surface wind circulation.
-
- Tropical depression
- - A tropical cyclone with one or more closed isobars and a one minute max sustained
surface wind of less than 34 knots (39 mph).
-
- Tropical storm
- - A tropical cyclone with closed isobars and a one minute max sustained surface wind of
34 knots (39 mph) to 63 knots (73 mph).
-
- Typhoon
- - Same as a hurricane with exception of geographical area. A tropical cyclone with
closed contours, a strong and very pronounced circulation, and one minute maximum
sustained surface winds of 64 knots (74 mph) or greater. A system is defined as a typhoon
over the North Pacific W of the dateline.
NOTE: It can be difficult to determine the central pressures of
tropical depressions, tropical storms, and hurricanes/typhoons and at times
no estimates or measurements is provided by a hurricane or typhoon
specialist. An estimate of central pressure may be provided over the
Atlantic. Otherwise an XXX is used in place of actual or estimated
pressures associated with these systems and an XX is used for forecast
central pressure.
SEAS
-
- Combined seas
- -The combination of both wind waves and swell which is generally referred to as
"seas".
-
- Primary swell direction
- - Prevailing direction of swell propagation.
-
- Significant wave height
- - The average height (trough to crest) of the 1/3rd highest waves.
An experienced observer will most frequently report the highest 1/3rd of
the waves observed.
- The generation of waves on water results not in a single wave height
but in a spectrum of waves distributed from the smallest capillary waves
to larger waves. Within this spectrum there is a finite possibility of
each of the wave heights to occur with the largest waves being the least
likely. The wave height most commonly observed and forecast is the
significant wave height. This is defined as the average of the one third
highest waves. The random nature of waves implies that individual waves
can be substantially higher than the significant wave height. In fact,
observations and theory show that the highest individual waves in a
typical storm with typical duration to be approximately two times the
significant wave height. Some reported rogue waves are well within this
factor of two envelope. Waves higher than roughly twice the significant
wave height fall into the category of extreme or rogue waves.
- Swell
- - Wind waves that have moved out of their fetch or wind generation area. Waves generated
by swell exhibit a regular and longer period than wind waves.
MISCELLANEOUS TERMINOLOGY
-
- Coastal Waters
- - Includes the area from a line approximating the mean high water
along the mainland or island as far out as sixty nautical miles
including the bays, harbors and sounds.
- High Seas
- - That portion of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans which extends off the
Western and Eastern US coasts and extends to 35W in the Atlantic ocean and to 160E in the
Pacific Ocean. The area includes both the coastal and offshore waters.
- Offshore waters
- - That portion of oceans, gulfs, and seas beyond coastal waters extending to a specified
distance from the coastline, to a specified depth contour, or covering an area defined by
a specific latitude and longitude points.
-
|


