|
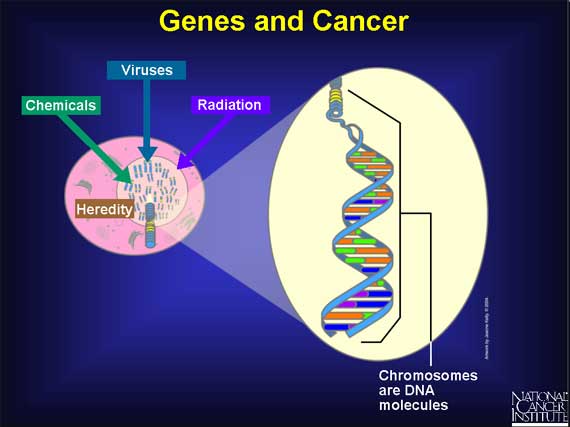
Chemicals (e.g., from smoking), radiation, viruses, and heredity all contribute to the development of cancer by triggering changes in a cell's genes. Chemicals and radiation act by damaging genes, viruses introduce their own genes into cells, and heredity passes on alterations in genes that make a person more susceptible to cancer. Genes are inherited instructions that reside within a person's chromosomes. Each gene instructs a cell how to build a specific product--in most cases, a particular kind of protein. Genes are altered, or "mutated," in various ways as part of the mechanism by which cancer arises.
< Previous | Index | Next Slide > |