|
 |

|
 |
 | |||||
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Drug Development and Drug
Interactions
Possible Model for Decision Making: CYP-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Studies Figure 1. CYP-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Studies
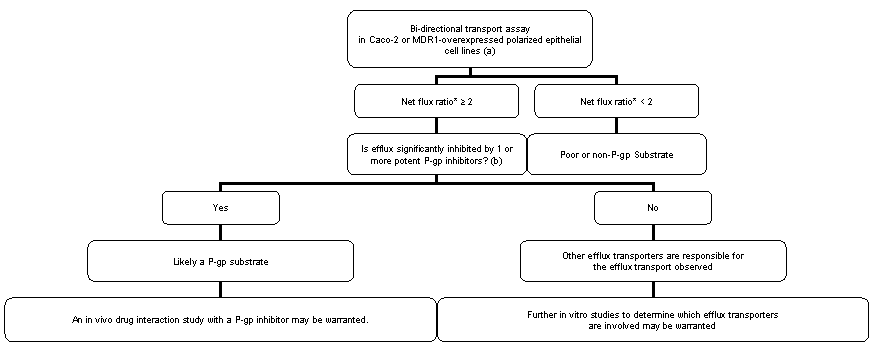
NME: New molecular entity * Additional population pharmacokinetic analysis may assist the overall evaluation. + negative results from an in vivo cocktail study would preclude further evaluation to determine whether an NME is an inhibitor or an inducer of a particular CYP enzyme Possible Models for Decision-Making: P-gp-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Studies Figure 2. Possible model for decision-making: whether an investigational drug is a substrate for P-gp and whether an in vivo drug interaction study with a P-gp inhibitor is needed. Reference: Lei Zhang, John M. Strong, Wei Qiu, Lawrence J. Lesko, and Shiew-Mei Huang. Modified from Scientific Perspectives on Drug Transporters and Their Role in Drug Interactions Mol Pharm. 2006; 3(1), 62-69, Epub Jan 4 2006. [PDF] [external link]
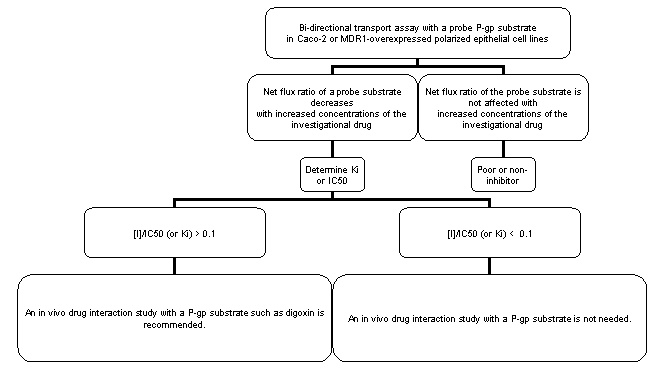
*For Caco-2 cells, net flux ratio is calculated as (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B); For MDR1-overexpressed cell lines, net flux ratio is calculated as ratio of (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B) MDR1 to (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B,) wild-type. Possible Model for Decision Making: P-gp Inhibitor and Digoxin Interaction Studies Figure 3. Possible model for decision-making: whether an investigational drug is an inhibitor for p-gp and whether in vivo drug interaction studies with a P-gp probe substrate, such as digoxin, is needed Reference: Lei Zhang, John M. Strong, Wei Qiu, Lawrence J. Lesko, and Shiew-Mei Huang. Modified from Scientific Perspectives on Drug Transporters and Their Role in Drug Interactions [PDF] [external link] Mol Pharm. 2006; 3(1), 62-69, Epub Jan 4 2006.
* For Caco-2 cells, net flux ratio is calculated as (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B); For MDR1-overexpressed cell lines, net flux ratio is calculated as ratio of (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B) MDR1 to (Permeability app, B-A/Permeability app, A-B,) wild-type. Note that [I] represents the mean steady state Cmax value for total drug (bound and unbound) following administration of the highest proposed clinical dose.
Date created: May 1, 2006
|