


   |
| FDA Home Page | CDRH Home Page | Search | A-Z Index |  |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
The Medical Device Export Decision Tree flow diagram below depicts a firm's options to export as revised by the FDA Export Reform and Enhancement Act of 1996 (FDERA). This quick reference chart shows when to export under sections 801(1), 801(e)(2), and 802 of the FD&C Act.
Medical Device Export Decision Tree
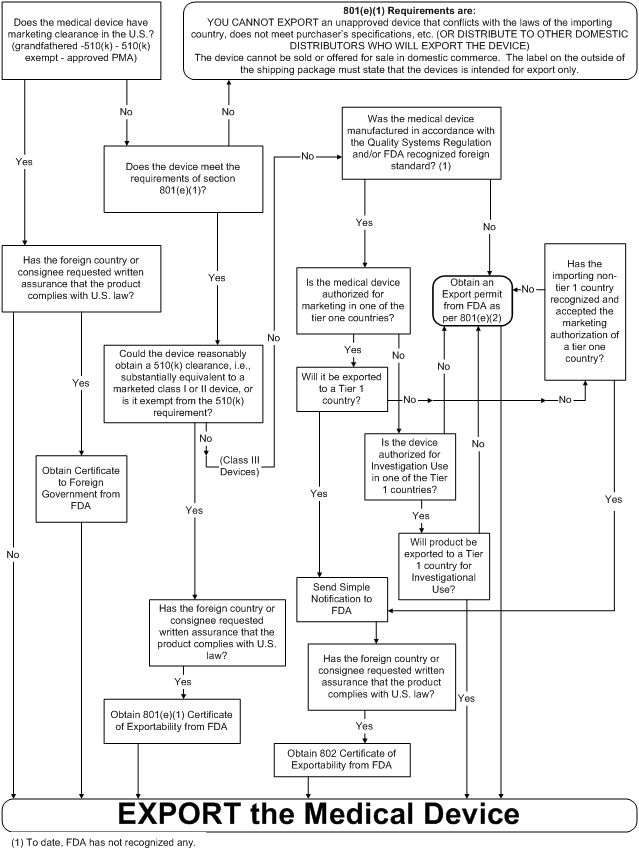
Please note that U.S. manufactures that export medical devices outside the U.S. are required to register their facility and list their devices (21 CFR 807).
Requirements
Any medical device that is legally in the U.S. may be exported anywhere in the world without prior FDA notification or approval. The export provisions of the FD&C Act only applies to unapproved devices. For a device to be legally in commercial distribution in the U.S., the following requirements must be met:
- The manufacturing facility must be registered with FDA ;
- The device must be listed with FDA;
- The device must have a cleared Premarket Notification 510(k) or Premarket Approval (PMA) unless exempted by regulation or if the device was on the market prior to May 28, 1976 (before the Medical Device Amendments to the FD&C Act);
- The device must meet the labeling requirements of 21 CFR Part 801and 21 CFR 809, if applicable;
- The device must be manufactured in accordance with the Quality Systems (QS) Regulation of 21 CFR Part 820 (also known as Good Manufacturing Practices or GMP), unless exempted by regulation.
In addition, the U.S. exporter must comply with the laws of the importing country.
Please note that U.S. manufactures that export medical devices outside the U.S. are required to register their facility and list their devices (21 CFR 807).
Certificates for Foreign Government
While FDA does not place any restrictions on the export of these devices, certain countries may require written certification that a firm or its devices are in compliance with U.S. law. In such instances FDA will accommodate U.S. firms by providing a Certificate for Foreign Government (CFG). These export certifications were formerly referred to as a Certificate for Products for Export or Certificate of Free Sale. The CFG is a self certification process that is used to speed the processing of requests. Original certificates will be provided on special counterfeit resistant paper with an embossed gold foil seal.
CDRH requires an initial fee of $175.00 per certificate and $15.00 per certificate for additional certificate(s) issued for the same product(s) in the same letter of request. Original certificates will be provided on special counterfeit resistant paper with an embossed gold foil seal.
You should submit your request for a CFG on form FDA-3613, Supplementary Information Certificate to Foreign Government Requests [PDF][Word]. Questions regarding the CFG should be directed to the Office of Compliance, Export Certificate Team, at 240-276-0132. (exportcert@cdrh.fda.gov)
Chapter VIII of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) addresses FDA regulation of the import and export of foods, drugs, cosmetics, biologics, medical devices, and radiation emitting electronic products. Sections 801 and 802 of Chapter VIII list the specific rules governing the import and export of products, including the export of unapproved products.
Until April 1996 the law that governed the export of medical devices not legally marketed in the U.S. was Sections 801(e)(1) and (e)(2) of the FD&C Act. Public Law 104-134, Food and Drug Export Reform and Enhancement Act of 1996 (FDERA) modified portions of Section 801 and Section 802. This law significantly modified Chapter VIII by enhancing the ability of U.S. firms to export unapproved FDA products under certain conditions without prior permission from FDA. The most notable change was the addition of provisions to and extension of section 802 to medical devices.
The basis for the regulation of imports and exports is contained in Chapter VIII of the FD&C Act. There are no regulations in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) that cover export requirements except for 21 CFR 812.18 regarding the export of investigational devices.
Section 803 provides for the establishment of an Office of International Relations to act as FDA liaison with foreign governments.
Please note that U.S. manufactures that export medical devices outside the U.S. are required to register their facility and list their devices (21 CFR 807).
Exporting Medical Devices Via Section 801(e)(1)
Requirements
A medical device which would be considered to be adulterated or misbranded, may be exported under Section 801(e)(1) of the FD&C Act provided the device is intended solely for export. Although such a device would not meet the requirements of the FD&C Act to be sold domestically for commercial distribution, it may be exported legally and without FDA permission in accord with Section 801(e)(1) provided the device is:
- in accordance with the specifications of the foreign purchaser;
- not in conflict with the laws of the country to which it is intended for export;
- labeled on the outside of the shipping package that it is intended for export; and
- not sold or offered for sale in domestic commerce.
Once an adulterated or misbranded device is sold or offered for sale in commercial distribution in the U.S., it may not be exported under Section 801(e)(1) as an alternative to bringing the device into compliance with the requirements of the Act. Devices that have been imported are considered to be in domestic commerce.
Unapproved Devices due to lack of 510(k) marketing clearance
The FDA is aware that in certain instances there may be devices which firms may wish to manufacture solely for export, or which they may wish to export during the interim period while their Premarket Notification 510(k) is under review. FDA allows the export of a device that does not have a 510(k) marketing clearance without prior FDA clearance if it meets two conditions:
- the device meets the requirements of 801(e)(1) listed above, and
- it is reasonably believed that the device could obtain 510(k) marketing clearance in the U.S. if reviewed by FDA.
This includes only devices which are similar in design, construction, and intended use to class I or class II devices or which the firm reasonably believes would be "substantially equivalent" to class I or class II devices. Devices which would not be included under this consideration are:
- Preenactment class III devices for which FDA has called for the submission of a PMA
- Postenactment class III devices, i.e. placed on the market after May 28, 1976, or
- Devices evaluated by a firm and found to be not substantially equivalent to a 510(k)'d device.
Recordkeeping Requirements
Persons exporting an article under section 801(e)(1) of the act or an article otherwise subject to section 801(e)(1) of the act must maintain records demonstrating that the product meets the requirements of section 801(e)(1) of the act. These records must be maintained for the same period of time as required for records subject to good manufacturing practice or quality systems regulations applicable to the product. That is, all records must be retained for a period of time equivalent to the design and expected life of the device, but in no case less than two years from the date of release for commercial distribution by the manufacturer (21 CFR 820.180). The records must be made available to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), upon request, during an inspection for review and copying by FDA. The records required to be maintained under 21 CFR 1.101 include the following:
Certificate of Exportability
The FDA implemented a new certification process referred to as a Certificate of Exportability (COE) to facilitate export of a medical device under 801(e)(1). Exporters applying for a COE are required to sign a statement indicating that they meet the four criteria of 801(e)(1) as detailed above. False statements are violations of United States Code Title 18, Chapter 47, Section 1001. Penalties for a false statement include up to $250,000 in fines and up to five years imprisonment.
CDRH requires an initial fee of $175.00 per certificate and $15.00 per certificate for additional certificate(s) issued for the same product(s) in the same letter of request. Original certificates will be provided on special counterfeit resistant paper with an embossed gold foil seal. CDRH should to issue the certification within 20 days upon the firm's showing that the product meets the applicable requirements.
You should submit your request for a COE on form FDA-3613a, Supplementary Information Certificate of Exportability Requests [PDF][Word]. Questions regarding the COE should be directed to the Office of Compliance, Export Certificate Team, at 240-276-0132. (exportcert@cdrh.fda.gov)
Exporting Medical Devices via Section 802
Requirements
Unapproved Class III devices and devices required to meet a performance standard under section 514 of the FD&C Act may be exported under section 802 if the firm and the device meets certain criteria. These devices include investigational devices, unapproved devices which would not be able to obtain a PMA (or for which a PMA has not been approved), and banned devices. (At the present time synthetic hair fibers intended for implant is the only banned medical device.) In order to qualify for export under 802, devices must meet the requirements under 801(e)(1) and pass the restrictions set forth in 802(f). That is, the devices must:
- meet the requirements of section 801(e)(1). The device is
- in accordance with the specifications of the foreign purchaser;
- not in conflict with the laws of the country to which it is intended for export;
- labeled on the outside of the shipping package that it is intended for export; and
- not sold or offered for sale in domestic commerce.
- substantially meet Quality Systems Regulation (also known as Good Manufacturing Practices) or an international quality standard recognized by FDA (currently, none are recognized),
- not be adulterated other than by the lack of marketing approval,
- not be the subject of a notice by Department of Health and Human Services that re-importation would pose an imminent hazard, nor pose an imminent hazard to the receiving country, and
- not be mislabeled other than by possessing the language, units of measure, or any other labeling authorized by the recipient country. In addition, the labeling must comply with the requirements and conditions of use in the listed country which gave marketing authorization, and must be promoted in accordance with its labeling.
Currently, electrode lead wires and patient cables (21 CFR 898) are the only devices with an FDA performance standard under section 514 of the FD&C Act.
In addition to the requirements above, the device must comply with the laws of the receiving country and have valid marketing authorization by the appropriate authority in a listed (Tier 1) country. This means that a firm whose device has received marketing authorization in any of the Tier 1 countries can export that device to any country in the world as long as the device meets applicable requirements of the FD&C Act and the marketing authorization by the Tier 1 country is acceptable to the appropriate authorities in the importing country. Some South American countries, for example, now permit marketing of any medical device with a CE mark. If the appropriate authorities of a non-Tier 1 country will not accept the marketing authorization of a Tier 1 country, you can obtain an export permit under section 801(e)(2).
The complete requirements of Section 802 can be found in the FD&C Act and a detailed discussion is contained in the February 1998 FDA Guidance Document.
The intent of FDERA was to expedite the export of products which do not comply with U.S. law, but which are in compliance with the laws of foreign countries. The primary advantage to exporting under section 802 instead of 801(e)(2) is that approval from FDA, i.e. submitting a request for and obtaining an Export Permit is not necessary in order to export. The exporter must submit a "Simple Notification" as per section 802(g) to FDA when the firm begins to export. No approval from FDA is required.
If the firm or device does not comply with the above criteria, the device cannot be exported under section 802. However, the device may qualify for exportation under section 801(e)(2).
Listed (Tier 1) Countries
The listed (or "Tier 1") countries are: Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, New Zealand, Switzerland, South Africa, a member of the European Union (United Kingdom, Spain, Ireland, Denmark, Greece, Belgium, Portugal, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Sweden, Finland, and Austria), or the European Economic Area (includes the European Union countries and Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein). As of May 2004, the European Union also includes Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia.
Simple Notification
Persons exporting a device under section 802 of the act must provide written notification to FDA. The notification must identify:
- The product's trade name;
- The type of device;
- The product's model number; and
- The country that is to receive the exported article if the export is to a country not listed (non tier 1 country). The notification may, but is not required to, identify the listed (tier 1) countries or may state that the export is intended for a listed (tier 1) country without identifying the listed country.
The notification shall be sent to the following address:
Food and Drug Administration
Center for Devices and Radiological Health
Division of Risk Management Operations
Regulatory Policy and Systems Branch (HFZ-307)
9200 Corporate Blvd.
Rockville, MD 20850
Telephone number: 240-276-0132
exportcert@cdrh.fda.govDevices that are regulated by the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research should mail the simple notification to the following address:
Food and Drug Administration
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
Office of Compliance and Biologics Quality
Division of Case Management (HFM- 610)
1401 Rockville Pike, rm. 200N
Rockville, MD 20852-1448
Recordkeeping Requirements
Any person exporting a product under any provision of section 802 of the act shall maintain records [section 802(g)] of all devices exported and the countries to which the products were exported. In addition to the requirements in 801(e)(1) noted above, such records include, but are not limited to, the following:
- The product's trade name;·
- The type of device;
- The product's model number;
- The consignee's name and address; and
- The date on which the product was exported and the quantity of product exported.
These records shall be kept at the site from which the products were exported or manufactured, and be maintained for the same period of time as required for records subject to good manufacturing practice or quality systems regulations applicable to the product. That is, all records must be retained for a period of time equivalent to the design and expected life of the device, but in no case less than 2 years from the date of release for commercial distribution by the manufacturer (21 CFR 820.180). The records shall be made available to FDA, upon request, during an inspection for review and copying by FDA.
Additional Provisions under 802
Additional situations where export permission is automatically granted under section 802:
Devices exported for investigational use - Medical devices may be exported under an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE), e.g. instances where clinical investigations are being conducted abroad. As per section 802(c), the export of a medical device for investigational use in any Tier 1 country may be exported in accordance with the laws of that country and is exempt from regulation under the IDE statutory requirements of the FD&C Act [section 520(g)]. Additional guidance can be found in Exporting for Investigational Use below and as well as Section 802 of the FD&C Act.
Exported devices intended for further processing - As per section 802(d), a medical device intended for further processing pending expected marketing authorization from a listed (tier 1) country may be exported for use in that country. The fundamental concept is that the device is being exported in anticipation of marketing approval. Additional guidance can be found in Exporting for Marketing or in Anticipation of Foreign Marketing Approval below as well as Section 802 of the FD&C Act.
Devices intended for treatment of non-U.S. diseases - As per section 802(e)(1) a medical device intended for the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of a tropical disease or another disease not prevalent in the U.S. which does not otherwise meet 802 criteria, may be exported with an FDA approved application for export if FDA finds that the device does not present:
- unreasonable risk
- the benefits outweigh the risks, and
- the risks of using available alternatives was considered.
Additional guidance can be found in Exports of Drugs and Devices for Diagnosing, Preventing, or Treating a Tropical Disease or a Disease "Not of Significant Prevalence in the United States" as well as Section 802 of the FD&C Act.
Certificate of Exportability
Even though FDA does not require a firm to obtain written permission prior to export under section 802, a foreign purchaser may request proof of compliance with U.S. law prior to export. FDA will provide a Certificate of Exportability (COE) to the exporter under section 802 to facilitate export of a medical device.
Exporters applying for a COE are required to sign a statement indicating that they are exporting legally under the provisions of section 802 as detailed above. False statements are violations of United States Code Title 18, Chapter 47, Section 1001. Penalties for a false statement include up to $250,000 in fines and up to five years imprisonment.
CDRH requires an initial fee of $175.00 per certificate and $15.00 per certificate for additional certificate(s) issued for the same product(s) in the same letter of request. Original certificates will be provided on special counterfeit resistant paper with an embossed gold foil seal. CDRH should to issue the certification within 20 days upon the firm's showing that the product meets the applicable requirements.
You should submit your request for a COE on form FDA-3613a, Supplementary Information Certificate of Exportability Requests [PDF][Word]. Questions regarding the COE should be directed to the Office of Compliance, Export Certificate Team, at 240-276-0132. (exportcert@cdrh.fda.gov)
Exporting Medical Devices via Section 801(e)(2)
Requirements
Class III investigational devices, banned devices, and unapproved devices for which a PMA has not been submitted to CDRH (or for which a PMA has not been approved) that do not meet the criteria under section 802 may qualify for export under section 801(e)(2).
The types of devices subject to section 801(e)(2) are:
- a device that does not comply with section 514 (performance standards) of the FD&C Act ;
- a device that requires an approved Premarket Approval but does not have one;
- a device undergoing clinical investigation ; and
- a device that is banned from the U.S. market under Section 516 of the FD&C Act
Currently, electrode lead wires and patient cables are the only devices with an FDA performance standard (21 CFR 898) and synthetic hair fibers intended for implant is the only banned medical device (21 CFR 895).
Export under section 801(e)(2) is required when exporting an unapproved Class III device in which:
- the importing country will not accept the marketing authorization of a listed (Tier 1) country as described in Section 802; or
- the intent is to conduct clinical investigations in a country not listed in Section 802; or
- the device is not manufactured in substantial conformance with the Quality System (GMPs).
The device must meet the following criteria to be exported:
- The device must meet the requirements under Section 801(e)(1) of the FD&C Act, that is, the device is
- in accordance with the specifications of the foreign purchaser;
- not in conflict with the laws of the country to which it is intended for export;
- labeled on the outside of the shipping package that it is intended for export; and
- not sold or offered for sale in domestic commerce.
- A review by FDA must determine that the exportation of the device is not contrary to public health and safety and
- The device has the approval of the country to which it is intended for export.
Export Permit
To obtain FDA's approval to export these devices in accord with Section 801(e)(2) of the FD&C Act, a request that includes the following information must be submitted to FDA:
- A complete description of the device intended for export;
- The status of the device in the U.S.; e.g., whether it is investigational, banned, etc.; and
- A letter from the appropriate foreign liaison (person with authority to sign a letter of acceptance for the foreign government identified in the CDRH Foreign Liaison Listing , which must be either in English or accompanied by a certified English translation, stating:
- the device is not in conflict with the laws of the country to which it is intended for export.
- the foreign government has full knowledge of the status of the device in the U.S.; and
- import is permitted or not objected to.
- a statement that the requestor conducted a search of the Medlars database and a summary of the search results, and a summary of safety data to demonstrate that export of the device will not be contrary to the public health and safety.
If the manufacturer is exporting to a country within the European Economic Area (EEA) a device that has been awarded the "CE mark," FDA will accept documentation of the "CE mark" in lieu of a letter from the foreign government approving importation.
Procedures recommend that the requester conduct a search of the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System (MEDLARS) database and provide safety data. MEDLARS is the computerized system of databases and databanks offered by the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
There are two circumstances in which FDA does not request a search of the MEDLARS database and submission of safety data with an export request:
- The device has an FDA-approved investigational device exemption (IDE) and will be marketed or used for clinical trials in the importing country for the same intended use; or
- The manufacturer has been informed by two Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in the U.S. that the device is a non-significant risk device and the device will be marketed or used for clinical trials in the importing country for the same intended use.
Submit your request for an Export Permit to the following address:
Food and Drug Administration
Center for Devices and Radiological Health
Office of Compliance
Division of Risk Management Operations
Regulatory Policy and Systems Branch (HFZ-307)
9200 Corporate Blvd.
Rockville, Maryland 20850
Telephone number: 240-276-0132
exportcert@cdrh.fda.gov
A manufacturer who wishes to export an unapproved device for investigational use may export the device under an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE), under section 801(e)(2), or under 802(c) of the act depending on which country the device is being exported.
Under section 802(c) of the act, an unapproved device intended for investigational use may be exported to Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, New Zealand, Switzerland, South Africa or member countries of the European Economic Area (EEA) without FDA authorization if the unapproved device is exported in accordance with the laws of that country. Devices being exported under 802(c) are not required to meet the requirements of the IDE regulation under 21 CFR 812. However, the firm and the device must meet the requirements of section 802 as noted above.
Exportation of an unapproved device for investigational use to any country other than the countries identified above requires authorization by the FDA under section 801(e)(2). The device must meet the following criteria under 801(e)(2):
Please refer to section 801(e)(2) above for additional guidance.
Section 802(d) of the act permits the exportation of an unapproved drug, biologic, or device "intended for formulation, filling, packaging, labeling, or further processing in anticipation of market authorization" in any of the listed countries. The only requirement for such exports are that the product comply with the laws of the foreign country and the requirements in section 802(f) of the act. Records for such exports must be kept in accordance with section 802(g) of the act. Please refer to section 802 above for further guidance
You should submit your request for an export certificate on the appropriate form.
Questions regarding the CFG and the COE should be directed to the Office of Compliance, Export Certificate Team, at 240-276-0132. (exportcert@cdrh.fda.gov)
CDRH requires an initial fee of $175.00 per certificate and $15.00 per certificate for additional certificate(s) issued for the same product(s) in the same letter of request. Original certificates will be provided on special counterfeit resistant paper with an embossed gold foil seal. CDRH should to issue the certification within 20 days upon the firm's showing that the product meets the applicable requirements.
Compliance Policy Guides
Regulations and Law
Updated February 28, 2008
![]()
CDRH Home Page | CDRH A-Z Index | Contact CDRH | Accessibility | Disclaimer
FDA Home Page | Search FDA Site | FDA A-Z Index | Contact FDA | HHS Home Page
Center for Devices and Radiological Health / CDRH