|
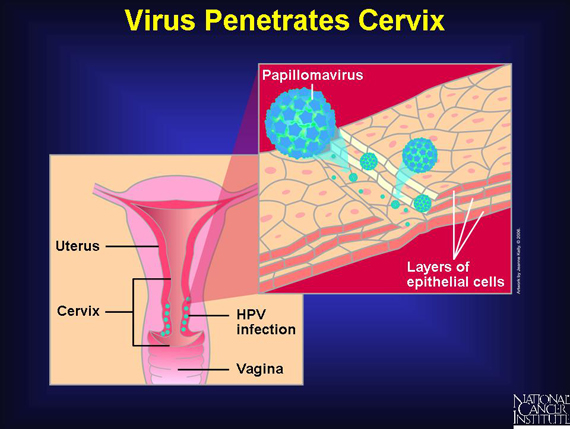
Both harmless and cancer-linked human papillomaviruses pass by skin-to-skin contact. The high-risk types of HPVs need to penetrate deeply into the lining of the cervix to establish a chronic infection. A vaginal sore or sex, which can abrade the lining, may provide a point of entry for the papillomavirus.
Once inside the cervical lining, the virus attaches to epithelial cells. As these cells take in nutrients and other molecules that are normally present in their environment, they also take in the virus. Over 99 percent of cervical cancer cases are linked to long-term infections with high-risk human papillomaviruses.
< Previous | Index | Next Slide > |