|
|
Space science
|
|
DLESE >> Space science
|
|
Movie
|
ID
|
Title
|

|
3412
|
Hinode's High-resolution view of solar granulation
|

|
3407
|
STEREO's Extreme UltraViolet Imager (EUVI)
|
|
3356
|
THEMIS Mission and Substorm Simulation
|

|
3336
|
The Visible Sun Revisited
|

|
3212
|
Space Weather Forecasting: Active Times Ahead
|

|
3211
|
Space Weather Forecasting: Quiet Times Ahead
|
|
3162
|
RHESSI and TRACE View of January 20, 2005 Solar Flare
|
|
3161
|
TRACE Ultraviolet View of January 20, 2005 Solar Flare
|

|
3160
|
January 2005 Solar Flares from SOHO/EIT
|

|
3159
|
SOHO/LASCO View of January 2005 Solar Events
|
|
3115
|
Gaps in the Earth's Radiation Belts
|

|
3111
|
Connections: Terrestrial Gamma Flashes and Lightning?
|

|
3052
|
Earth's Radiation Belts with Safe Zone Orbit
|
|
3051
|
Plasmapause Convects to the Magnetopause During Halloween Solar Storm
|

|
3050
|
Tour of the Plasmasphere and Plasmapause
|

|
3049
|
Radiation Belts and Plasmapause Fluctuate Under Solar Storm
|

|
3048
|
Earth's Radiation Belts Tremble Under Impact of Solar Storm
|

|
3028
|
A 3-Dimensional Model of the Magnetosphere (WMS)
|

|
2966
|
Venus Transit from GOES/SXI
|

|
2964
|
IMAGE Views of the Aurora from Space
|

|
2963
|
The NOAA POES Satellite Detects Record Particle Flows into the Earth's Upper Atmosphere
|
|
2962
|
Computer Simulations of the Martian Atmosphere Interacting with the Solar Wind
|

|
2961
|
Halloween Solar Storms from SOHO/EIT and SOHO/LASCO
|
|
2960
|
Halloween Solar Storms from SOHO/EIT, 304 Ångstroms
|

|
2959
|
Halloween Solar Storms from SOHO/EIT, 195 Ångstroms
|

|
2958
|
Building a 3-D Coronal Mass Ejection from 2-D Data
|

|
2950
|
Building a 3-D Coronal Mass Ejection from 2-D Data
|
|
2936
|
The fastest CME of Cycle 23 overtakes another fast CME
|

|
2924
|
Sun vs. Mission to Mars
|

|
2923
|
SOHO/MDI's 'Window' Through the Sun
|

|
2922
|
Solar Tsunamis - View with a Spin
|

|
2921
|
Solar Tsunamis
|

|
2918
|
SORCE Monitors Solar Variability during Record Solar Flares - Video version
|

|
2917
|
SORCE Monitors Solar Variability during Record Solar Flares
|

|
2891
|
Aurora over the North Pole on April 17, 1999 (WMS)
|

|
2882
|
Zoom down to the Gale Crater on Mars
|

|
2863
|
ViSBARD: The Wind from the Sun
|
|
2862
|
ViSBARD: Insights into the Sun-Earth Connection
|

|
2861
|
Reconnection: Solar Wind Breaches the Earth's Magnetic Shield
|
|
2857
|
Geomagnetic Storm: November 2003
|
|
2856
|
Model of the Heliosphere Over the Solar Cycle
|

|
2796
|
Hubble Space Telescope: Image Deblurring with a Parallel Comptuer
|
|
2780
|
Mars Odyssey: Water Ice/Summer Observations
|
|
2779
|
Mars Odyssey: Water Ice/Winter Observations
|

|
2778
|
Mars Odyssey: Mars' Northern Hemisphere
|

|
2771
|
Hi-resolution Solar Views from VAULT: Selected Still Images
|
|
2766
|
Hi-resolution Solar Views from VAULT: Quiet Region
|
|
2765
|
Hi-resolution Solar Views from VAULT: Active Region
|
|
2764
|
High Resolution Solar Views From VAULT
|
|
2750
|
RHESSI Observes 2.2 MeV Line Emission from a Solar Flare
|
|
2735
|
Mercury transit of the Sun
|

|
2718
|
Closeup of Solar 'Tadpoles' without time tags
|

|
2717
|
Closeup of Solar 'Tadpoles' with time tags
|

|
2690
|
GOES/SXI views the Sun in X-rays (3 Channels)
|
|
2689
|
GOES/SXI views the Sun in X-rays
|

|
2676
|
Tour of the Magnetosphere
|
|
2656
|
Zoom-out from the Sun
|

|
2655
|
Solar Eclipse: December 4, 2002
|

|
2644
|
The Solar 'Constant' - Faculae vs. Sunspots
|
|
2553
|
A Multi-Mission View of the AR9906 Solar Flare with Alternate Instrument Labels
|

|
2511
|
A Multi-Mission View of the AR9906 Solar Flare without Instrument Labels
|
|
2510
|
Mars Odyssey Science Cover Image
|
|
2509
|
A Multi-Mission View of the AR9906 Solar Flare with Instrument Labels
|

|
2508
|
Fires Near Sequoia National Forest
|

|
2496
|
SOHO/EIT Views Solar 'Grand Slam' with Zoom
|

|
2495
|
SOHO/EIT views solar 'Grand Slam'
|

|
2464
|
Another View of AR9906 from TRACE
|

|
2463
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - rotate view without times
|
|
2462
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - rotate view with times
|

|
2461
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - zoom without times
|

|
2460
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - zoom with times
|

|
2459
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - No time tags
|
|
2458
|
RHESSI Observes the Flare over AR9906 - Time Tagged
|

|
2455
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Full Globe, Viking True Color)
|
|
2454
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Full Globe, Unsmoothed)
|

|
2453
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Full Globe, Smoothed)
|

|
2452
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flyover, Viking True Color)
|
|
2451
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flyover, Unsmoothed)
|
|
2450
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flyover, Smoothed)
|

|
2449
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flat, Viking True Color)
|
|
2448
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flat, Unsmoothed)
|
|
2447
|
Mars Odyssey Epithermal Neutron Data overlayed on MGS/MOLA Topography Data (Flat, Smoothed)
|

|
2446
|
TRACE observes the X-ray flare over AR9906
|

|
2445
|
IMAGE/HENA views Oxygen in the Magnetosphere (blue version)
|

|
2444
|
IMAGE/HENA views Oxygen in the Magnetosphere (rainbow version)
|
|
2435
|
IMAGE/LENA Observes Oxygen Atoms in the near-Earth Environment
|
|
2430
|
MOLA-based Flyover of Korolev Crater
|

|
2429
|
MOLA-based Flyover of Gusev Crater
|

|
2428
|
MOLA-based Flyover of Tharsis Volcanos
|
|
2427
|
MOLA-based Flyover of Hellas Transitioning to Utopia Planitia
|
|
2426
|
TRACE Observes Flows over Active Regions (Fast play)
|

|
2425
|
TRACE Observes Flows over Active Regions (Slow play)
|
|
2404
|
First Flare movie for the RHESSI instrument (speed 26x normal)
|
|
2403
|
First Flare movie for the RHESSI instrument (speed 52x normal)
|

|
2402
|
First Flare movie for the RHESSI instrument (speed 105x normal)
|
|
2391
|
Magnetosphere II: The Solar Wind Strikes Back!
|
|
2387
|
The Magnetosphere - Earth Raises its Shields
|
|
2327
|
MOLA Stills for possible cover of 'Science'
|

|
2326
|
MOLA Stills for possible cover of 'Nature'
|
|
2324
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Polar Images
|

|
2314
|
Temperature and Flows under a Sunspot (Layers 0, 2, 4)
|
|
2313
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, clouds at north pole, with dates, with contours
|
|
2312
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, clouds at north pole, with dates, without contours
|
|
2311
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, clouds at both poles, with dates, with contours
|
|
2310
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, clouds at both poles, with dates, without contours
|
|
2309
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, graph showing snow variations at north pole, without dates
|
|
2308
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, graph showing snow variations at north pole, with dates
|
|
2307
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, graph showing snow variations at both poles, without dates
|
|
2306
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, graph showing snow variations at both poles, with dates
|

|
2305
|
FUSE/MOLA: Mars Once Had Oceans - match render w/o oceans
|
|
2304
|
Under the Rotating Sunspot (Layers 0, 1, 2)
|

|
2303
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Flyover and Slow Zoom out from Martian S. Pole: True Color
|
|
2302
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Zoom Out from the Martian North Pole: True Color
|

|
2301
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Zoom to the Martian North Pole: True Color
|

|
2300
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Zoom to the Martian South Pole: True Color
|

|
2299
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Flyover of the Martian South Pole: False Color
|
|
2298
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Zoom out from the Martian North Pole: True Color
|

|
2297
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Slow Flyover of the Martian North Pole: False Color
|

|
2296
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, Medium Zoom out from Martian South Pole: False Color
|
|
2295
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Medium Zoom to Martian North Pole: False Color
|

|
2294
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, Fast Zoom out from Martian South Pole: False Color
|
|
2293
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars: Fast Zoom to Martian North Pole: False Color
|

|
2292
|
MOLA: Seasonal Snow Variations on Mars, Zoom to Martian North Pole: True Color
|

|
2291
|
FUSE/MOLA: Mars Once had Oceans
|
|
2287
|
The Spinning Sunspot
|

|
2269
|
SOHO/MDI Views the Sun - 2001
|

|
2268
|
SOHO/MDI Views the Sun - 1998
|

|
2244
|
SOHO/MDI Views the Sun - 2001
|

|
2243
|
SOHO/MDI Views the Sun - 1998
|

|
2232
|
SOHO/MDI Investigates Solar Flows Under Sunspots
|
|
2089
|
Views of Mars with MOLA+Viking data
|

|
2061
|
NEAR views the Asteroid Eros ('true' color)
|
|
2060
|
NEAR Views the Asteroid Eros (Gravity Slope)
|
|
2043
|
Stills of the Polar Visible Aurora from July 16, 2000
|
|
2040
|
Stills of the Polar Visible Aurora from October 22, 1999
|
|
2038
|
Stills of the Polar Visible Aurora from January 10, 1997
|

|
2037
|
Polar Visible Aurora Animation: July 16, 2000
|

|
1601
|
Supporting Media for MOLA release
|
|
1418
|
High Resolution 2-D Numerical Simulation of Emergence of Magnetic Flux Through the Solar Atmosphere
|

|
1417
|
High Resolution 2-D Numerical Simulation of Emergence of Magnetic Flux Through the Solar Atmosphere
|

|
1416
|
High Resolution 2-D Numerical Simulation of Emergence of Magnetic Flux Through the Solar Atmosphere
|

|
1402
|
Earth Today 1998
|

|
1401
|
Earth Today 1998 Introduction
|

|
1393
|
Global Hybrid Versus MHD Modeling of the Magnetosphere: Density and Magnetic Field
|

|
1392
|
Two-Body Collision
|
|
1389
|
Motion in the R-Aquarii Jet 1991, 1992, 1993: 3-D Perspective
|

|
1388
|
Motion in the R-Aquarii Jet 1991, 1992, 1993: 2-D Motion
|
|
1387
|
SAMPEX - A Synoptic View of Earth's Electron Radiation Belts: South Pole Energetic Fluxes from PET
|
|
1386
|
SAMPEX - A Synoptic View of Earth's Electron Radiation Belts: North Pole Energetic Fluxes from PET
|
|
1385
|
SAMPEX - A Synoptic View of Earth's Electron Radiation Belts: South Pole Energetic Fluxes from HILT
|

|
1383
|
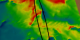
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Electron Fraction
|

|
1382
|
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Temperature
|

|
1381
|
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Density
|

|
1335
|
Mars Flyover Based on MOLA Data for the Carl Sagan Lecture
|

|
1211
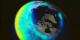
|
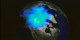
Polar Visible Aurora Animation: July 13, 2000
|

|
1210
|
Polar Visible Aurora Animation: July 15, 2000
|

|
1206
|
Polar Visible Aurora Animation: July 15, 2000 to July 16, 2000
|

|
1177
|
Plasmasphere without Earth Inset
|

|
1176
|
Plasmasphere with Earth Inset
|

|
1175
|
Aurora w/o Earth Inset
|

|
1174
|
IMAGE views the Plasmasphere in EUV
|

|
1173
|
Aurora Close-up w/Earth inset
|

|
1172
|
Plasmasphere close-up w/Earth Inset
|

|
1171
|
Aurora with Earth inset
|

|
1170
|
Plasmasphere with Earth inset in EUV
|

|
1169
|
Bastille Day Flare without Matter Motion
|

|
1168
|
'Bastille Day' Flare Animation
|

|
1105
|
Mars Crust Thickness
|
|
1104
|
MOLA Texture Zoom Down to Gravity Map Revealing Hidden
Channel
|

|
1103
|
Viking Texture Zoom Down to Gravity Map Revealing Hidden Channel
|
|
1102
|
Mars Cutaway
|

|
1101
|
Valles Marineris Flyover (Long Version)
|
|
1100
|
Gravity Flat Image Showing Hidden Channel (still)
|

|
1099
|
Viking Texture Zoom Down (slow)
|

|
1098
|
Viking Texture Zooming Down to Reveal a Hidden Channel (fast)
|
|
1097
|
MOLA Zooming Down to Reveal a Hidden Channel (slow)
|
|
1096
|
MOLA Zooming Down to Reveal a Hidden Channel (fast version)
|

|
1095
|
Mars North Pole flyover
|

|
1094
|
Olympus Mons Flyover.
|

|
1093
|
Valles Marineris Flyover (short version)
|

|
1092
|
Mars Mantle (MOHO) Topography with Mantle Elevation Texture Map
|

|
1091
|
MOLA Surface Topography with Viking Texture Map
|

|
1090
|
MOLA Surface Topography with Surface Elevation Texture Map
|
|
1089
|
MOLA Surface Topography with Gravity Texture Map
|

|
1088
|
Valles Marineris Flyover (long version)
|

|
833
|
Sun Spot Number Compared with Solar UV from SUSIM (1991-1997)
|

|
806
|
Digital Earth Workbench: Aurora
|

|
805
|
Digital Earth Workbench: Magnetospheric Pressure
|

|
804
|
Digital Earth Workbench: Magnetospheric Density
|

|
803
|
Digital Earth Workbench: The Earth's Magnetic Field
|

|
788
|
Polar Visible Aurora: Normal Solar Wind Conditions on November 13, 1999 over the North Pole
|

|
787
|
Polar Visible Aurora: Low Solar Wind Conditions on May 11, 1999 over the South Pole
|
|
786
|
Polar Visible Aurora: Low Solar Wind Conditions on May 11, 1999 over the North Pole
|
|
785
|
Polar Visible Aurora: High Solar Wind Conditions on April 17, 1999 over the North Pole
|
|
784
|
Polar Visible Aurora: North Pole Comparison between May 11, 1999 and November 13, 1999 (Grid)
|

|
783
|
Polar Visible Aurora: North Pole Comparison between May 11, 1999 and November 13, 1999 (Continents)
|

|
782
|
Polar: PIXIE at T055798 on May 11, 1999 at 22:55
|

|
781
|
Polar: PIXIE at T055798 on May 11, 1999 at 05:05
|

|
780
|
Polar: PIXIE at Perigee 2 on May 11, 1999 (South)
|

|
779
|
Polar: PIXIE at Perigee 1 on May 11, 1999 (South)
|

|
778
|
Polar: PIXIE at Perigee on May 11, 1999 (North)
|

|
777
|
Polar: PIXIE at Apogee on May 11, 1999 (North)
|
|
776
|
Mars Southern Hemisphere Rotation in False Color from MOLA
|

|
775
|
Mars Southern Hemisphere Rotation in True Color from Viking
|

|
774
|
Push in South of the Hellas Basin Showing Topography from MOLA: New Color Map
|
|
773
|
Push in South of the Hellas Basin Showing Topography from MOLA
|

|
772
|
Push in South of the Hellas Basin using Viking Imagery
|

|
771
|
A Rotating False Color View of the Martian South Pole from MOLA: New Color Map
|
|
770
|
A Rotating False Color View of the Martian South Pole from MOLA
|

|
769
|
A Rotating True Color View of the Martian South Pole
|

|
768
|
A Comparison of Visible and Topographic Data for the Martian South Pole: Version 2
|

|
767
|
A Comparison of Visible and Topographic Data for the Martian South Pole: Version 1
|
|
766
|
Close Up Fly Over of Mars Polar Lander Landing Area in False Color
|

|
765
|
Close Up Fly Over of Mars Polar Lander Landing Area in True Color
|

|
764
|
Mars Polar Lander Landing Site: Global View to False Color MOLA Inset
|

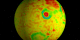
|
737
|
Images of Earth and Space: SC99 Edition
|

|
695
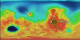
|
TRACE: 195 Angstrom Wavelength Image Showing MOSS Shockwave.
|

|
694
|
TRACE: 171 Angstrom Wavelength Image Showing MOSS Disc Center.
|

|
693
|
TRACE: Shot of MOSS at the Limb
|

|
692
|
TRACE: Still of TRACE Image
|

|
691
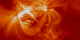
|
TRACE: A Coronal Loop with a Co-temporal Yohkoh Soft X-ray Image Overlaid.
|
|
690
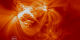
|
TRACE: Viewing a Coronal Loop
|
|
689
|
TRACE: Viewing a Coronal Loop with a Diagram of the Earth for Scale.
|

|
688
|
Polar Orbiter: Fly Up to Primary Landing Site with Altitude Map
|

|
687
|
Polar Orbiter: Fly Up to Primary Landing Site with Roughness Map
|

|
686
|
Polar Orbiter: Fly Up to the Primary Landing Site (Green)
|

|
685
|
Polar Orbiter: Fly Up to 4 Possible Landing Sites (Primary in Green, Secondary in Yellow)
|

|
684
|
Polar Orbiter: Fly Up to 4 Possible Landing Sites (Yellow)
|

|
683
|
False Color Moon Rotation with Flip Showing the South Pole
|

|
682
|
False Color Moon Rotation with Flip Showing Crash Site of the
Lunar Prospector
|

|
681
|
Rotating False Color Moon with Flip Showing the South Pole
|

|
680
|
True Color Moon using USGS Airbrush Texture
|

|
679
|
Lunar Prospector Crash Site in False Color Rotation with Flip
|

|
678
|
False Color Moon Rotation using Clementine Surface Texture Map
|

|
677
|
True Color Moon Rotation with Flip Showing the Crash Site of the Lunar Prospector
|

|
676
|
Airbrushed Moon
|
|
662
|
Rotating around the Tharsis Rise (False Color)
|

|
661
|
Rotating around the Tharsis Rise (True Color)
|

|
660
|
Mars Rotate (False Color)
|

|
659
|
Mars Rotate (True Color)
|

|
658
|
Hellas Crater Flat Flyover (True Color)
|
|
657
|
Mars Hellas Crater Flat Flyover (False Color)
|
|
656
|
Mars Topography: Downhill showing a gradient slope (False Color)
|

|
655
|
Tharsis Rise (False Color)
|

|
654
|
Tharsis Rise (True Color)
|

|
653
|
Mars Hellas Crater - Flat Spin (False Color)
|

|
652
|
Flyover of Mars' Valles Marineris (True Color)
|

|
651
|
Mola based Flyover of Valles Marineris (False Color)
|

|
650
|
Viewing North and South Poles of Mars (False Color)
|

|
649
|
Polar Lander Landing Site (Rect. Box) (False Color)
|

|
648
|
Polar Lander Landing Site (Curved Box) (False Color)
|

|
647
|
Onion Skin of Un-named Martian Crater
|

|
579
|
UARS: The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite
|

|
578
|
Solar Sigmoid: Zoom In, Pull Back
|

|
577
|
Solar Sigmoid: Zoom In, Move Around, Pull Back
|

|
576
|
Solar Sigmoid: Simple Spin Head-on to Limb
|

|
575
|
Solar Sigmoid: Match Frame for Simple Spin with Sigmoid and Field
|

|
574
|
Solar Sigmoid: Match Frame for Simple Spin with Sigmoid Only
|

|
573
|
Solar Sigmoid: Simple Spin - Limb to Head-on Move
|

|
560
|
Neutron Star Collision
|

|
559
|
Mars
|

|
558
|
Asteroid Castalia Impact Simulation
|
|
551
|
Delta Sunspot
|

|
550
|
Solar Dynamo
|
|
362
|
Mars North Polar Fly In From Above And Tilt
|

|
361
|
Fly over of Mars Mesa, Tounge, Dunes, Sasquatch Crater
|

|
360
|
Fly up to Dunes- thought to cover ice
|

|
359
|
Fly up to Sasquatch Crater view two
|

|
358
|
Fly up to Sasquatch Crater view one
|

|
357
|
Mars: Fly Straight over Pole
|

|
356
|
High Slow Fly around Pole
|

|
329
|
Images of Earth and Space II
|

|
328
|
Earth Today 1998 Countdown
|

|
302
|
Zoom and Fade to Animation of Solar Flare using TRACE Imagery
|

|
301
|
Zoom Around the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
300
|
Zoom into the Bottom Right of the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
299
|
Zoom into the Bottom Left of the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
298
|
Zoom into the Top Right of the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
297
|
Zoom into the Top Left of the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
296
|
Zoom in to a Center View of the Sun using TRACE Imagery
|

|
293
|
Pan around the Limb of the Sun with TRACE Imagery
|

|
292
|
Zoom in on the Sun with TRACE Imagery: Zoom 4
|

|
291
|
Zoom in on the Sun with TRACE Imagery: Zoom 3
|

|
290
|
Zoom in on the Sun with TRACE Imagery: Zoom 2
|

|
289
|
Zoom in on the Sun with TRACE Imagery: Zoom 1
|

|
251
|
Images of Earth and Space: SC97 Edition
|

|
182
|
Positron-electron Annihilation
|
|
181
|
Milky Way Antimatter Plume
|

|
127
|
Horizon to full Galaxy
|

|
118
|
VIS-5D VR Animations: R-Aquarii Jet
|

|
117
|
Global Hybrid Versus MHD Modeling of the Magnetosphere: Magnetic Potential
|

|
115
|
Numerical Simulation of Magnetic Flux Emerging Through a Model Solar Atmosphere: Density Gradient and Velocities
|

|
114
|
Numerical Simulation of Magnetic Flux Emerging Through a Model Solar Atmosphere: Density Gradient, Magnetic Field, and Mach Number
|

|
113
|
Numerical Simulation of Magnetic Flux Emerging Through a Model Solar Atmosphere: Density, Magnetic Field, and Mach Number
|

|
112
|
Numerical Simulation of Magnetic Flux Emerging Through a Model Solar Atmosphere: Density Gradient
|

|
111
|
Numerical Simulation of Magnetic Flux Emerging Through a Model Solar Atmosphere: Density
|

|
110
|
Images of Earth and Space: Supercomputing 96
|
|
107
|
High Resolution 2-D Numerical Simulation of Emergence of Magnetic Flux Through the Solar Atmosphere
|

|
97
|
Images of Earth and Space: The Role of Visualization in NASA Science
|

|
91
|
Motion in the R-Aquarii Jet 1991, 1992, 1993: Image Deconvolution of 1992 Data
|
|
90
|
SAMPEX - Yohkoh: Solar Modification of Relativistic Electrons in the Earth's Radiation Belts
|
|
89
|
SAMPEX - A Synoptic View of Earth's Electron Radiation Belts: North Pole Energetic Fluxes from HILT
|

|
88
|
Magnetic Cloud Event: October 18-20, 1995
|

|
87
|
2-D Unstructured Mesh Particle-MHD Solar Wind Flow Over the Earth:Density and Magnetic Field
|

|
86
|
2-D Unstructured Mesh Particle-MHD Solar Wind Flow Over the Earth: Magnetic Potential
|

|
85
|
Simulations of the Breakup of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 Employing a Swarm Model: Dynamical Evolution
|

|
84
|
Simulations of the Breakup of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 Employing a Swarm Model: Initial Conditions
|

|
80
|
Lunar Rotation and Flyby from Clementine Data
|

|
79
|
Lunar Rotation and Flyby from Clementine Data (with route map)
|

|
75
|
The Relationship of the Sun to the Earth
|

|
60
|
Nonlinear Studies of Coronal Heating by the Resonant Absorption of Alfven Waves
|

|
48
|
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Electron Fraction
|

|
47
|
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Temperature
|

|
46
|
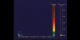
Instabilities in Very Young Neutron Stars: Density
|
|
45
|
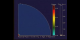
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Partial Density of Oxygen
|
|
44
|
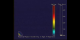
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Oxygen Mass Fraction
|
|
43
|
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Partial Density of Helium
|

|
42
|
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Helium Mass Fraction
|
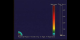
|
41
|
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Partial Density of Hydrogen
|
|
40
|
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Hydrogen Mass Fraction
|
|
39
|
Rayleigh-Taylor Instabilities in Supernovae Explosions: Density
|

|
9
|
Topological Features of a Compressible Plasma Vortex Sheet - a Model of the Outer Heliospheric Wind
|

|
8
|
Topological Features of a Compressible Plasma Vortex Sheet: 6 Cases
|

|
7
|
Stellar Wind Disruption by an Orbiting Neutron Star: Neutron Star Close-up
|

|
6
|
Stellar Wind Disruption by an Orbiting Neutron Star: High X-Ray Luminosity
|

|
5
|
Stellar Wind Disruption by an Orbiting Neutron Star: Moderate X-Ray Luminosity
|

|
4
|
Stellar Wind Disruption by an Orbiting Neutron Star: Low X-Ray Luminosity
|

|
3
|
Stellar Wind Disruption by an Orbiting Neutron Star
|
|
2
|
Tidal Streams in Massive X-ray Binary Systems: Neutron Star Close-up
|
|
1
|
Tidal Streams in Massive X-ray Binary Systems
|
|
10347
|
GLAST First Light All Sky Map
|

|
10345
|
GLASTcast in HD for Apple TV and iTunes
|

|
10325
|
GLASTcast Episode 5: Meet the U.S. Team
|

|
10324
|
GLASTcast Episode 4: Launching a Spacecraft
|

|
10323
|
GLASTCast Episode 3 - Swift and GLAST
|

|
10322
|
GLAST Soundbites
|

|
10298
|
Swift Spacecraft Animations
|

|
10251
|
GLAST Prelude, for Brass Quintet, Op.12
|

|
10250
|
GLASTcast for iTunes
|

|
10248
|
GLASTcast Episode 2: What are Gamma Rays?
|

|
10245
|
Gamma Ray Burst
|

|
10205
|
Gamma Rays in Pulsars
|

|
10200
|
Gamma Rays in Active Galactic Nuclei
|

|
10192
|
Venus: Long Time, No See
|

|
10172
|
GLAST Promo Video
|

|
10169
|
GLAST LAT Integration - B-Roll
|

|
10168
|
GLAST Launch and Deployment
|

|
10167
|
GLAST's LAT Instrument
|

|
10166
|
GLAST's New Window on the Universe
|

|
10165
|
GLAST LAT Testing - B-Roll
|

|
10164
|
360 Degrees of GLAST
|

|
10163
|
The GLAST Spacecraft in Orbit
|

|
10155
|
Gamma Ray Creation
|
|
10084
|
Cosmic Explosion Second Only to the Sun in Brightness
|

|
10068
|
Cutaway View of the Earth's Radiation Belts
|

|
10067
|
Lightning Makes a Safe Zone in the Earth's Radiation Belts
|

|
10066
|
Model for Coronal Mass Ejections
|

|
10065
|
Changing Solar Insolation
|

|
10064
|
STEREO Watches the Active Sun
|

|
10063
|
STEREO Enroute: Earth Flyby
|

|
10062
|
STEREO Spacecraft Beauty-Pass
|

|
10061
|
STEREO Enroute: The Lunar Flyby
|

|
10060
|
STEREO On-Station
|

|
10059
|
A CME Generates Reconnection in Earth's Magnetic Field
|

|
10058
|
Earth's Magnetic Field to Aurora
|

|
10045
|
Coronal Mass Ejections Blast their Way Through the Solar System
|

|
10044
|
Voyager Meets a Coronal Mass Ejection
|

|
10043
|
Conceptual Venus Transit
|

|
10042
|
From Venus to Venus Transit
|

|
10041
|
A Solar Tsunami
|

|
10040
|
Solar Dynamics Observatory On-Station
|

|
10039
|
Proton Aurora Forms from Reconnection Event
|

|
10038
|
IMAGE and Cluster View Magnetic Reconnection
|

|
10037
|
Coronal Mass Ejections Reach the Heliopause
|

|
10036
|
RHESSI Sees a Gamma-Ray Burst
|

|
10035
|
Simplified Model for a Solar Flare
|

|
10029
|
Venus Transit 2004
|