January 2001
A New Year's storm blanketed Texas, Louisiana, Arkansas and Oklahoma with up to eight inches (20 cm) of snow. Later on the 10th and 11th, storms dumped more than seven inches (178 mm) of rain on parts of southern California, including Los Angeles, where nearly four inches (102 mm) of rain fell. The heavy rains caused mudslides and road closures along much of California's central coast and up to three feet (91 cm) of snow was deposited in some coastal mountain areas.
February 2001
A February 5-6th snowstorm dumped 12-24 inches (30-61 cm) of snow across a swath from northern New Jersey through Maine, with lesser amounts elsewhere in the Northeast and New England. Alexandria, in central New Hampshire, reported 34 inches (86 cm) of snow. Strong winds which generated considerable blowing and drifting of the snow greatly increased the impact of the storm. A 10,000 acre (4047 hectare) wildfire on the 19th kept parts of major central Florida highways closed when heavy smoke forced drivers to make detours in traveling between Orlando and Tampa. Late in the month, a violent tornado cut a 23 mile (37 km) path across Pontotoc County, MS on the 24th, killing five people and injuring hundreds.
March 2001
A strong storm system hammered portions of the eastern U.S. during the first week of March. The storm dumped 9.21 inches (234 mm) of rain in Georgianna, AL in a four day period ending the 4th. The storm also dumped heavy snows on portions of the Northeast. The heaviest snows were across interior sections of Pennsylvania, New York and New England on the 5th and 6th with 24-36 inches (61-91 cm) quite common. Winds along the New England coast gusted to over 60 mph (27 m/sec). A cold flow behind the storm brought heavy snows across the backbone of the Appalachians from the Carolinas to Pennsylvania. Snowfall amounts in these areas ranged from 5-20 inches (12-51 cm), with Avery county, NC reporting up to 18 inches (46 cm) of snow. California was also hit by torrential rains during the first week of March. The heaviest rains fell across portions of Santa Barbara county, with coastal areas receiving about 7 inches (178 mm) of rain, and automated high mountain stations picking up over 19 inches (483 mm) of precipitation. Later in the month, a strong storm system hit the eastern seaboard during the week of the 20th, with heavy snows in parts of the southern Appalachians. As the storm continued north-northeastward, New England received more snow on top of the heavy snows received earlier in the month.
April 2001
Heavy flooding caused by rapid snowmelt and heavy rain plagued the upper Midwest in April. The Mississippi River kept residents in river basin areas on alert as it swept out of its banks and threatened to become the highest flood crest on record in spots. Later in the month, four people died, buildings were badly damaged, trees uprooted and cars overturned when numerous tornadoes hit the Midwest around the 11th. On the 20th, a tornado hit Hoisington, KS ripping the roof off a hospital just after it was evacuated, and damaging several blocks of homes. Wildfires continued to burn in Florida, where smoke blinded motorists and caused an 18 vehicle crash on the 28th resulting in one death and ten injuries.
May 2001
An early season heat wave in California boosted air conditioning demand
and prompted a Stage Two power alert and urgent requests for
conservation on the 7th. A Stage Two alert is called when operating
reserves drop below 5%. Rolling black outs occurred randomly in San
Francisco, Rosemead and San Diego.
A spring storm dumped more than 3 feet (91cm) of snow in central
Colorado�s Arkansas Valley on the 4th, shutting down most government and
private
businesses. The storm reportedly dumped 35-41 inches (89-104 cm) of snow across
Chaffee and Park
counties, closing many roads in the region.
A stretch of record-breaking temperatures hit the Northeast in early
May. Record highs were recorded in Syracuse, NY, Burlington, VT,
Portland, ME, Bridgeport, CT and New York City on the 3rd. The heat
stoked wildfires in the region, prompting officials in Maine and Rhode
Island to declare the fire risk extreme.
Lake Okeechobee, the back-up reservoir for
Florida�s heavily populated east coast, dropped to just 9 feet (2.7 m) above sea
level, the lowest on record.
The previous record of 9.79
feet (3 m), set in 1981, was broken in late April. Four years of drought in
Florida caused millions of dollars in damage to the
state�s fruit and vegetable crops and an estimated 10 million dollar
loss to the timber industry. Over 3100 wildfires burned more than
335,300 acres (135,700 hectares) during the first five months of the
year, including a fire that closed a 17 mile section of Interstate 4, a
heavily traveled route between Orlando and Tampa. Parts of of the state
were reported as suffering through
the worst dry spell in more than 100 years of record keeping.
The Associated Press reported on the 25th that a government estimate
confirmed that Kansas
farmers had abandoned 1 million acres of their hard red winter wheat
crop, and that
the remaining fields comprised the state�s fewest harvested acres since
1957. Drought
conditions during fall planting, followed by a cold winter, reportedly
took a heavy
toll on the nation�s winter wheat crop, particularly in Kansas and
Oklahoma.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the nation�s winter
wheat harvest was estimated at 1.34 billion bushels, down 14% from last
year, and the
smallest crop in 23 years.
June 2001
Tropical Storm Allison produced rainfall amounts of over 30 inches (762 mm) in portions of Louisiana and southeast Texas. Allison caused $5 billion dollars in damage in the Texas and Louisiana area, making it the most expensive tropical storm in U.S. history. Damage in the Houston area included 13,000 homes either destroyed or with major damage and over 43,000 homes with some damage. Flooding, lightning and tornadoes associated with the storm system claimed 41 lives and injured dozens. Mid month, a tornado hit the town of Siren, WI on the 18th killing three people and injuring eight. Approximately 100 buildings were destroyed or heavily damaged.
July 2001
On the 6th, a tornado formed over the ocean as a waterspout and moved ashore in the busy resort town of Myrtle Beach, SC. Several people were injured, mobile homes were destroyed, and buses were overturned. Farther north, significant flooding caused by a series of thunderstorms occurred in West Virginia and eastern Kentucky on the 8th. Up to 3000 homes were damaged or destroyed by flooding or mudslides and one person was killed in southern WV and two were killed in eastern KY. Nearly 8 inches (203 mm) of rain fell in Mullens, WV and as a result, the Guyandotte and Tug Fork rivers rose well above flood stage exceeding the 100-year flood level. In Wyoming county, 75 percent of the businesses were damaged or destroyed.
August 2001
At the beginning of the month, a heat wave affected much of the Midwest and was a factor in 56 deaths according to local health officials from the affected states. Farther south Tropical Storm Barry moved across the lower Gulf Coast states of Florida and Alabama on the 6th and brought heavy rains and some flooding. Rainfall amounts up to 9 inches (229 mm) were measured over the Florida panhandle with lesser amounts in parts of Alabama, Mississippi and southwest Georgia. On the 11th and 12th, more than 1500 homes were damaged in Washington, DC by flooding from heavy rains and tornadoes. This flooding prompted the first-ever request for federal disaster aid for residents of the nation's capital. In the west, lightning-triggered wildfires continued to burn in many western states around mid month. The number of fires and total acreage burned for the fire season were close to the ten year national average.
September 2001
Early season snows up to seven inches (18 cm) fell in the Rocky mountains in
Colorado above 7,000 feet (2 km) on the 7th and 8th.
October 2001
An early season blizzard piled snow in drifts up to two feet (61 cm) high in North Dakota on the 24th, closing schools and stranding hundreds of drivers. Although snow isn't that unusual at the end of October in the Northern Plains, the amount of snow and the extent of the snowfall were notable. In the warm sector of the storm, thunderstorms across Indiana killed one person and injured 14 others.
November 2001
Forest fires in tandem with drought occurred in eastern Tennessee and western North Carolina during the first half of the month. Elsewhere, up to 13 inches (330 mm) of rain fell in parts of Texas on the 15th and 16th, breaking daily extreme rainfall records in Austin and San Antonio and swelling creeks and waterways. Ten people died in southeast Texas from the storm. Violent thunderstorms and tornadoes spawned by a powerful storm system ravaged Mississippi Delta communities in Arkansas, Alabama and Mississippi, killing 12 people and injuring about 190 others on the 24th. A double-dose of ice and rain socked Arkansas as storms wreaked havoc across the South, dropping up to 14 inches (356 mm) of rain and causing at least two deaths. In Memphis, repeated downpours dumped 10 inches (254 mm) of rain on Tennessee's biggest city from the 26th through the 29th. Farther west, the first snowstorm of the season was blamed for hundreds of traffic accidents and at least 18 deaths in Texas and Oklahoma. At least 9 inches (23 cm) of snow fell in Aspermont, TX.
December 2001
In early December, news agencies reported that more counties in PA, NJ and
NY came under
a drought declaration as conditions continued to deteriorate despite
recent rain.
On the 13th, a strong storm system moved in to California causing high
winds, heavy rains and snowfall. Winds at South Lake Tahoe, CA gusted to
54 mph (38 m/sec) and lower elevation stations received up to 2.5 inches
(63.5 mm) of rain while high mountain stations were blanketed with up to
two feet (61 cm) of new snow.
On the 15th and 16th, fierce storms spawned at least one tornado and
gave north Texas as much as 10 inches (254 mm) of rain. Flooding and
hazardous weather were blamed for several deaths in Texas and Arkansas.
On the 20th, a tornado with hail and heavy rain affected the Los
Angeles, CA area, downing trees and power lines.
After nearly no lake effect snow in December, an extended period of
heavy snow buried areas east of Lakes Erie and Ontario. From the 24th
through the 31st, Buffalo, NY received 81.6 inches (207.3 cm) of snow,
breaking the previous record of 68.4 inches (173.7 cm) set in 1985. Not
to be outdone, Montague, NY received 127 inches (322.6 cm) of snow in
the same period.
For more information on Weather and Climate Extremes, refer to ...
Extreme Weather and Climate Events

 Review of Global Events Review of Global Events
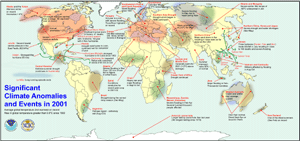
larger image
January 2001
The Australian summer (December 2000 -February 2001) saw warmer than average conditions across the southern third of the continent due to a high pressure system centered off the south-east coast. This was a continuation of the previous seasonal pattern. Temperature anomalies were in excess of 4C (7.2F) in parts of the region.
Flooding caused major damage in Kenya's capitol, Nairobi. Kenya's meteorological office in Nairobi recorded 128mm (5 inches) of rain in 9 hours on the 13th and reported it was the wettest January in 40 years.
In the Kemerovo region, 1800 miles east of Moscow, some areas had mid January temperatures as low as -50�C (-70�F), and extreme cold, 3�C to 6�C (5.4 - 10.8F) below average, was experienced throughout much of central and eastern Russia as well as eastern Mongolia and northeast China.
Northwest China also experienced heavy snow that led to the death of hundreds of thousands of cattle and damaged over 16,000 homes, leaving approximately 350,000 individuals with only limited shelter.
February 2001
Torrential rainfall and flooding occurred on the 10th and 11th of February in Java, western Indonesia. Thousands were left homeless and close to a hundred people died after the rains triggered floods and landslides. Most of those who died were buried in the landslides, while others were swept away by floodwaters. The floodwaters inundated at least 19 districts in Java, and most of the victims were reported in the hard hit area of Lebak. Flooding destroyed 20,000 houses and thousands of hectares of rice fields in 130 villages in 11 districts in East Java.
February also continued the run of anomalous warmth over the southeast and central parts of Australia, helping South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria record their hottest summers since 1950.
March 2001
A third consecutive year of severe flooding occurred in Hungary and parts of eastern Europe this spring. The rain-swollen Tisza River, which rose to 25 feet at the village of Zahony, Hungary, reached its highest level in 100 years in early March. Tens of thousands of people were forced to leave their homes through evacuation and/or inundation.
Southern Africa, including portions of Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Zambia, experienced at least 2 months of above normal rainfall resulting in considerable flooding. Persistent heavy rains, which were exacerbated by the development of Tropical Cyclone Dera in the Mozambique Channel around March 9, led to further flooding. Over 80 people were killed by the floods near the swollen Zambezi River and the number of people displaced by flood waters reached 235,000 in the four affected provinces of Mozambique (Manica, Sofala, Tete and Zambezia). In neighboring Zimbabwe, nearly 30,000 people were affected with 13 fatalities reported.
April 2001
A strong mid-latitude storm system moved across Mongolia and northeastern China during April 6-8th and produced a massive sandstorm as it crossed the Gobi Desert. Haze could be seen as far away as the USA.
Torrential flooding rains affected western Brazil during the week of the 23rd, killing at least 13 people. Heavy rains hit the coastal provinces of Angola with 11 deaths reported due to flooding and landslides. Over 20,000 people were displaced from their homes in Benguela and Namibe provinces, with some of the worst flooding along the Bero River in the provincial capital of Namibe.
April was a dry month across much of Afghanistan and Pakistan where severe long-term drought conditions continued.
May 2001
Western Australia had above average rainfall in May. Near record amounts were recorded at some locations.
Temperatures reaching as high as 50C (122�F) occurred in parts of Pakistan during the weekend of the 5th and 6th of May. In both Pakistan and India, the intense heat caused dozens of deaths. Above average temperatures were observed in these areas between March and May.
A rapid thaw following a severe winter across Siberia resulted in widespread flooding from the Ural Mountains to the Russian Far East. Temperatures during May were 2-5�C (3.6-9�F) above average, which accelerated snowmelt and caused many rivers to overflow their banks. Some of the worst flooding occurred in the Sakha region along the Lena River. Emergencies Ministry officials called flooding along the Lena the worst in 100 years. More than 300,000 people lost their homes in the Siberian Republic of Yakutia with a further 14,000 in the city of Lensk.
Adolph became the strongest May hurricane on record in the eastern Pacific basin with sustained winds of 65m/s (145mph) at its peak intensity.
June 2001
The first named tropical storm of the Atlantic this year, Allison, became the costliest tropical storm in US history. It caused over 5 billion dollars worth of damage and produced rainfall totals of well over 760mm (30 inches) in some Louisiana and south east Texas locations in the middle of June. As a direct result of the storm, 24 people died.
In Chile, more than 10,000 farmers were displaced and hundreds of dwellings damaged due to rain and wind. In Uruguay, heavy rains brought flooding at the beginning of the month, where 5,000 people lost their homes in the northern city of Artigas. A powerful mid-latitude storm system brought strong winds gusting as high as 41m/s (93 mph) to the southern part of the country during the 15th-17th. The storm killed 3 people and caused millions of dollars in damage. Drought continued in northeastern Brazil, where a state of emergency was declared in the state of Pernambuco due to severe food shortages that resulted in widespread hunger and looting. The drought has severely impacted the country's hydroelectric generation, which provides 90% of Brazil's power.
Cold weather that affected much of the La Paz state of Bolivia on the 28th was responsible for 9 deaths as temperatures dipped to -5.6�C (22�F) in El Alto and snow accumulated to a depth of 10 cm (4 inches).
July 2001
The weather of June and early July 2001 in southern China was marked by persistent heavy rain and thunderstorms under the repeated influence of active troughs of low pressure near the south China coast which brought heavy rain episodes to Hong Kong and surrounding areas. Also, Qinghai Province in western China was hit by heavy rains, resulting in 8 deaths and 7 people missing.
Southern China was hit by two typhoons, Durian and Utor, with the two worst affected areas being the Guangdong Province and the Guangxi Autonomous Region. Typhoon Utor resulted in 121 deaths in the Philippines, including at least 28 in the northern city of Baguio. Additionally, 130 individuals were injured. The government reported that almost 1 million people in approximately 20 provinces were affected by Utor, over 3700 homes were destroyed, and at least 8390 homes were damaged. Typhoon Utor is also reportedly responsible for 1 death in Taiwan.
August 2001
Thunderstorms with torrential rains partially offset severe drought conditions and caused flash flooding in parts of the Golestan and Khorasan provinces of Iran just before mid-August, killing at least 500 people and rendering 10,000 homeless. Heavy rains caused considerable flooding in Delhi during the first 2 weeks of August. Also during the first week of August, several days of heavy rains and subsequent flooding in northern Pakistan resulted in over 180 deaths.
Typhoon Usagi pounded the north-central coast of Vietnam on the 11th bringing high winds and torrential rains. Officials said tens of thousands of people were left homeless and at least one person was killed.
According to government reports, heavy rains caused flash flooding in northern Thailand which claimed at least 73 lives. Heavy mountain rains triggered a flash flood on the 11th in mountainside villages in the Lomsak district of Phetchabun province. The southwest monsoon brought abundant rains to the country in the May - October period.
Typhoon Pabuk made a direct strike on central Japan but weakened on the 21st and was downgraded to a tropical storm as it moved inland. Six individuals died with 50,000 evacuated from their homes. Over 300mm (12 inches) of rain were reported in some areas of southwestern and central Japan, before the remnants of the storm moved northeastward into the Pacific.
According to the U.N. World Food Program, three months of drought, in what is normally the rainy season, caused as many as 1.6 million people in Central America to suffer from hunger. The drought was the most severe in Guatemala, El Salvador, Nicaragua and Honduras.
In South Africa, parts of Cape Town were declared disaster areas on August 29th due to heavy rains and flooding. The heavy rains drove thousands of people from their homes. Rivers also overflowed and mudslides engulfed homes in Hout Bay - a fishing village south of the city.
September 2001
Some tempering of the drought conditions in central America occurred in the form of heavy rainfall from Atlantic tropical depression #9 as it moved into Nicaragua on the 20th of September and then continued into El Salvador.
In West Africa, a band of heavy rains (150-300 mm / 5.91-11.8 inches) stretched across the region from Mali, Senegal and Guinea to southern Chad. Flooding along the Niger River and adjacent tributaries in Guinea was reportedly the worst in 10 years. Nearly 70,000 people were affected, with 17,000 hectares (42,000 acres) of agricultural land submerged. Across Chad, flooding along the Logone, Chari and Batha rivers damaged more than 10,000 houses and drowned many domesticated animals. Flooding continued into October where rainfall totals were up to 200% of normal.
There were 4 Atlantic hurricanes and a tropical depression in September. Hurricane Gabrielle impacted Florida while still a strong tropical storm, producing significant rainfall totals in the state before intensifying as it moved into the western Atlantic. In the eastern Pacific, Juliette produced the 2nd lowest central pressure ever recorded in the basin at 923mb.
Tropical storm Nari killed 80 people in northern Taiwan, as the capital was submerged under floodwater. The storm left 32 inches of rainfall in its wake.
October 2001
At least 38 people died when a cyclone caused heavy rainfall and havoc in India's southeastern state of Andhra Pradesh on the 17th. The rainfall was perhaps the region's heaviest in four years.
Tropical depression #15 (later to become hurricane Michelle) which developed off the coast of Nicaragua at the end of October produced torrential rainfall and flooding in Nicaragua and Honduras. As hurricane Michelle continued into the Caribbean, it also caused an estimated $10 million (USD) damage to agriculture in Jamaica, including a sizable portion of the coffee crop. However, drought in Guatemala and neighboring regions continued into October.
Heavy rains flooded large areas of the Argentine Pampas causing the evacuation of 4,000 people. The fertile farming regions of Buenos Aires province were particularly hard-hit, where thousands of acres of fields and grazing lands were submerged. Authorities estimated more than 8.6 million acres were under water. Buenos Aires reported nearly 250mm (9.84 inches) of rainfall during October which is more than double the normal amount.
Flooding in the Mekong Delta region caused at least several hundred deaths between August and October. In Vinh, Vietnam, 27 inches (686mm) of rain fell between the 21st and the 27th of the month.
There were 2 hurricanes and 3 tropical storms in October. Iris, though small, was intense with sustained winds of 65m/s (145mph) at its maximum strength and impacted the coast of Belize causing 31 deaths.
November 2001
In November there were 3 named Atlantic storms, all of which became hurricanes - Michelle, Noel and Olga. This is the first time in recorded history that 3 hurricanes have formed in November in the Atlantic/Caribbean. Michelle caused heavy rain and flooding in Honduras while still a tropical storm. It then moved over Cuba after intensifying to hurricane strength causing 600,000 people to be evacuated. Hurricane Olga developed in late in November but remained in the Atlantic and did not threaten land.
Algeria's worst floods in nearly 40 years killed at least 618 people, with 577 dead in the capital, Algiers, alone. More than 100 mm (4 inches) of rain fell in a few hours in central Algiers, which compares to an average 93 mm (3.7 inches) the city normally receives in November.
Typhoon Lingling impacted central Vietnam, killing at least 18 people, knocking out power and destroying hundreds of homes. The storm, which left 171 confirmed dead and another 118 missing in the Philippines, brought 37m/s (83 mph) gusts when it hit Vietnam between Phu Yen and Binh Dinh provinces.
December 2001
Somalia is possibly on a verge of economic collapse caused by drought and other social and economic factors. The United Nations appealed for humanitarian aid for the 800,000 Somalis most affected by the drought. Recent rains in Ethiopia caused an overflow of rivers in southern Somalia, displacing large numbers of people and aggravating the food supply situation.
Much of Europe suffered with unusual cold and snow throughout December. Areas particularly hard-hit were Turkey, Greece, France, Spain, and Poland, also Romania and parts of Russia (especially Yakutia). Effects of the snow included many power outages, traffic disruption, agricultural losses and deaths.
Hunger and cold killed 177 people, the majority of them children, in a refugee camp near Kunduz in northern Afghanistan during November and December. According to UNICEF, some 100,000 children are at risk of dying from cold and hunger this winter, in addition to the 300,000 children who die in Afghanistan each year. Heavy rain and snow hit much of Afghanistan, bringing hope that the three-year drought might be ending. The recent rain is not enough however, to allow for the winter planting of wheat, which is already two months late.
The World Food Program reported that Honduras continued to be involved in two emergency situations: a drought, which affected this year�s crops and floods caused by tropical storm Michelle. Over 30,000 people have been assisted by the WFP so far.
In Australia, more than 100 wildfires burned out of control across the state of New South Wales. The fires began on Thursday Dec 20th fueled by dry conditions and high summer temperatures, though, at least half of the wildfires are believed to have been deliberately lit. Nearly 2 dozen arson suspects, including 15 children were arrested. About 5,000 firefighters were battling the flames with fifteen regions being declared natural disaster areas. Fires left many towns without electricity, cut freeways and roads, and halted service on railroads linking Sydney with south and southwest of the country. No fatalities were reported, but ambulance crews treated hundreds of firefighters and residents for respiratory problems. The fires burned 1.2 million acres of forest and farmland and 170 homes were destroyed. The blazes came within 11miles of Sydney, where ash fell on office blocks and air pollution reached record levels. More than 4,400 people were evacuated and insurance officials estimate the damages at $36 million. The temperatures in the region rose above 100 degrees and humidity levels dropped below 5%, the lowest recorded in 50 years.
For more information on Weather and Climate Extremes, refer to ...
Extreme Weather and Climate Events

For further information, contact:
Jay Lawrimore
NOAA/National Climatic Data Center
151 Patton Avenue
Asheville, NC 28801-5001
fax: 828-271-4328
email: Jay.Lawrimore@noaa.gov
-or-
Dimitri Chappas
NOAA/National Climatic Data Center
151 Patton Avenue
Asheville, NC 28801-5001
fax: 828-271-4328
email: Dimitri.Chappas@noaa.gov
-or-
Scott Stephens
NOAA/National Climatic Data Center
151 Patton Avenue
Asheville, NC 28801-5001
fax: 828-271-4328
email: Scott.Stephens@noaa.gov
 NCDC / Climate Monitoring / 2001 / Annual / Events / Search / Help NCDC / Climate Monitoring / 2001 / Annual / Events / Search / Help
http://lwf.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/climate/research/2001/ann/events.html
Downloaded Tuesday, 23-Sep-2008 02:09:27 EDT
Last Updated Thursday, 07-Jul-2005 13:51:33 EDT
Please see the NCDC Contact Page if you have questions or comments.
|

