|
 |
 |
Other Health Topics:
-
Related Topics
-
Go Local
- Services and providers for Hiatal Hernia in the U.S.
-
National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Hiatal Hernia is the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
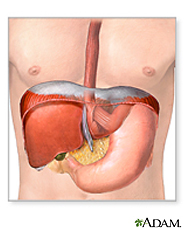
A hiatal hernia is a condition in which the upper part of the stomach bulges through an opening in the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle wall that separates the stomach from the chest. The diaphragm helps keep acid from coming up into the esophagus. When you have a hiatal hernia, it's easier for the acid to come up. The leaking of acid from the stomach into the esophagus is called gastroesophageal reflux (GERD). GERD may cause symptoms such as
- Heartburn
- Problems swallowing
- A dry cough
- Bad breath
Hiatal hernias are common, especially in people over age 50. If you have symptoms, eating small meals, avoiding certain foods, not smoking or drinking alcohol, and losing weight may help. Your doctor may recommend antacids or other medicines. If these don't help, you may need surgery.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
| Basics | Learn More | Multimedia & Cool Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Research | Reference Shelf | For You |
-
Overviews
- Hiatal Hernia(InteliHealth)
- Hiatal Hernia(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
-
Diagnosis/Symptoms
-
Upper Endoscopy
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases)
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases)
-
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract X-Ray (Radiography)(American College of Radiology, Radiological Society of North America)
Also available in Spanish
-
Upper GI Endoscopy
 (Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
(Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
Also available in Spanish
-
Upper Endoscopy
-
Related Issues
-
Heartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER), and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases)
(National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases)
-
Heartburn, Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER), and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
-
Tutorials
-
Upper GI Endoscopy(Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
Also available in Spanish
-
Upper GI Endoscopy(Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
-
Videos
- Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication Surgery(OR-Live) - Requires media player - One hour program - 11/29/2006
-
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Hernia, Hiatal
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Hernia, Hiatal
-
Journal Articles
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: Elastic fiber depletion in the supporting ligaments of the gastroesophageal...
- Article: Esophageal mythology.
- Article: Strategy for treatment of nonerosive reflux disease in Asia.
- Hiatal Hernia -- see more articles
-
Directories
- American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Find a Doctor(American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy)
- GI Physician Locator(American College of Gastroenterology)
-
Organizations
- American College of Gastroenterology
-
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases

-
Children
- Diaphragmatic Hernia(Children's Hospital Boston)
-
Teenagers
- Hernias(Nemours Foundation)
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Disclaimers | Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 27 July 2008 Topic last reviewed: 09 June 2008 |