|
 |
 |
Other Health Topics:
-
Related Topics
-
Go Local
- Services and providers for Pulmonary Embolism in the U.S.
-
National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Pulmonary Embolism is the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
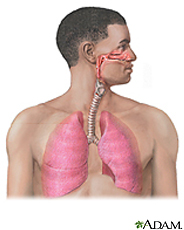
A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause
- Permanent damage to the affected lung
- Low oxygen levels in your blood
- Damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen
If a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death.
Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot include warmth, swelling, pain, tenderness and redness of the leg. The goal of treatment is to break up clots and help keep other clots from forming.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
-
JAMA Patient Page: Pulmonary Embolism(American Medical Association)
Also available in Spanish
-
Pulmonary Embolism
 (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
(National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
| Basics | Learn More | Multimedia & Cool Tools |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Research | Reference Shelf | For You |
|
-
Overviews
- Pulmonary Embolism(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
- Pulmonary Embolism(Society for Vascular Surgery)
-
Diagnosis/Symptoms
-
Chest X Ray
 (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
(National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
-
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)(American College of Radiology, Radiological Society of North America)
Also available in Spanish
- D-dimer(American Association for Clinical Chemistry)
-
Lung Ventilation/Perfusion Scan
 (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
(National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute)
-
Chest X Ray
-
Treatment
- Catheter-directed Thrombolysis(Radiological Society of North America)
- Thrombolytic Therapy(Society for Vascular Surgery)
- Warfarin: Any Harm in Long-Term Use?(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
-
What Are Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Agents?
 (American Heart Association) - Links to PDF
(American Heart Association) - Links to PDF
-
Prevention/Screening
- Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism(American Heart Association) - Links to PDF
-
Specific Conditions
- Deep Vein Thrombosis(American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons)
-
Related Issues
- Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia(American Heart Association)
- Updated Labeling for Coumadin (Warfarin)(Food and Drug Administration)
-
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Pulmonary Embolism
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Pulmonary Embolism
-
Research
- Occurrence of Venous Thromboembolism in Women Taking Low-Dose Aspirin(American College of Physicians)
- Risk for Fatal Pulmonary Embolism after Discontinuing Anticoagulation(American College of Physicians)
-
Journal Articles
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: American College of Chest...
- Article: Optimized imaging of pulmonary embolism.
- Article: Low-molecular-weight heparin versus compression stockings for thromboprophylaxis after knee arthroscopy:...
- Pulmonary Embolism -- see more articles
-
Dictionaries/Glossaries
- Thrombolysis, Thrombosis, Thrombus and Embolus(American Heart Association)
-
Directories
- Find a Vascular Specialist(Society for Vascular Surgery)
- Organizations Return to top
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 07 July 2008 Topic last reviewed: 31 May 2008 |