|
CONTACT: Media Interviews (415) 625-2270 (415) 625-2245 Internet address: http://www.bls.gov/ro9/news.htm
BLS 08-49 |
UNION MEMBERSHIP IN CALIFORNIA, 2007
In 2007, 16.7 percent of wage and salary workers in California were union members, up from 15.7 percent in 2006, according to the U.S. Department of Labor’s Bureau of Labor Statistics. Regional Commissioner Richard J. Holden noted that California had the largest number of union members—nearly 2.5 million—among all states nationwide. At its peak in 1989, the first year for which comparable state data were available, 18.9 percent of workers in California belonged to a union. (See table A.)
Nationally, union members accounted for 12.1 percent of employed wage and salary workers in 2007, essentially unchanged from 12.0 percent in 2006. The union membership rate for the U.S. has declined from a high of 20.1 percent in 1983, the first year for which comparable national union data were available. California was 1 of 20 states that had union membership rates above the U.S. average in 2007.
In addition to California’s nearly 2.5 million wage and salary workers who were union members in 2007, another 176,000 workers were represented by a union on their main job or were covered by an employee association or contract, while not being union members themselves. Nationwide, nearly 15.7 million wage and salary workers were union members in 2007, while an additional 1.6 million wage and salary workers were represented by a union on their main job but not union members themselves.
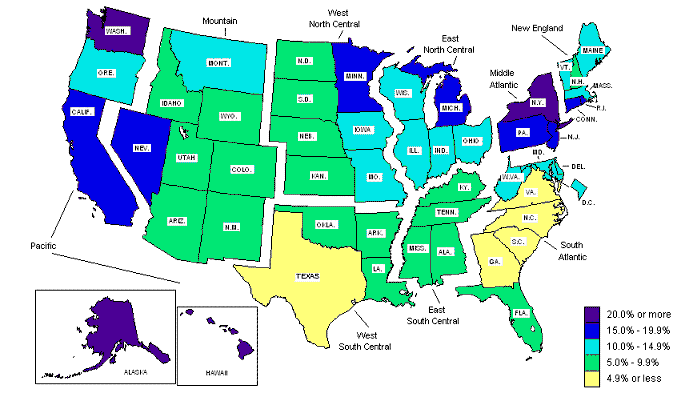
In 2007, 30 states and the District of Columbia had union membership rates below that of the U.S. average, 12.1 percent, while 20 states had higher rates. (See table 1.) All five states in the Pacific division (which includes California) had union membership rates above the national average in 2007. The three states in the Middle Atlantic division also reported union membership rates above the national average, while all states in the East South Central and West South Central divisions had rates below the national average. (See chart 1.) Relative to 2006, 27 states registered lower union membership rates, 20 states recorded higher membership rates, and 3 states and the District of Columbia had no changes in their rates.
Five states reported union membership rates below 5.0 percent in 2007— North Carolina (3.0 percent), Virginia (3.7 percent), South Carolina (4.1 percent), Georgia (4.4 percent), and Texas (4.7 percent). Four states had union membership rates over 20.0 percent— New York (25.2 percent), Alaska (23.8 percent), Hawaii (23.4 percent), and Washington (20.2 percent).
Nearly half (7.8 million) of the 15.7 million union members in the United States lived in 6 states (California, 2.5 million; New York, 2.1 million; Illinois, Michigan, and Pennsylvania, 0.8 million each; and New Jersey, 0.7 million), though these states accounted for only about one-third of wage and salary employment nationally.
State union membership levels depend on both the union membership rate and the employment level. For example, California had more than five times as many union members as Texas, despite having only 50 percent more wage and salary workers. Also, Pennsylvania had nearly 80 percent more union members than Texas, despite having 4.4 million fewer wage and salary workers. Similarly, Virginia and Hawaii had virtually the same number of union members in 2007, even though Virginia’s wage and salary employment level was more than six times that of Hawaii.
| Year | Total | Members of unions(1) | Represented by unions (2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employed | Total | Percent of employed | Total | Percent of employed | |
1989 |
11,826 | 2,239 | 18.9 | 2,584 | 21.9 |
1990 |
12,526 | 2,268 | 18.1 | 2,624 | 21.0 |
1991 |
12,116 | 2,185 | 18.0 | 2,503 | 20.7 |
1992 |
12,077 | 2,169 | 18.0 | 2,520 | 20.9 |
1993 |
12,018 | 2,139 | 17.8 | 2,415 | 20.1 |
1994 |
n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
1995 |
12,320 | 2,176 | 17.7 | 2,463 | 20.0 |
1996 |
12,461 | 2,061 | 16.5 | 2,340 | 18.8 |
1997 |
12,878 | 2,067 | 16.0 | 2,321 | 18.0 |
1998 |
13,338 | 2,154 | 16.1 | 2,408 | 18.1 |
1999 |
13,811 | 2,286 | 16.6 | 2,527 | 18.3 |
2000 |
14,359 | 2,295 | 16.0 | 2,546 | 17.7 |
2001 |
14,219 | 2,299 | 16.2 | 2,526 | 17.8 |
2002 |
13,955 | 2,444 | 17.5 | 2,619 | 18.8 |
2003 |
14,350 | 2,414 | 16.8 | 2,647 | 18.4 |
2004 |
14,414 | 2,385 | 16.5 | 2,588 | 18.0 |
2005 |
14,687 | 2,424 | 16.5 | 2,610 | 17.8 |
2006 |
14,501 | 2,273 | 15.7 | 2,444 | 16.9 |
2007 |
14,856 | 2,474 | 16.7 | 2,650 | 17.8 |
|
Footnotes: |
|||||
|
n/a – Not available. |
|||||
The estimates in this release are obtained from the Current Population Survey (CPS), which provides the basic information on the labor force, employment, and unemployment in the U.S.. The survey is conducted monthly for the Bureau of Labor Statistics by the U.S. Census Bureau from a scientifically selected sample of about 60,000 households nationwide. The union membership data are tabulated from one-quarter of the CPS monthly sample and are limited to wage and salary workers. All self-employed workers are excluded.
Union membership data, particularly levels, for each year are not strictly comparable with data for earlier years because of the introduction of revised population controls used in the CPS. The effect of the revised population controls on the union membership estimates is unknown. However, as an example, the effect of the new controls in 2007 on the monthly CPS estimates for the U.S. was to increase the December 2006 employment level by 153,000 and the unemployment level by 10,000. The updated controls had little or no effect on unemployment rates and other ratios, such as union membership rates. For additional information, see "Adjustments to Household Survey Population Estimates in January 2007" in the February 2007 issue of Employment and Earnings, available on the Internet at www.bls.gov/cps/cps07adj.pdf.
For personal assistance or further information on union membership, as well as other Bureau programs, contact the Western Information Office at 415-625-2270 from 9:00 a.m. to 11:30 a.m. and 1:30 pm to 4:30 p.m. PT. Information in this release will be made available to sensory impaired individuals upon request. Voice phone: 202-692-5200, TDD message referral phone number: 1-800-877-8339.
Reliability of the estimates
Statistics based on the CPS are subject to both sampling and nonsampling error. When a sample, rather than the entire population, is surveyed, there is a chance that the sample estimates may differ from the "true" population values they represent. The exact difference, or sampling error, varies depending upon the particular sample selected, and this variability is measured by the standard error of the estimate. There is about a 90-percent chance, or level of confidence, that an estimate based on a sample will differ by no more than 1.6 standard errors from the "true" population value because of sampling error.
The CPS data also are affected by nonsampling error. Nonsampling error can occur for many reasons, including the failure to sample a segment of the population, inability to obtain information for all respondents in the sample, inability or unwillingness of respondents to provide correct information, and errors made in the collection or processing of the data.
For a full discussion of the reliability of data from the CPS and information on estimating standard errors, see the "Explanatory Notes and Estimates of Error" section of Employment and Earnings.
Definitions
The principal definitions used in this release are described briefly below.
Union members. Data refer to members of a labor union or an employee association similar to a union.
Represented by unions. Data refer to union members, as well as workers who have no union affiliation but whose jobs are covered by a union or an employee association contract.
Wage and salary workers. Workers who receive wages, salaries, commissions, tips, payment in kind, or piece rates. The group includes employees in both the private and public sectors, but, for the purposes of the union membership and earnings series, excludes all self-employed persons, regardless of whether or not their businesses are incorporated.
| State | 2006 | 2007 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total employed | Members of unions(1) | Represented by unions(2) | Total employed | Members of unions(1) | Represented by unions(2) | |||||
| Total | Percent of employed | Total | Percent of employed | Total | Percent of employed | Total | Percent of employed | |||
Alabama |
1,930 | 170 | 8.8 | 194 | 10.0 | 1,895 | 180 | 9.5 | 201 | 10.6 |
Alaska |
280 | 62 | 22.2 | 67 | 23.8 | 284 | 68 | 23.8 | 70 | 24.7 |
Arizona |
2,584 | 197 | 7.6 | 250 | 9.7 | 2,619 | 230 | 8.8 | 255 | 9.7 |
Arkansas |
1,130 | 58 | 5.1 | 67 | 6.0 | 1,154 | 62 | 5.4 | 75 | 6.5 |
California |
14,501 | 2,273 | 15.7 | 2,444 | 16.9 | 14,856 | 2,474 | 16.7 | 2,650 | 17.8 |
Colorado |
2,154 | 165 | 7.7 | 186 | 8.6 | 2,204 | 191 | 8.7 | 202 | 9.2 |
Connecticut |
1,591 | 247 | 15.6 | 263 | 16.5 | 1,617 | 253 | 15.6 | 269 | 16.6 |
Delaware |
396 | 43 | 10.8 | 45 | 11.4 | 396 | 47 | 12.0 | 50 | 12.8 |
District of Columbia |
246 | 25 | 10.3 | 30 | 12.2 | 278 | 29 | 10.3 | 38 | 13.6 |
Florida |
7,676 | 397 | 5.2 | 497 | 6.5 | 7,741 | 455 | 5.9 | 562 | 7.3 |
Georgia |
3,974 | 176 | 4.4 | 230 | 5.8 | 4,181 | 186 | 4.4 | 226 | 5.4 |
Hawaii |
562 | 139 | 24.7 | 146 | 25.9 | 556 | 130 | 23.4 | 135 | 24.2 |
Idaho |
620 | 37 | 6.0 | 45 | 7.2 | 635 | 33 | 5.3 | 41 | 6.4 |
Illinois |
5,684 | 931 | 16.4 | 979 | 17.2 | 5,802 | 842 | 14.5 | 884 | 15.2 |
Indiana |
2,787 | 334 | 12.0 | 362 | 13.0 | 2,779 | 333 | 12.0 | 359 | 12.9 |
Iowa |
1,424 | 161 | 11.3 | 199 | 14.0 | 1,417 | 149 | 10.5 | 185 | 13.1 |
Kansas |
1,236 | 99 | 8.0 | 115 | 9.3 | 1,274 | 89 | 7.0 | 110 | 8.7 |
Kentucky |
1,752 | 172 | 9.8 | 196 | 11.2 | 1,734 | 157 | 9.1 | 192 | 11.1 |
Louisiana |
1,676 | 107 | 6.4 | 121 | 7.2 | 1,670 | 94 | 5.6 | 108 | 6.5 |
Maine |
584 | 69 | 11.9 | 79 | 13.5 | 574 | 67 | 11.7 | 79 | 13.8 |
Maryland |
2,614 | 342 | 13.1 | 386 | 14.8 | 2,598 | 335 | 12.9 | 376 | 14.5 |
Massachusetts |
2,859 | 414 | 14.5 | 438 | 15.3 | 2,882 | 379 | 13.2 | 402 | 14.0 |
Michigan |
4,299 | 842 | 19.6 | 879 | 20.4 | 4,193 | 819 | 19.5 | 865 | 20.6 |
Minnesota |
2,479 | 395 | 16.0 | 416 | 16.8 | 2,460 | 400 | 16.3 | 419 | 17.0 |
Mississippi |
1,065 | 60 | 5.6 | 78 | 7.3 | 1,068 | 72 | 6.7 | 95 | 8.9 |
Missouri |
2,610 | 284 | 10.9 | 310 | 11.9 | 2,585 | 275 | 10.7 | 308 | 11.9 |
Montana |
397 | 48 | 12.2 | 52 | 13.1 | 399 | 54 | 13.5 | 62 | 15.6 |
Nebraska |
831 | 66 | 7.9 | 79 | 9.5 | 836 | 65 | 7.8 | 81 | 9.7 |
Nevada |
1,124 | 167 | 14.8 | 191 | 17.0 | 1,177 | 182 | 15.4 | 208 | 17.7 |
New Hampshire |
620 | 63 | 10.1 | 70 | 11.3 | 631 | 61 | 9.7 | 70 | 11.2 |
New Jersey |
3,827 | 770 | 20.1 | 825 | 21.6 | 3,897 | 748 | 19.2 | 802 | 20.6 |
New Mexico |
796 | 62 | 7.8 | 92 | 11.5 | 800 | 62 | 7.7 | 91 | 11.4 |
New York |
8,115 | 1,981 | 24.4 | 2,060 | 25.4 | 8,150 | 2,055 | 25.2 | 2,146 | 26.3 |
North Carolina |
3,810 | 126 | 3.3 | 155 | 4.1 | 3,771 | 114 | 3.0 | 147 | 3.9 |
North Dakota |
300 | 20 | 6.8 | 24 | 8.0 | 303 | 19 | 6.4 | 23 | 7.6 |
Ohio |
5,170 | 734 | 14.2 | 801 | 15.5 | 5,187 | 730 | 14.1 | 797 | 15.4 |
Oklahoma |
1,453 | 93 | 6.4 | 112 | 7.7 | 1,456 | 103 | 7.1 | 124 | 8.5 |
Oregon |
1,527 | 211 | 13.8 | 225 | 14.7 | 1,582 | 227 | 14.3 | 243 | 15.4 |
Pennsylvania |
5,457 | 745 | 13.6 | 802 | 14.7 | 5,496 | 830 | 15.1 | 910 | 16.6 |
Rhode Island |
498 | 76 | 15.3 | 79 | 16.0 | 497 | 75 | 15.0 | 78 | 15.8 |
South Carolina |
1,775 | 59 | 3.3 | 74 | 4.2 | 1,873 | 78 | 4.1 | 111 | 5.9 |
South Dakota |
351 | 21 | 5.9 | 25 | 7.2 | 354 | 23 | 6.5 | 27 | 7.7 |
Tennessee |
2,550 | 153 | 6.0 | 174 | 6.8 | 2,596 | 138 | 5.3 | 166 | 6.4 |
Texas |
9,751 | 476 | 4.9 | 576 | 5.9 | 9,899 | 463 | 4.7 | 566 | 5.7 |
Utah |
1,121 | 61 | 5.4 | 69 | 6.1 | 1,153 | 67 | 5.8 | 78 | 6.8 |
Vermont |
305 | 34 | 11.0 | 39 | 12.9 | 288 | 30 | 10.4 | 35 | 12.2 |
Virginia |
3,446 | 139 | 4.0 | 179 | 5.2 | 3,502 | 129 | 3.7 | 167 | 4.8 |
Washington |
2,772 | 549 | 19.8 | 583 | 21.0 | 2,874 | 579 | 20.2 | 616 | 21.4 |
West Virginia |
710 | 101 | 14.2 | 110 | 15.5 | 724 | 97 | 13.3 | 107 | 14.7 |
Wisconsin |
2,587 | 386 | 14.9 | 415 | 16.1 | 2,631 | 376 | 14.3 | 405 | 15.4 |
Wyoming |
235 | 19 | 8.3 | 24 | 10.0 | 239 | 19 | 7.9 | 22 | 9.4 |
Footnotes: |
||||||||||
Chart 1. Union membership rates by state, 2007 annual averages
Last Modified Date: June 24, 2008