|
 |
 |
Other Health Topics:
-
Related Topics
-
Go Local
- Services and providers for Lymphoma in the U.S.
-
National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Lymphoma is the National Cancer Institute
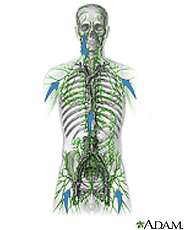
Lymphoma is a cancer of a part of the immune system called the lymphatic system. There are many types of lymphoma. One type is called Hodgkin's disease. The rest are called non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas begin when a type of white blood cell, called a T cell or B cell, becomes abnormal. The cell divides again and again, making more and more abnormal cells. These abnormal cells can spread to almost any other part of the body. Most of the time, doctors can't determine why a person gets non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can cause many symptoms, such as
- Swollen, painless lymph nodes in the neck, armpits or groin
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever
- Soaking night sweats
- Coughing, trouble breathing or chest pain
- Weakness and tiredness that don't go away
- Pain, swelling or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
Your doctor will perform an exam and lab tests to determine if you have lymphoma.
National Cancer Institute
-
What Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?(American Cancer Society)
Also available in Spanish
-
What You Need to Know about Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
| Basics | Learn More | Multimedia & Cool Tools |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Research | Reference Shelf | For You |
-
Overviews
-
Lymphomas: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Large PDF file
Also available in Spanish
-
Lymphomas: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Large PDF file
-
Latest News
- Survival Rates Improve for Kids with Blood Cancers(09/10/2008, HealthDay)
- New Lymphoma Drug Shows Promise(08/14/2008, HealthDay)
- Incidence of Mantle Cell Lymphoma on Rise(07/18/2008, HealthDay)
-
Diagnosis/Symptoms
-
How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
Also available in Spanish
- How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Staged?(American Cancer Society)
- How Is Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
-
Understanding Blood Counts(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
Also available in Spanish
-
How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
-
Treatment
-
Adult Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
-
AIDS-Related Lymphoma (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
-
MedlinePlus: Bone Marrow Transplantation
 (National Library of Medicine)
(National Library of Medicine)
Also available in Spanish
-
Mycosis Fungoides and the Sezary Syndrome (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
- New Approaches to Treatment(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
-
Primary CNS Lymphoma (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
- Radiation Therapy for Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma(American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology)
- Treatment of Extranodal Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma(American Cancer Society)
- Treatment of Intermediate Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma -- Stages I and II(American Cancer Society)
- Treatment of Intermediate Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma -- Stages III and IV and High Grade Lymphomas(American Cancer Society)
- Treatment of People with Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia(American Cancer Society)
-
Understanding Drug Therapy and Managing Side Effects(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Large PDF file
Also available in Spanish
-
Adult Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (PDQ): Treatment
-
Prevention/Screening
- Can Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Be Prevented?(American Cancer Society)
- What Are the Risk Factors for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma?(American Cancer Society)
- What Are the Risk Factors for Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia?(American Cancer Society)
-
Alternative Therapy
- Integrative Medicine & Complementary and Alternative Therapies As Part of Blood Cancer Care(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
-
Coping
- Coping with Lymphoma(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
- Relationships and Recovery for Young Adult Lymphoma Survivors(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
-
Disease Management
- Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin Type: What Happens After Treatment?(American Cancer Society)
- What Happens After Treatment of Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia?(American Cancer Society)
-
Specific Conditions
- Common Types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
-
Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
Also available in Spanish
-
Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Related Issues
- Hodgkin's vs. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: What's the Difference?(Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
- Pain Management(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
- What You Should Know Before Starting Treatment(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
-
Anatomy/Physiology
- Atlas of the Body: The Lymphatic System(American Medical Association)
-
Financial Issues
- Financial Support(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- Patient Aid Grant and Healthcare Provider Grant Program(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
-
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Lymphoma
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Lymphoma
-
Research
- Antibiotics Work Against Eye Lymphoma(American Cancer Society)
-
Follicular Lymphoma Treatment Better with Rituximab
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Initial Treatment with Rituximab Is a New Standard for Elderly Patients with B-Cell Lymphoma
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Less-Intense Chemotherapy Benefits Some Children with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Radiation Might be Avoided for Older Patients with Good Prognosis Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Rituximab Helps Patients with Recurrent Lymphomas
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Rituximab Improves Response Rate in Mantle Cell Lymphoma
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
- What's New in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Research and Treatment?(American Cancer Society)
-
Journal Articles
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: New targets for lymphoma treatment.
- Article: MicroRNAs and lymphomas.
- Article: New response criteria for lymphomas in clinical trials.
- Lymphoma -- see more articles
- Non-hodgkin lymphoma -- see more articles
-
Dictionaries/Glossaries
- Learning about Lymphoma: Glossary of Terms(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Glossary(Lymphoma Research Foundation)
-
Organizations
- American Cancer Society
- Leukemia & Lymphoma Society
- Lymphoma Research Foundation
-
National Cancer Institute

-
Newsletters/Print Publications
- Blood & Marrow Transplant Newsletter(BMT InfoNet)
-
Statistics
- Facts 2007-2008(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Large PDF file
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Facts & Statistics(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- What Are the Key Statistics about Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children?(American Cancer Society)
-
Children
- Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) and Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation (PBSCT)(American Cancer Society)
-
Childhood Cancer: Lymphoma(Nemours Foundation)
Also available in Spanish
-
Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
- Do We Know What Causes Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children?(American Cancer Society)
- How Is Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated?(American Cancer Society)
- How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
- How Is Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children Staged?(American Cancer Society)
-
Long-Term and Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Leukemia or Lymphoma(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
Also available in Spanish
-
Some Kinds of Cancer Kids Get(Nemours Foundation)
Also available in Spanish
- What Are the Risk Factors for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children?(American Cancer Society)
- What's New in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children Research and Treatment?(American Cancer Society)
-
Teenagers
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma(Nemours Foundation)
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 11 September 2008 Topic last reviewed: 21 July 2008 |