|
 |
 |
Other Health Topics:
-
Related Topics
-
Go Local
- Services and providers for Leukemia, Adult Acute in the U.S.
-
National Institutes of Health
- The primary NIH organization for research on Leukemia, Adult Acute is the National Cancer Institute
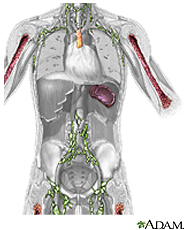
Leukemia is cancer of the white blood cells. White blood cells help your body fight infection. Your blood cells form in your bone marrow. In leukemia, however, the bone marrow produces abnormal white blood cells. These cells crowd out the healthy blood cells, making it hard for blood to do its work.
Leukemia can develop quickly or slowly. Chronic leukemia grows slowly. In acute leukemia, the cells are very abnormal and their number increases rapidly. Adult acute leukemia can cause
- Infections
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Tiredness
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Adult acute leukemia can often be cured. Treatments may include chemotherapy, radiation and stem cell transplantation. Even if symptoms disappear, you might need therapy to prevent a relapse.
National Cancer Institute
-
Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
-
Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia (PDQ): Treatment
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
-
Leukemia
 (Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
(Patient Education Institute) - Requires Flash Player
Also available in Spanish
| Basics | Learn More | Multimedia & Cool Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Research | Reference Shelf | For You |
|
-
Overviews
-
What You Need to Know about Leukemia
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
What You Need to Know about Leukemia
-
Latest News
- Methadone Kills Resistant Leukemia Cells(08/01/2008, HealthDay)
-
Diagnosis/Symptoms
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia(College of American Pathologists) - Links to PDF
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia(College of American Pathologists) - Links to PDF
- Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy(American Association for Clinical Chemistry)
- How Is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Classified?(American Cancer Society)
-
How Is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
Also available in Spanish
- How Is Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Classified?(American Cancer Society)
- How Is Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Diagnosed?(American Cancer Society)
- Platelet Count(American Association for Clinical Chemistry)
-
Understanding Blood Counts(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
Also available in Spanish
- White Blood Cell Differential Count(American Association for Clinical Chemistry)
-
Treatment
- Blood Transfusion(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- How Is Acute Lymphocitic Leukemia Treated?(American Cancer Society)
- Immunotherapy(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
-
Long-Term and Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Leukemia or Lymphoma(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
Also available in Spanish
-
MedlinePlus: Bone Marrow Transplantation
 (National Library of Medicine)
(National Library of Medicine)
Also available in Spanish
- New Approaches to Treatment(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- Targeted Therapy for Acute Lymphocytic (ALL)(American Cancer Society)
- Treatment of Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia(American Cancer Society)
- Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)(American Cancer Society)
-
Understanding Drug Therapy and Managing Side Effects(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Large PDF file
Also available in Spanish
- What If the Leukemia Doesn't Respond or Comes Back After Treatment? (ALL)(American Cancer Society)
- What If the Leukemia Doesn't Respond or Comes Back After Treatment? (AML)(American Cancer Society)
-
Prevention/Screening
- Can Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Be Prevented?(American Cancer Society)
- Can Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Be Prevented?(American Cancer Society)
- What Are the Risk Factors for Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?(American Cancer Society)
- What Are the Risk Factors for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?(American Cancer Society)
-
Alternative Therapy
- Integrative Medicine & Complementary and Alternative Therapies As Part of Blood Cancer Care(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
-
Coping
-
Coping with Survival(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
Also available in Spanish
-
Coping with Survival(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
-
Specific Conditions
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
-
What Is Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL)?(American Cancer Society)
Also available in Spanish
- What Is Acute Myeloid Leukemia?(American Cancer Society)
-
Related Issues
- Pain Management(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) - Links to PDF
- What Should You Ask Your Doctor about Adult Acute Leukemia?(American Cancer Society)
- Tutorials Return to top
-
Financial Issues
- Insurance(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- Patient Financial Aid(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
-
Clinical Trials
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Leukemia
 (National Institutes of Health)
(National Institutes of Health)
-
ClinicalTrials.gov: Leukemia
-
Genetics
- Do We Know What Causes Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia?(American Cancer Society)
- Do We Know What Causes Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?(American Cancer Society)
-
Research
-
Allogeneic (Donor) Stem-Cell Transplant Boosts Survival in Ph-Negative, Standard-Risk Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Low-Dose Cytarabine Improves Survival of Older Patients with Leukemia
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
- What's New in Adult Acute Leukemia Research and Treatment?(American Cancer Society)
-
Allogeneic (Donor) Stem-Cell Transplant Boosts Survival in Ph-Negative, Standard-Risk Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
-
Journal Articles
References and abstracts from MEDLINE/PubMed (National Library of Medicine)
- Article: Loss of the Y chromosome: an age-related or clonal phenomenon...
- Article: Chemoimmunotherapy reinduction with epratuzumab in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia...
- Article: The usefulness of growth hormone treatment for psychological status in...
- Leukemia, Adult Acute -- see more articles
-
Dictionaries/Glossaries
- National Marrow Donor Program: Glossary(National Marrow Donor Program)
-
Directories
-
National Cancer Institute Cancer Centers Program
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
Also available in Spanish
-
National Cancer Institute Cancer Centers Program
-
Organizations
- American Cancer Society
- Leukemia & Lymphoma Society
-
National Cancer Institute

- National Marrow Donor Program
-
Newsletters/Print Publications
- Latest News(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
-
Leukemia Trial Results
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
-
Statistics
-
Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia
 (National Cancer Institute)
(National Cancer Institute)
- Leukemia Facts and Statistics(Leukemia & Lymphoma Society)
- What Are the Key Statistics about Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?(American Cancer Society)
-
Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 04 August 2008 Topic last reviewed: 25 June 2008 |