Data & Statistics
Other Features
Featured Data & Statistics
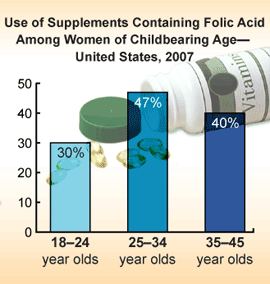
Use of Supplements Containing Folic Acid Among Women of Childbearing Age - United States, 2007
January is National Birth Defects Prevention Month. Birth defects affect approximately one in 33 newborns and are a leading cause of infant mortality in the United States. The cost of lifetime care for infants born in a single year with one or more of 17 severe birth defects has been estimated at $6 billion (1).
Health care professionals should encourage every woman who might become pregnant to consume 400 micrograms of synthetic folic acid every day in a vitamin supplement or in foods enriched with folic acid. Following this regimen before and during early pregnancy can prevent serious birth defects of the spine and brain (2).
A recent report of data from 2007 found that among all women of childbearing age, women aged 25 - 34 years were the most likely to report consuming a daily supplement containing folic acid (47%), followed by women aged 35 - 45 years (40%) and women aged 18 - 24 years (30%).
In 2007, women aged 18 - 24 years had the least awareness regarding folic acid consumption (61%), the least knowledge regarding when folic acid should be taken (6%), and the lowest reported daily use of supplements containing folic acid (30%). Because women in this age group account for nearly one third of all births in the United States (3), promotion of folic acid consumption should be targeted to this population. Innovative and effective messages tailored to women aged 18-24 years are needed to help change behaviors, increase awareness and knowledge regarding folic acid consumption, and ultimately reduce the incidence of neural tube defects (NTDs).
1. CDC. Economic costs of birth defects and cerebral palsy---United States, 1992. MMWR 1995;44:694-9.
2. CDC. Recommendation for the use of folic acid to reduce the number of cases of spina bifida and other neural tube defects. MMWR 1992;41(No. RR-14).
3. Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Sutton PD, et al. Births: final data for 2005. Natl Vital Stat Rep 2007;56(6).
Additional Information:
- Learn More About Folic Acid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Preview and Order Folic Acid Educational Materials
- Folic Acid: All Women, Every Day, 400 Micrograms
 |
Folic Acid: Helping to Ensure a Healthy Pregnancy |
Health-e-Cards
 |
Know someone who is thinking about getting pregnant? |
 |
Know someone who is pregnant? |
 |
Know someone who just had a baby? |
Page last reviewed: January 16, 2008
Page last updated: January 16, 2008
Content source: National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
Content owner: National Center for Health Marketing
URL for this page: http://www.cdc.gov/datastatistics/2008/folicAcid/
