|
The Afterschool Investments project has developed profiles for each state to provide a snapshot of the "state of afterschool," as well as an opportunity to compare afterschool activities across the country. This profile provides key data and descriptions of the afterschool landscape, which includes a range of out-of-school time programming that can occur before and after school, on weekends, and during summer months. It is designed to serve as a resource for policymakers, administrators, and providers.
Quick Facts
Demographics
| Total population: |
5,615,727 |
Number of children ages 5-12: |
584,908 |
| Percent of population: |
10.4% |
Percent of students eligible for free and reduced-price lunch: |
31.4% |
Percent of K-12 students in Title I "Schoolwide" schools: |
16.8% |
For more demographic information, visit http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov/statedata/statepro/index.html
Child Care and Development Fund (CCDF)
• CCDF Administrative Overview
Administering agency: |
Maryland Department of Education,
Division of Early Childhood Development |
|
Total FFY06 federal and state CCDF funds: |
$136,001,772 |
FFY06 total federal share: |
$81,134,019 |
FFY06 state MOE plus match: |
$54,867,753 |
FFY06 School Age & Resource and Referral Targeted Funds: |
$228,225 |
FFY06 Tribal CCDF Allocation: |
$0 |
FFY05 Total Quality Expenditures: |
$5,838,941 |
Percent of children receiving CCDF subsidies who are ages
5-12: |
51.3% |
• Settings
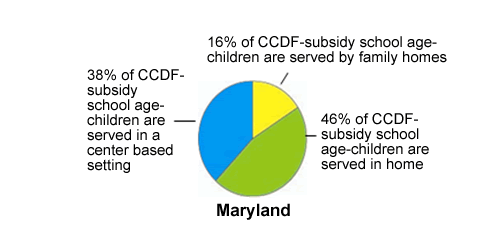
Where CCDF-Subsidy school age-children are served:
| In a center based setting |
38% |
| By family homes |
16% |
| In home |
46% |
• Uses of CCDF Targeted Funds and Quality Dollars for Afterschool
"Resource and referral and school-age" targeted funds:
Funds may be used to provide for technical assistance, training, and regional conferences to child care workers. The Department of Human Resources may also contract with numerous non-profit agencies to fund several before- and afterschool programs for school-age children.
Other quality activities:
CCDF quality dollars may be used to expand programs to serve more school-age children.
• Provider Reimbursement Rates
Label assigned by state for school-age rate category: |
Regular |
Maximum rate for center-based school-age category: |
$433.00/month |
Notes: Rates vary by Region (groups
of counties). Rates for Region BC
(Baltimore City ) given. |
Standardized monthly center-based school-age rate: |
$659 |
Are separate subsidy rates offered for part-time and full-time care? |
No |
Tiered Reimbursement Rate System:
A tiered reimbursement system includes higher payments for providers who provide better quality child care, as demonstrated through a credentialing program; payment rates vary for children with disabilities/ special needs, and care provided during non-traditional hours.
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) and Child Care
FFY05 state TANF transfer to CCDF: |
$0 |
FFY05 TANF direct spending on child care: |
$639,909 |
Program Licensing and Accreditation Policies
| Are there separate licensing standards governing the care of school-age children? |
No |
Are there specialized requirements for center-based care for school-age children? |
Yes |
Ratio of children to adults in school-age centers: |
15:1 |
Number of National AfterSchool Association (NAA) accredited programs: |
15 |
21st Century Community Learning Centers (21st CCLC)
FY06 state formula grant amount: |
$12,837,925 |
Most recent competition: |
May 2007 |
Applications funded: |
9 |
Total first year grant awards: |
Data Not Available |
| Fiscal agent type: |
44.4% school district
55.6% other |
| Licensing required? |
No |
Return to top
Statewide Initiatives
-
Maryland After School Opportunity Fund: The After School Opportunity Fund and its accompanying Advisory Board were created by the 1999 Maryland General Assembly to provide resources for local jurisdictions in Maryland to expand afterschool activities for at-risk youth. Beginning in FY 2001, $10 million in TANF funds were allocated for the Fund. The Advisory Board developed program standards, funding priorities, and an administrative structure to guide the afterschool expansion. Local Management Boards (LMBs) plan and coordinate child and family service delivery in each jurisdiction and provide a central place for discussion and decision-making. The Department of Human Resources supports LMBs with training, technical assistance, and monitoring.
-
Associated Black Charities: In 2003, Associated Black Charities, which acts as a coordinating body for delivery of services of special significance to Maryland’s African American communities, received funding from the HHS Office of Community Services to administer the Compassion Capital Fund Demonstration Program (CCFDP) in Central Maryland and Dorchester and Wicomico counties. Associated Black Charities provides technical assistance and capacity-building activities and runs funding competitions for a range of community-based organizations (CBOs) and faith-based organizations (FBOs), many of which administer afterschool programs.
Return to top
Notable Local Initiatives
-
The After-school Institute (TASI). Baltimore’s Safe and Sound Campaign, an initiative of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s Urban Health Initiative, seeks to improve the health and well-being of Baltimore’s children and youth using systems change strategies. One of the campaign’s key strategies is to build a citywide system that supports the expansion and improvement of afterschool programs. The After-school Institute (TASI), an intermediary organization, grew out of the Safe and Sound afterschool strategy. TASI works to build the capacity and quality of afterschool programs in Baltimore and surrounding Maryland communities, and receives grants from a range of state, local and private agencies, including the Department of Human Resources, the Maryland State Department of Education, and Associated Black Charities.
-
Baltimore City and Afterschool Programs Partnership. In strengthening its partnership with afterschool programs in the local community, the Mayor of Baltimore and the City Council allocated over $6 million of surplus funds in 2005 to support afterschool programs. $4.4 million will go to BOOST or school-based afterschool programs ($973,000 in the budget, and $3.4 million in supplemental funds, of which $140,000 will go toward the Afterschool Institute). YouthPlaces and A-Teams, which are both community-based afterschool programs, will each receive $500,000. $2.5 million will go to summer jobs for youth. Additionally, the city will provide funds for other youth services including those for maintenance and repairs at schools, libraries, and recreation centers.
Return to top
Statewide Organizations
National AfterSchool Association Affiliate:
Maryland School Age Child Care Alliance
PO Box 4811
Timonium, MD 21094-4811
Phone: 410-484-6220
Email: sstenner@comcast.net
Statewide Child Care Resource & Referral Network:
Maryland Committee for Children, Inc
608 Water Street
Baltimore, MD 21202
Phone: 410-752-7588
Fax: 410-752-6286
Email: mcc@md.childcare.org
Web: http://mdchildcare.org/mdcfc/mcc.html
Return to top
Additional Resources
State Child Care Administrators:
http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov/statedata/dirs/display.cfm?title=ccdf
State TANF Contacts:
http://www.acf.hhs.gov/programs/ofa/tanf-dir.htm
21st Century Community Learning Centers Contacts:
http://www.ed.gov/programs/21stcclc/contacts.html
Return to top
Notes and Sources
Demographics
Total population: Annual Estimates of the Population for the United States and States, and for Puerto Rico: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2006, U.S. Census Bureau.
Number of children ages 5-12: Estimates of the Resident Population by Single-Year of Age and Sex for the United States and States: July 1, 2006, U.S. Census Bureau.
Percent of students eligible for free and reduced-price lunch rate: Numbers and Types of Public Elementary and Secondary Schools from the Common Core of Data: School Year 2005-06. U.S. Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics.
Percent of K-12 students in Title I "schoolwide" schools: Numbers and Types of Public Elementary and Secondary Schools from the Common Core of Data: School Year 2005-06. U.S. Department of Education. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics. The federal Title I program provides funding to local school districts and schools with high percentages of poor children to help ensure that all children meet challenging state academic content and student academic achievement standards. Schools enrolling at least 40 percent of students from poor families are eligible to use Title I funds for schoolwide programs that serve all children in the school.
Child Care and Development Fund
The Child Care and Development Fund (CCDF) is the largest federal funding source for child care. States receive a funding allocation determined by formula and have broad flexibility to design programs that provide child care subsidies for low-income children under the age of 13 and to enhance the quality of child care for all children. Federal CCDF funding consists of mandatory, matching, and discretionary funds. Federal law requires that states spend at least 4 percent of their CCDF funds as well as additional targeted funds on activities to improve the quality and availability of child care. CCDF administrative data in this and the following sections is from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Child Care Bureau, as reported by States, unless otherwise noted.
FFY06 state MOE plus match: In order to receive Federal matching funds, a state must expend Maintenance of Effort funds. Note that this does not capture actual expenditures, only the minimum required to draw down all available federal funds.
FFY06 Tribal CCDF Allocation: Federal CCDF Funds are awarded directly to Federally-recognized Indian Tribes.
FFY05 total quality expenditures: This data includes FY05 and prior year funds expended for quality from each of the CCDF funding streams (mandatory, matching, and discretionary) and expenditures under targeted funds for infant and toddler, school-age care and resource and referral. This figure provides information obtained from state financial reports submitted for FY05.
Uses of CCDF Targeted Funds and Quality Dollars for Afterschool: Portions of CCDF discretionary funds are targeted specifically for resource and referral and school-age child care activities as well as for quality expansion. (These funds are in addition to the required 4 percent minimum quality expenditure.)
Maximum rate for school-age category: Rate listed applies to center-based care; where rates vary by region or county, the rate for the most populated urban area is given.
Standardized monthly school-age rate: Monthly rate for a child, age 8, in care after school during the school year at a center in the most costly district for four hours per day, 20 days per month. Calculated (in the lowest tier of a tiered system) using information from the FY2006-2007. State CCDF Plan, including rate structures, as submitted to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.
Separate subsidy rates for part-time vs. full time and Tiered Reimbursement Rate Systems: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Child Care Bureau. Report of State Plans FY2006-2007.
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) and Child Care
In addition to spending TANF funds directly on child care, a state may transfer up to 30 percent of its TANF grant to CCDF. Expenditures represent TANF funds spent in FY05 that were awarded in FY05 and prior years. Data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.
Program Licensing and Accreditation Policies
States with separate school-age licensing standards and states with specialized requirements for child care centers serving school-age children: National Association for Regulatory Administration, 2005 Child Care Licensing Study, available at http://www.nara.affiniscape.com/displaycommon.cfm?an=1&subarticlenbr=104.
Ratio of children to adults in school-age setting: Data from the National Child Care Information Center (NCCIC), available at: http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov.
Number of NAA-accredited programs: Data from the National AfterSchool Association, March 2007, available at: http://www.naaweb.org.
21st Century Community Learning Centers
The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 converted the 21st Century Community Learning Centers’ authority to a state formula grant. In past years, the U.S. Department of Education made competitive awards directly to school districts. Under the reauthorized law, funds flow to states based on their share of Title I, Part A funds. States use their allocations to make competitive awards to eligible entities. Data from the U.S. Department of Education 21st Century Community Learning Centers Office and the 21st CCLC Profile and Performance Information Collection System.
Return to top
The Child Care Bureau awarded a technical assistance contract to The Finance Project and their partner, the National Governors Association Center for Best Practices, for the Afterschool Investments project. The goals of the Afterschool Investments project include:
- Identifying ways that state and communities are using Child Care and Development Fund (CCDF) subsidy and quality dollars to support out-of-school time programs, and sharing these practices and approaches with other states;
- Identifying administrative and implementation issues related to CCDF investments in out-of-school time programs, and providing information and context (about barriers, problems, opportunities) as well as practical tools that will help CCDF administrators make decisions; and
- Identifying other major programs and sectors that are potential partners for CCDF in supporting out-of-school time programs and providing models, strategies, and tools for coordination with other programs and sectors.
Contact Us:
Email:
afterschool@financeproject.org
Web:
http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov/afterschool/
The Finance Project
1401 New York Avenue, NW
Suite 800
Washington, DC 20005
Phone: 202-587-1000
Web: www.financeproject.org
National Governors Association
Center for Best Practices
444 North Capitol Street, NW
Washington, DC 20001
Phone: 202-624-5300
Web: www.nga.org
The Afterschool Investments project’s State Profiles are designed to provide a comprehensive overview of noteworthy State and local initiatives across the country. Inclusion of an initiative in the Profiles does not represent an endorsement of a particular policy or practice.
|





